The selection of an appropriate coating for passage closures significantly impacts both the aesthetic appeal and the longevity of these architectural elements. The type of topcoat chosen affects resistance to wear and tear, ease of cleaning, and overall visual impact. A well-chosen surface treatment enhances the visual appeal of the door and protects the underlying material from environmental factors and daily use. For example, a high-gloss application might be suitable for interior applications, reflecting light and providing a durable, washable surface, whereas a satin sheen may be preferred for its subtle elegance and ability to conceal imperfections.
The right surface treatment for these building components is crucial due to its protective capabilities and contribution to the overall design scheme of a building. Historically, choices were limited to basic oil-based formulations. However, advances in polymer chemistry have yielded a wide array of options with improved durability, color retention, and environmental impact. Benefits include extended lifespan of the substrate, reduced maintenance requirements, and the ability to achieve specific design objectives. These attributes contribute to both the long-term value and the aesthetic enjoyment of a property.
Understanding the specific characteristics of various coating options, including durability, sheen level, and application requirements, is essential for making an informed decision. Subsequent sections will delve into the nuances of different types available, providing a detailed analysis to assist in selecting the optimal solution for specific needs and applications. This will involve evaluating factors such as resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and moisture, along with considering the intended usage environment, to ensure long-lasting performance and visual satisfaction.
Selecting the Optimal Coating
Achieving a durable and aesthetically pleasing surface on passage closures requires careful consideration and adherence to best practices. The following recommendations will assist in navigating the selection and application process, ensuring a professional and long-lasting result.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to any coating application, thorough surface preparation is essential. This includes cleaning to remove dirt, grease, and any loose or flaking material. Sanding to create a smooth, uniform profile is also crucial for proper adhesion.
Tip 2: Primer Selection: Applying a primer specifically formulated for the door material is a critical step. Primers enhance adhesion, block stains, and create a uniform base for the topcoat, ultimately improving its appearance and longevity. Consider an oil-based primer for raw wood to seal the grain and prevent moisture absorption.
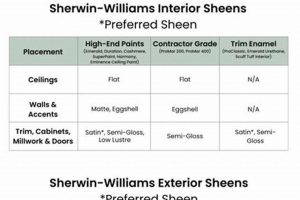
Tip 3: Sheen Level Consideration: The desired sheen level should be determined based on the intended use and aesthetic preference. Higher gloss levels offer increased durability and cleanability but may highlight imperfections. Lower sheens, such as matte or eggshell, conceal imperfections better but are generally less resistant to abrasion.
Tip 4: Product Compatibility: Ensure that all products used, including primer, topcoat, and any sealants, are compatible. Mixing incompatible formulations can lead to adhesion problems, discoloration, or premature failure of the coating system.
Tip 5: Application Technique: Employ proper application techniques to achieve a smooth, even finish. Use high-quality brushes, rollers, or spray equipment as appropriate. Multiple thin coats are preferable to a single thick coat, as this minimizes the risk of drips, runs, and uneven drying.
Tip 6: Environmental Conditions: Apply coatings under optimal environmental conditions. Avoid extreme temperatures or humidity, as these can negatively impact drying time and adhesion. Ensure adequate ventilation during application and drying.
Tip 7: Curing Time: Allow adequate curing time for each coat, as specified by the manufacturer. Premature use or handling can damage the finish and compromise its durability. Extended curing times may be necessary in humid environments.
The successful implementation of these suggestions will yield a coating that not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of passage closures but also provides lasting protection against wear, tear, and environmental factors. By prioritizing surface preparation, product compatibility, and proper application techniques, a professional-grade result can be achieved.
The following sections will provide insights into maintenance and repair strategies, ensuring the continued performance and appearance of the applied coating system.
1. Durability
The concept of durability is central to the selection of an appropriate coating for passage closures. It dictates the longevity of the aesthetic appearance and the protective qualities of the finish, directly impacting maintenance needs and overall cost-effectiveness. A durable coating withstands environmental stressors and physical wear, ensuring a prolonged lifespan.
- Resistance to Abrasion
Abrasion resistance refers to the ability of a coating to withstand surface wear from contact with objects or repeated cleaning. Higher abrasion resistance is crucial in high-traffic areas, such as hallways and entryways. Examples include enamel paints, which form a hard, durable layer capable of resisting scratches and scuffs. A lack of abrasion resistance leads to premature wear, requiring more frequent reapplication.
- Resistance to Impact
Impact resistance is the capacity of a surface treatment to withstand sudden forces without chipping, cracking, or denting. This is particularly important for doors subject to frequent use or potential impacts from objects. Coatings with higher flexibility and impact resistance, such as those containing urethane, provide enhanced protection. Insufficient impact resistance can result in cosmetic damage and compromise the underlying material.
- Resistance to Environmental Factors
Environmental resistance encompasses the ability of a coating to withstand exposure to sunlight (UV radiation), moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure. UV radiation can cause fading and degradation of colors, while moisture can lead to blistering and peeling. Coatings formulated with UV inhibitors and water-resistant polymers offer enhanced protection against these elements. Failure to provide adequate environmental resistance results in premature degradation and reduced lifespan.
- Resistance to Chemical Exposure
Resistance to chemical exposure refers to the ability of a surface treatment to withstand contact with cleaning agents, solvents, and other chemicals without degradation or discoloration. This is especially important in environments where frequent cleaning is necessary, such as kitchens and bathrooms. Coatings formulated with chemical-resistant resins, such as epoxy-based paints, offer enhanced protection. Inadequate chemical resistance can lead to staining, etching, and compromised surface integrity.
The interrelation of abrasion, impact, environmental, and chemical resistance properties defines the overall durability of a surface treatment for passage closures. Selecting a coating that adequately addresses these factors ensures a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing, and cost-effective solution. Prioritizing durability translates to reduced maintenance, extended lifespan, and sustained visual appeal, making it a paramount consideration in the selection process.
2. Appearance
The visual attributes imparted by a coating significantly influence the perceived quality and aesthetic integration of passage closures within a designed space. Consequently, careful selection regarding hue, sheen, and surface uniformity is essential. The final visual presentation directly affects the overall impression of the interior or exterior environment. For instance, a flawlessly applied, high-gloss coating on an entry door might convey sophistication and meticulous attention to detail, while a poorly executed matte finish could suggest neglect or lower quality workmanship. The choice must align with the architectural style, intended ambiance, and functional requirements of the space.
Considerations extend beyond mere color selection. Light reflectance values (LRV) influence the perceived brightness and spatial dimensions of a room. A light-colored surface treatment enhances illumination by reflecting ambient light, making it a practical choice for dimly lit hallways or entryways. Sheen levels, ranging from matte to high gloss, impact the visibility of surface imperfections and the durability of the surface. High-gloss coatings are typically easier to clean but may accentuate flaws, while matte coatings conceal imperfections but are less resistant to abrasion. The desired visual effect directly impacts the practical considerations of maintenance and longevity.
The relationship between visual appeal and coating selection underscores the importance of considering both aesthetic and functional requirements. Achieving the desired visual effect demands careful planning and execution, from surface preparation to application technique. Ignoring these details can result in a finish that detracts from the overall design and fails to provide the necessary durability. A well-considered selection, therefore, enhances the aesthetic qualities of the passage closure while ensuring long-term performance and visual satisfaction. This careful evaluation prevents the need for premature reapplication and ensures the visual integrity of the space over time.
3. Application
The effectiveness of any surface treatment for passage closures is intrinsically linked to the application process. Regardless of the inherent qualities of a coating, improper application techniques can negate its benefits and lead to premature failure. Factors such as surface preparation, environmental conditions during application, and the method of application directly influence the final appearance, durability, and adhesion of the coating. For example, a high-quality enamel, prized for its resilience, may exhibit poor adhesion if applied to an unprepared surface, resulting in chipping and peeling. Therefore, application is not merely a procedural step but an integral component of achieving an optimal and long-lasting result.
The practical significance of understanding this connection is evident in the prevention of common coating failures. Inadequate surface preparation, such as failing to remove loose paint or clean contaminants, creates a barrier that inhibits proper adhesion. Similarly, applying a coating in excessively humid or cold conditions can disrupt the curing process, leading to blistering or cracking. The selection of application toolsbrush, roller, or sprayeralso impacts the final finish. A poorly chosen brush may leave unsightly brushstrokes, while an improperly adjusted sprayer can result in uneven coverage or excessive overspray. These practical considerations underscore the necessity of skilled labor and adherence to manufacturer specifications to ensure a successful outcome.
In conclusion, the application process is inextricably linked to the overall performance of any coating selected for passage closures. Achieving the intended benefits of the surface treatment requires a holistic approach that prioritizes meticulous preparation, controlled environmental conditions, and the selection of appropriate application techniques. Neglecting these factors can compromise the integrity of the coating and undermine its intended purpose, regardless of its inherent qualities. The challenge lies in recognizing the critical role of application and investing in the expertise and resources necessary to execute it effectively, thus ensuring a durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
4. Adhesion
The durability and longevity of a surface treatment on passage closures are fundamentally dependent on adhesion. This property, referring to the ability of a coating to bond strongly and remain affixed to the substrate, dictates the resistance to peeling, chipping, and other forms of detachment. Without adequate adhesion, even the most technically advanced coating is prone to premature failure, rendering its other attributes largely irrelevant. The connection between robust adhesion and a high-quality surface treatment is therefore a direct cause-and-effect relationship. A superior application, in the absence of sound adhesion, becomes an exercise in futility. For example, an epoxy paint known for its resilience and resistance to chemicals, when applied to a poorly prepared or incompatible surface, may exhibit minimal adherence and quickly degrade.
The importance of adhesion as a critical component can be further elucidated through practical examples. In exterior applications, temperature fluctuations and moisture exposure exert constant stress on the bond between coating and substrate. If the adhesive force is insufficient, the coating will eventually separate, leading to aesthetic degradation and compromised protection of the underlying material. Similarly, in high-traffic interior environments, repeated contact and abrasion demand strong adhesion to prevent wear and tear. Consider the impact of a door subjected to frequent use; a coating with weak adhesion will quickly show signs of damage, necessitating costly and time-consuming repairs. Adhesion promoters, primers, and proper surface preparation techniques are therefore crucial for maximizing the adhesive force.
Understanding the interplay between adhesion and the long-term performance of coatings on passage closures carries significant practical implications. By prioritizing surface preparation, selecting compatible primers, and adhering to manufacturer specifications, stakeholders can ensure that the coating effectively fulfills its intended function. In situations where demanding performance characteristics are required, such as in commercial or industrial settings, specialized adhesion-promoting treatments may be necessary. Addressing adhesion is not merely a precautionary measure but a fundamental requirement for achieving a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and cost-effective coating system. The challenge lies in recognizing the subtle nuances of surface chemistry and selecting the appropriate techniques to optimize the adhesive bond, ultimately extending the lifespan and enhancing the value of the architectural element.
5. Cleanability
The ease with which a surface can be cleansed directly correlates with the sustained aesthetic appeal and hygienic integrity of passage closures. A coating’s resistance to staining, its ability to withstand repeated cleaning cycles, and the effort required to remove contaminants are key indicators of its practical value. Selecting a surface treatment that facilitates effortless cleaning minimizes maintenance demands and preserves the intended visual appearance over an extended period. The absence of easy cleanability can lead to the accumulation of dirt, grime, and other unsightly marks, detracting from the overall aesthetic and potentially compromising hygiene standards. Therefore, cleanability constitutes a significant factor when determining the optimal finish for passage closures. Consider, for example, a door in a healthcare facility; frequent disinfection is paramount, necessitating a coating capable of withstanding harsh cleaning agents without degradation. Similarly, in residential settings, doors frequently exposed to fingerprints, food splatters, or pet-related messes require surfaces that can be readily wiped clean.
The practical implications of cleanability extend beyond mere aesthetics and hygiene. Coatings that resist staining and are easily cleaned often exhibit increased durability. The ability to withstand repeated cleaning cycles without compromising the integrity of the surface translates to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Furthermore, the choice of cleaning agents compatible with the coating plays a crucial role. Harsh chemicals may effectively remove stains but can simultaneously damage the finish, leading to discoloration, cracking, or peeling. Selecting a coating that tolerates commonly used cleaning solutions ensures both effective cleaning and sustained surface integrity. One can envision, in a school setting, a coating that resists markings from crayons, pens, or general wear and tear, which would significantly reduce the workload of maintenance personnel, while also sustaining a more presentable environment. The appropriate cleaning regimen, tailored to the specific coating and application environment, is thus an integral component of maintaining a clean and appealing surface.
In summation, cleanability is not merely a desirable attribute but a functional necessity when selecting a finish for passage closures. Its contribution to sustained aesthetics, hygiene, and reduced maintenance costs underscores its importance. Addressing the practical considerations of staining, cleaning cycle resistance, and compatibility with cleaning agents allows stakeholders to make informed decisions that balance both visual appeal and long-term performance. Neglecting this aspect can result in increased cleaning efforts, premature degradation of the surface, and compromised aesthetic integrity. Therefore, prioritizing cleanability directly contributes to the preservation of the value and visual appeal of passage closures throughout their service life.
6. Cost
The economic considerations associated with selecting a surface treatment for passage closures are integral to informed decision-making. Initial expenditure, long-term maintenance expenses, and potential replacement costs must be carefully weighed to determine the most fiscally responsible option. The pursuit of the “best” finish necessitates a balanced assessment that accounts for both upfront investment and lifecycle costs.
- Material Expenses
The cost of the coating itself represents a significant portion of the overall expenditure. Different formulations, such as alkyd, latex, acrylic, or specialty epoxies, exhibit varying price points. High-performance coatings with enhanced durability and resistance to wear often command a premium price. The selection process should consider the balance between initial cost and the expected lifespan of the coating. For example, a less expensive latex might suffice for low-traffic interior applications, while a higher-priced epoxy may be more appropriate for high-use exterior surfaces.
- Labor Costs
The application of any surface treatment requires labor, the cost of which can vary considerably depending on the complexity of the project and the skill level required. Intricate surface preparation, specialized application techniques (such as spraying), and the number of coats needed all influence labor expenses. In some instances, professional application may be necessary to ensure a flawless finish and maximize the coating’s performance. For instance, achieving a smooth, uniform finish with high-gloss enamel typically necessitates skilled labor and specialized equipment, thereby increasing the overall project cost.
- Maintenance Requirements
Long-term maintenance represents a recurring expense that must be factored into the total cost of ownership. Some surface treatments require more frequent cleaning or touch-ups than others. Coatings that are easily damaged or prone to staining may necessitate more intensive maintenance regimes, resulting in higher ongoing expenses. The selection of a durable and easy-to-clean finish can minimize these costs over the lifespan of the passage closure. Consider, for example, a matte finish on a high-traffic exterior, which may require more frequent cleaning and reapplication compared to a more durable semi-gloss.
- Lifecycle Assessment
A comprehensive lifecycle assessment considers the total cost of a surface treatment over its entire lifespan, from initial purchase and installation to maintenance and eventual replacement. This assessment accounts for all associated expenses, providing a more accurate reflection of the true cost of ownership. While a less expensive coating may appear attractive initially, its shorter lifespan and higher maintenance demands could ultimately make it a more costly option in the long run. Conversely, a more expensive, higher-quality coating with a longer lifespan and lower maintenance needs may prove to be more economical over the long term. For example, the initial investment for an oil-based topcoat could be offset against less requent need to repaint over a long time period.
The interplay between material expenses, labor costs, maintenance requirements, and lifecycle assessment highlights the complexity of cost-related considerations when selecting a surface treatment for passage closures. The “best” finish is not necessarily the least expensive option, but rather the one that offers the optimal balance between initial investment and long-term performance. Informed decision-making requires a thorough evaluation of all cost factors to ensure a fiscally responsible and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and application of coatings for passage closures, providing concise and informative responses to guide decision-making.
Question 1: What is the most durable option for an exterior passage closure frequently exposed to harsh weather?
A marine-grade polyurethane coating provides superior protection against UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, offering enhanced durability in demanding environments.
Question 2: How does sheen level impact the visual perception and maintenance of passage closures?
Higher gloss levels offer increased durability and ease of cleaning but accentuate surface imperfections. Lower sheens conceal imperfections better but are generally less resistant to abrasion.
Question 3: Is surface preparation truly critical, or can a high-quality coating compensate for minor imperfections?
Thorough surface preparation is paramount. A high-quality coating cannot compensate for inadequate surface preparation; proper adhesion and a uniform finish require a clean, smooth, and properly primed substrate.
Question 4: What is the best method for applying a smooth, even coating to a passage closure with intricate details?
Spraying is often the preferred method for achieving a smooth, even coating on intricate surfaces. It allows for uniform coverage and minimizes the risk of brushstrokes.
Question 5: How can blistering or peeling be prevented after the application of a coating on a passage closure?
Blistering and peeling can be prevented by ensuring proper surface preparation, applying coatings under optimal environmental conditions (avoiding extreme temperatures and humidity), and allowing adequate curing time.
Question 6: What are the key considerations when selecting a coating for a passage closure in a high-traffic area prone to scuffs and abrasions?
Abrasion resistance, impact resistance, and ease of cleaning are crucial considerations. Opt for coatings formulated with durable resins, such as alkyd or urethane, and consider a higher sheen level for enhanced cleanability.
Selecting an appropriate coating and diligently implementing best practices yields a durable and aesthetically pleasing surface. Considering the environmental condition during application is the key to have long lasting result.
The succeeding section will address the environmental aspects associated with surface treatment solutions for doors.
Achieving Optimal Results
The selection of the “best paint finish for doors” necessitates a comprehensive understanding of material science, application techniques, and environmental factors. The preceding exploration has illuminated the critical parameters that influence performance: durability, aesthetics, application feasibility, adhesion properties, cleanability characteristics, and budgetary constraints. Mastery of these elements is paramount to achieving sustained aesthetic value and functional integrity.
The pursuit of excellence in architectural finishing is an ongoing endeavor. Diligent consideration of the scientific principles outlined herein, coupled with adherence to industry best practices, empowers stakeholders to elevate the quality and longevity of their projects. Continued investigation into emerging coating technologies and refinement of application methods will undoubtedly yield further advancements in the field, enhancing both the visual appeal and the protective capabilities of door finishes.