The selection of a protective coating for repainted or newly installed cabinetry is a crucial decision impacting both the aesthetic appearance and the long-term durability of the surfaces. This choice dictates the level of sheen, resistance to moisture, ease of cleaning, and overall longevity of the painted finish. Considerations include gloss level, application characteristics, and the environment in which the cabinets are situated. For instance, a higher gloss level typically offers superior cleanability and moisture resistance, ideal for kitchens and bathrooms.
The correct application of a suitable protective layer provides several benefits. It enhances resistance to everyday wear and tear, protects against stains and water damage, and simplifies cleaning. Historically, oil-based coatings were favored for their durability, but advancements in water-based acrylic and hybrid formulations have provided comparable performance with lower VOC content and faster drying times. Selecting appropriately extends the lifespan of the cabinetry, preserving its visual appeal and structural integrity.
This discussion will explore the spectrum of available options, analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of each. Specific attention will be given to factors influencing the selection process, including preparation methods, application techniques, and considerations for different types of cabinet materials and environments. The following sections will delve into specific types and their impact on the final outcome.
Guidance on Protective Coatings for Cabinetry
The following recommendations offer insights into selecting the appropriate protective layer for cabinetry, optimizing for durability and aesthetics.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to applying any protective coating, thorough cleaning, sanding, and priming are essential. This ensures proper adhesion and prevents imperfections from telegraphing through the final layer.
Tip 2: Consider the Environment: High-humidity environments, such as bathrooms and kitchens, necessitate moisture-resistant formulations. Coatings designed for interior use may not withstand prolonged exposure to high humidity.
Tip 3: Understand Sheen Levels: The desired level of gloss significantly impacts the overall appearance and ease of maintenance. Matte or satin finishes conceal imperfections better but may be more challenging to clean. High-gloss options offer superior cleanability but highlight any surface flaws.
Tip 4: Evaluate Coating Composition: Water-based acrylics offer low VOC content and easy cleanup, while oil-based options generally provide enhanced durability. Hybrid formulations often combine the benefits of both.
Tip 5: Test Application Techniques: Prior to applying the coating to the entire cabinet surface, test the application method on a discrete area. This allows for adjusting application techniques and identifying any compatibility issues with the primer or substrate.
Tip 6: Apply Thin, Even Coats: Multiple thin coats are preferable to a single thick coat, minimizing the risk of drips, runs, and uneven drying. Allow sufficient drying time between coats, as specified by the manufacturer.
Tip 7: Invest in Quality Application Tools: Using high-quality brushes, rollers, or spray equipment contributes to a smoother, more uniform finish. Clean tools thoroughly after each use to prolong their lifespan.
Adhering to these recommendations ensures a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting result. Proper selection and application safeguards the investment in cabinetry, preserving its value and appearance for years to come.
The subsequent section will address common challenges encountered during the application process and offer practical solutions for achieving a professional-grade outcome.
1. Durability
Durability is a paramount consideration when determining the appropriate protective layer for cabinetry. It directly influences the lifespan of the painted surface and its resistance to common forms of wear and tear. The selection of a finish significantly impacts the cabinet’s ability to withstand daily use, cleaning, and environmental factors.
- Resistance to Abrasion
A durable topcoat provides a barrier against scratches, scuffs, and abrasions caused by everyday contact with utensils, dishes, and cleaning implements. Finishes formulated with higher solids content or specialized polymers exhibit superior abrasion resistance, preserving the integrity of the painted surface over time. For instance, catalyzed conversion varnishes offer exceptional protection against abrasion in high-use kitchen environments.
- Impact Resistance
The capacity to resist chipping and cracking from impacts is crucial, particularly in areas prone to accidental bumps or collisions. Durable coatings possess the flexibility to absorb impact energy, minimizing damage. Two-part epoxy coatings, known for their hardness and impact resistance, are often employed in demanding applications.
- Chemical Resistance
Cabinetry frequently encounters exposure to cleaning agents, food spills, and household chemicals. A durable protective layer resists staining, discoloration, and degradation from these substances. Pre-catalyzed lacquers, for example, provide a good balance of durability and chemical resistance for general household use.
- Moisture Resistance
In environments with elevated humidity levels, such as kitchens and bathrooms, moisture resistance is essential to prevent swelling, blistering, and peeling of the finish. Durable coatings form a protective barrier against water penetration, safeguarding the underlying wood substrate. Water-based acrylic polyurethanes, known for their flexibility and moisture resistance, are frequently used in these environments.
The connection between a protective layer and its durability extends beyond immediate cosmetic appearance. It impacts long-term maintenance requirements and the overall life cycle of the cabinetry. Investing in a durable option reduces the need for frequent repainting and repairs, ultimately providing greater value. The facets discussed highlight the critical role it plays in preserving the beauty and functionality of painted cabinets.
2. Cleanability
The ease with which cabinetry surfaces can be cleaned is a critical factor in selecting an appropriate protective layer. The chosen finish directly impacts the ability to remove dirt, grease, and other contaminants without damaging the painted surface. This characteristic is particularly important in kitchens and bathrooms, where cabinets are routinely exposed to spills and splatters.
- Surface Porosity
The degree of porosity in a finish directly influences its cleanability. Highly porous surfaces trap dirt and grime, making them difficult to clean effectively. Non-porous or low-porosity surfaces, such as those achieved with gloss or semi-gloss coatings, prevent contaminants from penetrating the finish, facilitating easier cleaning. For example, a high-gloss polyurethane finish, due to its tightly sealed surface, allows for simple removal of grease splatters with a damp cloth.
- Chemical Resistance to Cleaning Agents
The selected protective layer must withstand repeated exposure to common household cleaning products without degrading or discoloring. Finishes with poor chemical resistance may become dull, sticky, or otherwise damaged by cleaning agents, compromising both their appearance and protective qualities. Conversion varnishes and catalyzed lacquers, known for their chemical inertness, provide a durable and cleanable surface that resists damage from typical cleaning solutions.
- Resistance to Staining
A cleanable finish effectively resists staining from food, liquids, and other common household substances. Surfaces that readily absorb stains require more aggressive cleaning methods, which can potentially damage the underlying paint layer. Coatings with inherent stain-resistant properties, such as acrylic polyurethanes, prevent penetration and allow for easy removal of spills before they become permanent blemishes.
- Sheen Level and Texture
Higher sheen levels, such as gloss and semi-gloss, generally offer superior cleanability due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces. Matte finishes, while aesthetically pleasing, often have a slightly textured surface that can trap dirt and make cleaning more challenging. The texture of the finish, whether smooth or slightly rough, directly impacts the ease with which contaminants can be removed. For instance, a smooth, semi-gloss finish allows for wiping away dirt with minimal effort, while a matte finish might require gentle scrubbing.
In summary, the selection of a protective layer that prioritizes cleanability contributes significantly to the long-term maintenance and aesthetic appeal of cabinetry. Balancing the need for easy cleaning with other factors, such as durability and sheen level, ensures a practical and visually pleasing outcome. Choosing the right one is an essential decision.
3. Sheen Level
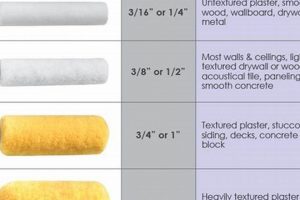
Sheen level is an integral attribute when determining the appropriate protective layer for cabinetry, directly influencing both the aesthetic appearance and functional properties of the painted surface. The selected sheen ranging from matte to high gloss determines the amount of light reflected, thus affecting the perceived color, texture, and overall visual impact. The effect of the light can change from a high-traffic kitchen, as opposed to a more quiet office, so the finish should be durable, as well as pleasing to the eye.
The sheen level has a practical impact beyond aesthetics. Higher gloss levels, for example, tend to offer greater durability and ease of cleaning due to their less porous surfaces. This makes them suitable for high-traffic areas or environments prone to spills. A high-gloss paint in the kitchen, will make it easier to clean than a matte finish. Lower sheen levels, such as matte or eggshell, conceal imperfections more effectively and provide a softer, more muted appearance. This might be advantageous in areas where minimizing the visibility of surface irregularities is desired.
Selecting the appropriate sheen level requires careful consideration of the intended use, desired aesthetic, and practical maintenance requirements of the cabinetry. A balance must be struck between visual appeal, durability, and cleanability. Ultimately, the appropriate sheen is a critical component, shaping both the appearance and performance of the finished product. A carefully considered sheen level ensures a satisfying and long-lasting result.
4. Moisture Resistance
Moisture resistance is a critical characteristic inextricably linked to the selection of protective coatings for cabinetry, particularly in environments characterized by elevated humidity levels or frequent exposure to water. The relationship between finish and its ability to resist moisture dictates the long-term integrity and aesthetic appeal of the cabinet surfaces. Failure to select a coating with adequate moisture resistance can lead to swelling, warping, cracking, peeling, and eventual degradation of the substrate. For example, cabinets in kitchens and bathrooms are routinely subjected to moisture from cooking, cleaning, and bathing, thus necessitating a finish capable of withstanding these conditions. The protective layer acts as a barrier, preventing water from penetrating the wood or composite material and causing irreversible damage. The presence of moisture can also foster mold and mildew growth, creating unsanitary conditions and further compromising the structural integrity of the cabinets. Therefore, the finish is a key component when the cabinets can stay durable in areas where spills and vapor will occur.
The selection of a moisture-resistant finish involves consideration of the coating’s composition and its inherent properties. Oil-based paints and varnishes traditionally offer superior water resistance compared to some water-based alternatives, though advancements in acrylic and hybrid formulations have significantly improved the moisture resistance of water-based options. The application process also plays a crucial role. Proper surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and priming, is essential to ensure optimal adhesion and prevent moisture from penetrating the coating. Multiple thin coats, rather than a single thick coat, typically provide more effective moisture protection. The use of sealants on exposed edges and joints can further enhance water resistance, particularly in vulnerable areas such as around sinks and dishwashers.
In conclusion, moisture resistance is a fundamental attribute influencing the suitability of a finish for cabinetry, especially in moisture-prone environments. Selecting a protective layer with appropriate water-resistant properties, combined with proper surface preparation and application techniques, is essential to preserving the longevity, aesthetic appeal, and structural integrity of cabinet surfaces. A lack of appropriate safeguards can lead to costly repairs or replacements. Selecting and applying the right cabinet paint protects and extends the life of the cabinetry, as well as your investment.
5. Application method
The method of application exerts a significant influence on the ultimate appearance, durability, and performance of any protective layer selected for cabinetry. The choice of application technique dictates the uniformity of the coating, the potential for imperfections, and the overall effectiveness of the protection provided. Specifically, the selection of a suitable option directly affects the achievement of the desired aesthetic outcome and the longevity of the cabinet finish. For instance, spraying typically yields a smoother, more even finish than brushing or rolling, particularly when applying fast-drying lacquers or varnishes. However, spraying necessitates specialized equipment and proper ventilation, whereas brushing is more readily accessible for smaller projects. The selected material must be compatible with the chosen method to ensure optimal results. Applying a high-viscosity paint with a low-pressure sprayer, for example, may result in an uneven or speckled finish. The chosen application is a vital part of preserving the cabinets for an extended time.
Surface preparation techniques and characteristics are critical when it comes to the method. Improper surface cleaning, sanding, or priming can lead to adhesion failures, regardless of the quality or type of finish. Techniques such as sanding between coats can enhance adhesion and smoothness, especially when applying multiple layers of paint or varnish. Moreover, the skill and experience of the applicator play a crucial role in achieving a professional-grade result. An experienced painter will be able to adjust application techniques based on the specific characteristics of the chosen material, ensuring a uniform and durable coating. Choosing the best and appropriate method is directly linked to the outcome and success rate.
In summary, the success of any cabinet finishing project hinges on the careful consideration and execution of the application process. Selecting a method that is appropriate for the chosen material, combined with proper surface preparation and skilled application, is essential to achieving a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting outcome. Challenges such as uneven application, brush strokes, or drips can be avoided with careful planning and execution, highlighting the integral role that the choice of this approach plays in the overall success of any cabinetry finishing endeavor. The success and the best result can be found with all the proper planning.
6. Surface preparation
Surface preparation is inextricably linked to the successful application and longevity of any protective coating selected for cabinetry. The quality of this groundwork directly dictates the adhesion, uniformity, and overall durability of the applied material. A compromised surface will invariably lead to premature failure, regardless of the inherent properties of the finish itself. For instance, applying a high-performance polyurethane over a surface contaminated with grease or residual sanding dust will prevent proper bonding, resulting in peeling or chipping even under normal use. Similarly, inadequate sanding can leave behind imperfections that telegraph through the finish, detracting from the aesthetic outcome. The protective coating serves as the final layer, but its effectiveness is entirely dependent on the integrity of the underlying prepared surface.
The correct surface preparation techniques vary depending on the existing condition of the cabinetry and the type of coating to be applied. Previously painted or varnished surfaces require thorough cleaning to remove dirt, grime, and any loose or flaking material. Sanding creates a profile for improved adhesion and smooths out imperfections. Bare wood surfaces may require filling of any cracks or imperfections prior to priming. Priming provides a uniform base for the protective layer, ensuring consistent color and sheen. The choice of primer is also critical, as it must be compatible with both the substrate and the topcoat. For example, using an oil-based primer under a water-based paint can lead to adhesion problems. The finish is the cherry on top but is ruined if the surface isn’t prepared correctly.
In summation, meticulous surface preparation is not merely a preliminary step but an integral component of the overall coating process. Neglecting this aspect compromises the performance and aesthetic qualities, irrespective of the material’s inherent properties. Investing time and effort in thorough surface preparation is a critical investment in the longevity and beauty of the finished cabinetry. It is the foundation upon which a durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome is built, reinforcing the inherent link between a well-prepared surface and the success of a well-selected finish.
7. Cost
The economic aspect of a protective layer for cabinetry is a significant determinant in the selection process, directly influencing the range of feasible options and the long-term financial implications. The initial expenditure on materials represents only a portion of the total cost, which encompasses surface preparation, application, and potential maintenance expenses. A less expensive finish may necessitate more frequent reapplication, thereby increasing the cumulative expenditure over the lifespan of the cabinetry. Conversely, a higher-priced finish with enhanced durability may prove more economical in the long run by minimizing the need for repairs or replacements. The interplay between material prices, labor costs, and the expected lifespan of the finish constitutes a critical element in the decision-making process. For instance, selecting a budget-friendly lacquer may seem appealing initially, but its susceptibility to scratches and moisture damage could lead to premature wear, requiring more frequent and costly refinishing.
The cost extends beyond the initial purchase price to encompass the labor involved in application and the potential need for specialized equipment. Some coatings necessitate professional application due to their technical complexity or the requirement for controlled environments. For example, catalyzed conversion varnishes often require spray application by trained professionals, adding to the overall project expense. Moreover, the environmental regulations governing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions can impact the cost of certain finishes, as compliant formulations may be more expensive. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including material expenses, labor charges, and potential environmental compliance fees, provides a more accurate assessment of the economic implications of different protective layer options. A homeowner choosing a water-based acrylic finish, despite a slightly higher upfront cost, may benefit from easier DIY application and reduced VOC emissions, resulting in long-term savings.
Ultimately, understanding the intricate relationship between price and performance is crucial for making informed decisions. Balancing the desire for a durable and aesthetically pleasing result with budgetary constraints requires careful consideration of all associated expenses. While selecting the least expensive option may appear financially prudent in the short term, it is essential to evaluate the long-term implications for maintenance, repair, and replacement costs. The optimal approach involves selecting a material that provides the best value proposition, balancing initial expenditure with expected longevity and minimizing the total cost of ownership. A long-term investment yields the best savings in future costs of refinishing, or even cabinet replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns and misconceptions regarding the selection and application of protective coatings for cabinetry, providing concise, evidence-based answers.
Question 1: What distinguishes different sheen levels for cabinet coatings?
Sheen level refers to the amount of light reflected by a coating, ranging from matte (minimal reflection) to high-gloss (maximum reflection). Higher sheen levels typically exhibit greater durability and ease of cleaning, while lower sheen levels effectively conceal surface imperfections.
Question 2: How does surface preparation impact the performance of cabinet coatings?
Thorough surface preparation, encompassing cleaning, sanding, and priming, is essential for ensuring proper adhesion and preventing imperfections from telegraphing through the protective layer. Insufficient preparation can lead to premature coating failure.
Question 3: What factors should influence the choice between water-based and oil-based coatings?
Water-based coatings offer lower VOC content and easier cleanup, while oil-based options generally provide enhanced durability and moisture resistance. The selection depends on the specific environmental requirements and desired performance characteristics.
Question 4: Does the application technique significantly affect the outcome of cabinet finishing?
Yes, the application method significantly impacts the smoothness, uniformity, and overall appearance of the coating. Spraying typically yields a more even finish, while brushing and rolling are suitable for smaller projects but may leave brush marks or texture.
Question 5: How crucial is moisture resistance in coatings applied to bathroom cabinetry?
Moisture resistance is paramount in bathroom environments due to elevated humidity levels. Coatings lacking adequate water resistance can lead to swelling, warping, and eventual degradation of the cabinet surfaces.
Question 6: What are the long-term economic implications of selecting a low-cost protective layer?
While a less expensive finish may reduce initial costs, it may necessitate more frequent reapplication due to reduced durability, potentially increasing the cumulative expenditure over the lifespan of the cabinetry. The longevity and ease of maintenance are key to cabinet success.
Selecting a cabinet paint for your cabinets depends on its location, budget, durability, and the look you want to get from its finish.
The subsequent section will address common challenges encountered during the application process and offer practical solutions for achieving a professional-grade outcome.
Protective Coatings for Cabinetry
This exploration into the selection of protective coatings for cabinetry has underscored the multifaceted nature of the decision-making process. Factors ranging from durability and cleanability to sheen level, moisture resistance, application method, surface preparation, and cost all contribute to the ultimate suitability of a given material. Optimal cabinet paints require a nuanced understanding of these elements and their interdependencies.
The careful consideration of these factors will ensure the long-term preservation of cabinetry, balancing aesthetic preferences with practical considerations of maintenance and environmental conditions. Selecting the right layer is not merely a cosmetic choice, but a commitment to the enduring quality and value of the cabinetry itself. Further research and consultation with industry experts are encouraged to ensure a tailored and effective protective solution. Ensuring the correct finish is a serious matter that requires research and professional consideration.