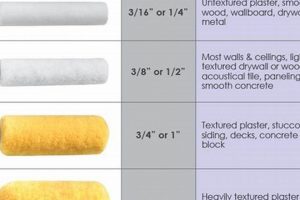
Surface coatings from Sherwin-Williams offer a diverse array of options for protecting and beautifying substrates. These products, designed for both interior and exterior applications, range from flat sheens that minimize imperfections to high-gloss enamels that provide durability and ease of cleaning. For example, an acrylic latex formula might be selected for walls requiring a matte appearance, while an alkyd-based option could be used for trim demanding a tougher, shinier surface.
The selection of appropriate coatings is crucial for achieving desired aesthetics, longevity, and performance characteristics. Historically, choices were limited, but advancements in chemistry have led to a broader spectrum of products tailored to specific needs. Key benefits include enhanced resistance to wear and tear, improved color retention, and specialized formulations designed to combat moisture, mildew, and UV degradation. These factors contribute to reduced maintenance costs and extended lifecycles of coated surfaces.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific product categories, application techniques, and selection criteria pertinent to achieving optimal results with these surface treatments. Topics to be covered include the characteristics of different sheen levels, the suitability of various product types for different substrates, and best practices for surface preparation and application.
Application Advice for Optimal Results
Achieving a professional and durable finish requires careful consideration and execution. These guidelines are intended to improve the longevity and aesthetic appeal of coated surfaces.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to application, thorough cleaning and priming are essential. Remove loose paint, dirt, and grease. Priming ensures proper adhesion and uniform absorption, which is critical for color consistency.
Tip 2: Select the Appropriate Sheen: Different sheens offer varying levels of durability and reflectivity. Matte finishes are suitable for low-traffic areas, while higher sheens are recommended for surfaces requiring frequent cleaning.
Tip 3: Understand Product Compatibility: Verify that primers, undercoats, and topcoats are compatible. Incompatible products can lead to adhesion failures, blistering, or discoloration.
Tip 4: Apply Even Coats: Consistent application thickness is crucial for uniform color and durability. Avoid applying excessive amounts in a single coat, as this can lead to sagging or runs.
Tip 5: Control Environmental Conditions: Adhere to recommended temperature and humidity ranges during application and drying. Extreme conditions can negatively impact the curing process and lead to premature failure.
Tip 6: Utilize Proper Application Tools: The choice of brushes, rollers, or spray equipment should be appropriate for the selected product and the substrate being coated. Consider the nap length of rollers for optimal coverage on textured surfaces.
Tip 7: Allow Adequate Drying Time: Respect the recommended drying times between coats. Insufficient drying can compromise adhesion and durability.
Consistent adherence to these recommendations will significantly improve the overall outcome, ensuring a durable and aesthetically pleasing coated surface.
The subsequent section will provide an overview of specific product lines and their intended applications, offering further guidance for selecting the most appropriate product for a given project.
1. Durability and longevity
The relationship between coating products from Sherwin-Williams and the attributes of durability and longevity is central to their value proposition. A surface treatment’s capacity to withstand physical wear, chemical exposure, and environmental degradation directly influences its service life and the frequency of required maintenance. The selection of an appropriate Sherwin-Williams product is thus a critical determinant of a project’s long-term cost-effectiveness.
For example, consider the application of an exterior acrylic coating on a commercial building. A product with superior UV resistance will exhibit less fading and chalking over time, maintaining its aesthetic appearance and protective function for an extended period compared to a lower-grade alternative. Similarly, in high-traffic interior areas, a durable epoxy coating will resist scuffing and abrasion, reducing the need for frequent repainting and minimizing disruption to operations. The specification of coatings is therefore not merely an aesthetic decision, but a financial one with long-term implications.
Understanding the correlation between coating selection and long-term performance is essential for informed decision-making. While initial cost may be a factor, the extended service life and reduced maintenance associated with durable and long-lasting products often result in a lower total cost of ownership. The selection process should, therefore, prioritize products that demonstrably exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to degradation in the specific application environment. Overlooking these considerations can lead to premature coating failure and increased lifecycle costs.
2. Color retention capabilities
The ability of surface coatings to maintain their original color fidelity over time is a critical performance characteristic. The color retention capabilities of coatings directly influence their long-term aesthetic appeal and reduce the need for frequent recoating, thereby impacting lifecycle costs.
- Pigment Selection and Formulation
The choice of pigments and the formulation of the coating matrix are primary determinants of color retention. Inorganic pigments, such as iron oxides and titanium dioxide, generally exhibit superior lightfastness compared to organic pigments. The binder resin also plays a crucial role, as it must protect the pigments from degradation caused by UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure. A well-formulated coating will incorporate UV absorbers and stabilizers to enhance color retention.
- Exposure Conditions and Environmental Factors
The severity of environmental conditions significantly affects color retention. Coatings exposed to intense sunlight, high humidity, or industrial pollutants will experience accelerated color degradation. Exterior applications, particularly those in regions with high UV indices, require coatings specifically formulated for extended color retention. The orientation of the coated surface also matters, as south-facing surfaces typically experience greater UV exposure.
- Sheen Level and Surface Texture
The sheen level and surface texture of a coating can influence the perceived color retention. Glossy surfaces tend to accentuate color changes, while matte surfaces may mask subtle fading. Rough or textured surfaces can create variations in light reflection, making color shifts less noticeable. The selection of an appropriate sheen and texture can therefore mitigate the visual impact of color degradation.
- Testing and Quality Control Standards
Rigorous testing and quality control procedures are essential for ensuring consistent color retention. Accelerated weathering tests, such as xenon arc and QUV testing, simulate long-term exposure to sunlight and moisture, allowing manufacturers to assess the color stability of their products. Adherence to industry standards, such as ASTM D4587 and ISO 11507, provides a benchmark for evaluating color retention performance.
The interplay of pigment selection, environmental factors, sheen level, and quality control collectively determines the color retention capabilities of coatings. Specifying coatings formulated for superior color retention in the intended application environment is crucial for maintaining the aesthetic value and extending the lifespan of coated surfaces. Products offering advanced protection against UV degradation and weathering provide significant long-term benefits, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring lasting visual appeal.
3. Substrate compatibility factors
The interaction between Sherwin-Williams surface coatings and the underlying material, or substrate, is a critical determinant of coating performance. The chemical and physical properties of the substrate must be considered in conjunction with the coating formulation to ensure proper adhesion, prevent premature failure, and achieve the desired aesthetic outcome. Incompatible combinations can lead to a range of issues, from blistering and peeling to discoloration and compromised durability. For instance, applying a water-based coating directly to a previously oil-based painted surface without proper preparation can result in poor adhesion and subsequent coating failure. Understanding these compatibility factors is therefore paramount for successful coating applications.
Selecting the appropriate Sherwin-Williams product requires a thorough assessment of the substrate. Porous surfaces, such as concrete or wood, necessitate primers or sealers to reduce absorption and promote uniform coating. Metal substrates may require specific pre-treatment to inhibit corrosion and ensure adhesion. Non-ferrous metals, like aluminum, present unique challenges and often require specialized primers designed to etch the surface and create a mechanical bond. Furthermore, existing coatings on the substrate must be evaluated for compatibility with the new coating system. Testing a small, inconspicuous area before full application is a prudent measure to identify potential issues early on. A real-world example is the application of an epoxy coating to a concrete floor in a warehouse. If the concrete is not properly prepared and sealed, moisture vapor transmission can cause the epoxy to delaminate, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
In conclusion, the importance of substrate compatibility factors in the application of Sherwin-Williams coatings cannot be overstated. Ignoring these considerations can lead to significant problems, ranging from aesthetic imperfections to complete coating failure. A comprehensive understanding of substrate properties and the selection of compatible coatings are essential for achieving optimal performance and extending the lifespan of coated surfaces. While the range of available coatings and preparation techniques may seem daunting, careful planning and attention to detail will ultimately yield a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and cost-effective finish.
4. Application ease characteristics
The practicality and efficiency of surface coating application are directly related to the characteristics inherent in the chosen product. Application ease encompasses factors that influence the speed, uniformity, and overall quality of the finish achieved, impacting labor costs and project timelines when employing various Sherwin-Williams coating solutions.
- Viscosity and Flow Properties
A coating’s viscosity and flow characteristics significantly influence its ease of application. Products with optimal viscosity spread smoothly and evenly, minimizing brushstrokes, roller marks, or spray patterns. Coatings that are too viscous may require excessive thinning, potentially compromising their protective properties. Conversely, coatings that are too thin may run or sag, leading to uneven coverage. Self-leveling coatings, which minimize surface imperfections, exemplify the benefits of optimized viscosity and flow.
- Drying and Curing Times
The drying and curing times of surface coatings directly impact project timelines. Fast-drying products allow for quicker recoating and reduced downtime, but may also present challenges in achieving a smooth finish. Conversely, slow-drying coatings offer greater workability but extend project completion times. The selection of appropriate drying and curing characteristics depends on factors such as environmental conditions, application method, and project deadlines. For instance, a quick-drying acrylic lacquer may be preferred for furniture refinishing, while a slower-curing epoxy may be more suitable for industrial flooring.
- Application Method Suitability
Different Sherwin-Williams coating formulations exhibit varying degrees of suitability for different application methods, such as brushing, rolling, or spraying. Some coatings are specifically designed for airless spray application, while others are better suited for traditional brush or roller application. Factors such as viscosity, solids content, and drying time influence the choice of application method. Incorrect selection can lead to uneven coverage, excessive material waste, or compromised finish quality. For example, applying a high-solids epoxy coating with a standard brush may result in poor leveling and brushstroke marks.
- Surface Preparation Requirements
The complexity and extent of surface preparation required prior to coating application directly impact the overall ease of the process. Some surface treatments require extensive cleaning, sanding, or priming to ensure proper adhesion and a uniform finish. Self-priming coatings, which eliminate the need for a separate primer coat, streamline the application process and reduce labor costs. The choice of coating should be aligned with the available resources and the desired level of finish quality. For instance, a direct-to-metal coating can significantly reduce preparation time compared to a traditional multi-coat system.
These application ease characteristics are integral to the selection and utilization of Sherwin-Williams surface coatings. By considering factors such as viscosity, drying time, application method suitability, and surface preparation requirements, professionals can optimize the coating process, minimize labor costs, and achieve high-quality, durable finishes. Careful evaluation of these characteristics ensures that the chosen product aligns with the specific project requirements and available resources.
5. Environmental resistance properties
Environmental resistance is a critical performance attribute of surface coatings, influencing their longevity and protective capabilities in various environmental conditions. The ability of Sherwin-Williams products to withstand degradation from factors such as moisture, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and abrasion directly affects their suitability for specific applications and their long-term cost-effectiveness.
- Moisture Resistance
Resistance to moisture is essential for preventing corrosion, blistering, and microbial growth on coated surfaces. Coatings formulated with hydrophobic resins and additives can effectively repel water and prevent moisture penetration. For example, coatings used in marine environments require exceptional moisture resistance to withstand constant exposure to saltwater. The presence of effective moisture barriers extends the lifespan of coated substrates and reduces maintenance requirements.
- UV Resistance
Ultraviolet radiation is a significant cause of coating degradation, leading to fading, chalking, and embrittlement. Coatings incorporating UV absorbers and stabilizers can mitigate the effects of UV exposure, preserving color and gloss retention. Exterior applications, particularly in regions with high UV indices, demand coatings with robust UV resistance properties. An example is the use of acrylic polyurethane coatings on aircraft exteriors to withstand prolonged sun exposure at high altitudes.
- Chemical Resistance
Resistance to chemical exposure is crucial in industrial and commercial settings where coatings may come into contact with acids, alkalis, solvents, and other corrosive substances. Coatings formulated with epoxy or polyurethane resins often exhibit superior chemical resistance. For instance, coatings used in chemical processing plants must withstand continuous exposure to harsh chemicals without degradation. Proper chemical resistance ensures the integrity and safety of coated equipment and structures.
- Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is important for coatings subjected to mechanical wear and tear, such as those used on floors, decks, and equipment. Coatings incorporating hard aggregates or crosslinking polymers can withstand repeated abrasion without significant damage. An example is the use of epoxy coatings on warehouse floors to resist abrasion from forklift traffic. High abrasion resistance prolongs the lifespan of coated surfaces and reduces the need for frequent recoating.
These facets of environmental resistance properties are integral to the performance and selection of Sherwin-Williams coatings. The ability of these coatings to withstand moisture, UV radiation, chemical exposure, and abrasion directly impacts their durability, longevity, and suitability for diverse applications. Specifying coatings with appropriate environmental resistance characteristics is essential for achieving optimal performance and minimizing lifecycle costs.
6. Aesthetic sheen selection
The choice of sheen level in surface coatings is a critical decision, influencing not only the visual appearance of a space but also its functional characteristics. The selection of a specific sheen from Sherwin-Williams’ product line is a deliberate aesthetic choice with implications for light reflectivity, durability, and maintenance requirements.
- Light Reflectivity and Ambience
Sheen levels directly affect how light interacts with a surface, impacting the perceived brightness and ambience of a room. High-gloss sheens reflect the most light, creating a bright and vibrant atmosphere, but also accentuating imperfections. Matte sheens, conversely, absorb light, producing a softer, more subdued effect, and effectively hiding surface irregularities. For example, a high-gloss finish may be appropriate for trim work to highlight architectural details, while a matte finish is often preferred for ceilings to minimize glare.
- Durability and Cleanability
Higher sheen levels typically offer greater durability and cleanability compared to lower sheens. Glossy surfaces are more resistant to staining and easier to wipe clean, making them suitable for high-traffic areas and surfaces prone to spills. Matte finishes, while less durable, offer a more forgiving aesthetic, concealing imperfections and providing a subtle, sophisticated appearance. A semi-gloss or satin finish may strike a balance between durability and aesthetic appeal for walls in living areas.
- Surface Imperfections and Coverage
The chosen sheen can either accentuate or minimize surface imperfections. High-gloss sheens highlight any irregularities in the substrate, requiring meticulous surface preparation. Matte sheens, due to their light-absorbing properties, effectively mask imperfections, providing a smoother and more uniform appearance. In older homes with uneven walls, a matte finish may be a practical choice to minimize the visibility of surface flaws.
- Application Considerations
The ease of application can be influenced by the sheen level. High-gloss finishes often require greater skill to apply evenly, as imperfections in the application are more noticeable. Matte finishes are generally more forgiving and easier to achieve a consistent, uniform appearance. When applying Sherwin-Williams coatings, it is important to consider the applicator’s skill level and the desired aesthetic outcome in selecting the appropriate sheen.
In summary, the selection of an appropriate sheen level from the range of Sherwin-Williams paint finishes requires careful consideration of both aesthetic preferences and functional requirements. The choice should reflect the desired ambience, the level of durability needed, the presence of surface imperfections, and the skill of the applicator. A well-informed decision will result in a coating that not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the space but also provides long-lasting protection and ease of maintenance.
7. Product line variations
Sherwin-Williams offers an extensive array of surface coating options, categorized into distinct product lines, each engineered to address specific performance requirements and application scenarios. These variations are not arbitrary; they represent a deliberate tailoring of chemical composition, physical properties, and application characteristics to optimize outcomes for diverse substrates, environmental conditions, and aesthetic preferences. The availability of these product line variations is therefore a fundamental component of the capabilities associated with Sherwin-Williams paint finishes. Without a diverse range, the ability to effectively address the complexities of varied painting projects would be severely limited.
The effect of product line variations is evident in real-world applications. For example, the “Duration” line offers enhanced exterior durability and weather resistance, making it suitable for residential siding exposed to harsh climates. Conversely, the “Pro Industrial” line provides superior chemical resistance and abrasion resistance, catering to the demanding needs of industrial facilities. The selection of the “Harmony” line, known for its low-VOC formulation, aligns with projects prioritizing indoor air quality and environmental sustainability. These examples illustrate how the specific properties of each product line directly address unique project demands. The absence of these distinct options would force reliance on generalized products, leading to compromised performance and potentially increased long-term costs due to premature failure or increased maintenance. Understanding these variations allows professionals to select the optimal product, maximizing both the aesthetic appeal and the functional lifespan of the coating.
In conclusion, product line variations are an intrinsic and crucial element within the broader context of Sherwin-Williams paint finishes. They enable precise matching of coating properties to specific project needs, resulting in enhanced performance, durability, and aesthetic outcomes. While navigating this extensive product portfolio can present a challenge, the practical significance of informed selection cannot be overstated. A comprehensive understanding of product line variations empowers users to achieve optimal results, ensuring the long-term success and value of coating projects.
Frequently Asked Questions About Surface Coatings
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, application, and performance characteristics of Sherwin-Williams products. These answers are intended to provide clarity and assist in informed decision-making.
Question 1: What factors should influence the selection of a specific coating?
Substrate type, environmental conditions, desired sheen level, and performance requirements are primary considerations. Assess the substrate material (e.g., wood, metal, concrete), the level of exposure to moisture, UV radiation, or chemicals, and the desired aesthetic outcome. Also, evaluate the need for abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, or other specialized properties. Matching these factors with the appropriate product characteristics ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Question 2: How critical is surface preparation prior to coating application?
Surface preparation is paramount for achieving proper adhesion and a uniform finish. Remove any loose paint, dirt, grease, or contaminants. Sand or abrade smooth surfaces to create a mechanical bond. Prime porous surfaces to reduce absorption and ensure uniform color. Failure to adequately prepare the surface can result in adhesion failures, blistering, or discoloration, significantly reducing the lifespan of the coating.
Question 3: What is the significance of VOC content in surface coatings?
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that evaporate from coatings as they dry. High VOC levels can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. Select low-VOC or zero-VOC coatings to minimize environmental impact and improve indoor air quality, particularly in enclosed spaces. Regulations often specify maximum VOC limits for different coating categories, so ensure compliance with local and national requirements.
Question 4: How does sheen level affect coating performance?
Sheen level influences light reflectivity, durability, and cleanability. High-gloss sheens reflect more light, are more durable and easier to clean, but highlight surface imperfections. Matte sheens absorb light, conceal imperfections, but are less durable and more difficult to clean. Select a sheen level that balances aesthetic preferences with functional requirements, considering the specific application and traffic level.
Question 5: What are the common causes of coating failure?
Common causes include inadequate surface preparation, improper coating selection, incorrect application techniques, and exposure to harsh environmental conditions. Moisture intrusion, UV degradation, chemical exposure, and physical abrasion can also contribute to coating failure. Addressing these factors through proper planning and execution is essential for extending coating lifespan.
Question 6: How can coating lifespan be maximized?
Maximize coating lifespan through thorough surface preparation, selection of appropriate products, proper application techniques, and regular maintenance. Inspect coated surfaces periodically for signs of damage or degradation, and address any issues promptly. Re-coating or touching up damaged areas can prevent further deterioration and extend the overall lifespan of the coating system.
The information provided in this FAQ is intended for general guidance only. Consult with a qualified coating specialist for specific project recommendations and technical advice.
The following section will explore innovative coating technologies and their potential applications in various industries.
Concluding Remarks on Sherwin-Williams Surface Coatings
This exposition has presented a comprehensive overview of Sherwin-Williams surface coatings, addressing key aspects such as durability, color retention, substrate compatibility, application ease, environmental resistance, sheen selection, and product line variations. A thorough understanding of these elements is crucial for informed decision-making and optimal coating performance. The selection and application of appropriate coatings are not merely aesthetic considerations but involve significant financial and operational implications.
Given the critical role of surface coatings in protecting and enhancing structures and equipment, continued research and development in this field are essential. Professionals involved in construction, manufacturing, and maintenance should prioritize ongoing education and training to remain abreast of advancements in coating technologies. Diligence in these practices will ensure the selection and utilization of surface treatments that deliver lasting value and performance.