Warning: Undefined array key "https://bestfinaltouch.com/contact" in /www/wwwroot/bestfinaltouch.com/wp-content/plugins/wpa-seo-auto-linker/wpa-seo-auto-linker.php on line 192
This pneumatic tool, commonly employed in woodworking and construction, drives fasteners into materials to affix trim, molding, and other finish carpentry elements. An example application includes securing baseboards to walls or attaching door casings to jambs, creating seamless and aesthetically pleasing results.
The significance of such a device lies in its ability to provide a consistent and precise fastening solution. This precision minimizes surface damage and allows for a professional-looking finish. Historically, these types of tools have increased efficiency in construction and carpentry, significantly reducing the time required for fastening compared to manual methods.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects such as product features, operational guidelines, maintenance procedures, and considerations for selecting the appropriate model for various applications.
Operation and Maintenance Tips
The following guidelines aim to enhance the performance and longevity of the pneumatic fastening instrument, promoting both efficiency and safety during operation.
Tip 1: Regulate Air Pressure. Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended air pressure specifications. Excessive pressure can result in damage to the tool or the workpiece, while insufficient pressure may lead to incomplete fastener driving.
Tip 2: Use Correct Fastener Length. Employ fasteners of the appropriate length for the materials being joined. Fasteners that are too long may protrude, while those that are too short may compromise joint integrity.
Tip 3: Maintain Consistent Contact. Ensure the tool’s nosepiece is flush against the work surface before initiating fastener driving. Inconsistent contact can result in angled or improperly set fasteners.
Tip 4: Employ Safety Glasses. Always wear appropriate eye protection to guard against flying debris or errant fasteners. Safety glasses are an indispensable component of responsible tool operation.
Tip 5: Lubricate Regularly. Apply a few drops of pneumatic tool oil to the air inlet before each use. Proper lubrication minimizes friction and wear, extending the tool’s operational life.
Tip 6: Inspect Air Hose Connections. Periodically examine air hose connections for leaks or damage. Air leaks reduce efficiency and can compromise the tool’s performance.
Tip 7: Store Properly. When not in use, disconnect the tool from the air supply and store it in a clean, dry environment. Proper storage prevents corrosion and damage.
Implementing these practices will contribute to optimal functionality, prolonged lifespan, and safer operation of the pneumatic fastening instrument.
The subsequent sections will address troubleshooting common issues and provide further insights into advanced operational techniques.
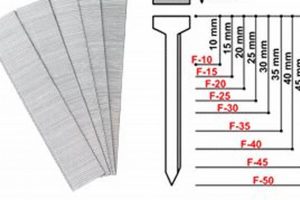
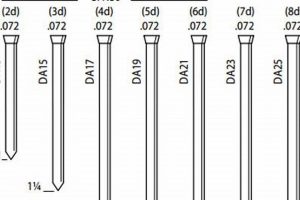
1. Gauge selection
Gauge selection is a critical parameter in the operation of a pneumatic finishing tool. It dictates the range of fastener sizes compatible with the tool. An incorrect gauge selection, for instance, attempting to use a larger gauge fastener than the tool is designed to handle, will result in jamming, potential damage to the tool’s internal mechanisms, and an inability to properly drive the fastener. Conversely, using a smaller gauge fastener than specified may lead to inconsistent setting depth and poor holding power.
Consider the common application of installing door or window casings. A finishing tool designed for 16-gauge fasteners cannot effectively utilize 18-gauge brads; the smaller diameter brads will not properly engage with the driving mechanism. This mismatch can lead to misfires, damage to the workpiece, or simply ineffective fastening. The correct gauge is thus a foundational requirement for proper tool function and achieving the desired result.
Therefore, understanding gauge selection is paramount for maximizing the effectiveness and longevity of such a tool. Mismatched fastener gauges lead to operational failures, increased maintenance, and compromised finish quality. Adherence to the tool’s specified gauge range ensures consistent performance, reduces the risk of damage, and ultimately contributes to professional-quality results in finish carpentry applications.
2. Depth adjustment
Depth adjustment is a critical feature impacting the performance and utility of a finish nailer. This function regulates the force with which fasteners are driven, ensuring they are set precisely flush with or slightly below the surface of the material. Incorrect depth adjustment can lead to fasteners protruding above the surface, compromising the aesthetic appeal of the finished piece and potentially posing a safety hazard. Conversely, driving fasteners too deep can weaken the material or create unsightly depressions.
Consider the installation of delicate trim around a window. If the depth is set too high, the nailer might drive fasteners excessively deep, leaving noticeable craters in the trim. Conversely, an insufficient depth setting may leave the nail head protruding, detracting from the finished appearance. The depth adjustment mechanism, often a dial or screw on the tool, allows the operator to fine-tune the driving force for various wood densities and fastener lengths. This precise control is essential for achieving a professional-grade finish.
Therefore, proficiency in utilizing the depth adjustment feature is paramount. It prevents damage to materials, ensures aesthetic integrity, and contributes to overall project quality. Mastery of this aspect allows for versatility across a wide range of finishing applications, making it an indispensable skill for carpenters and construction professionals. Ignoring the significance of proper depth adjustment leads to rework, material waste, and substandard results.
3. Air pressure
Air pressure serves as the driving force behind the operation of a pneumatic fastening tool. This parameter dictates the velocity and force with which fasteners are propelled, directly impacting the tool’s ability to consistently and accurately drive nails into various materials. Insufficient air pressure results in incomplete fastener insertion, while excessive pressure can cause damage to the workpiece or the tool itself. The manufacturer’s specifications for the equipment dictate the optimal pressure range, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). For example, attempting to drive 2-inch finishing nails into hardwood with an air pressure below the recommended level will invariably result in protruding nail heads and compromised joint integrity.
Maintaining consistent air pressure is equally important. Fluctuations in pressure, caused by an undersized compressor or leaks in the air hose, lead to inconsistent fastener setting. This inconsistency necessitates manual correction and increases the likelihood of damaging the material. In applications such as installing intricate crown molding, where precision and uniformity are paramount, stable air pressure ensures clean, professional results. The air compressor regulator becomes an essential component for maintaining stable air pressure. A quality regulator helps to prevent pressure spikes and drops, maintaining consistent driving power throughout the work process.
In summary, the pneumatic fastening tool’s effectiveness hinges on the precise management of air pressure. Adherence to the manufacturer’s recommended PSI, coupled with consistent pressure delivery, ensures optimal performance, reduces the risk of material damage, and contributes to a professional finish. Understanding the relationship between air pressure and fastener performance is, therefore, crucial for efficient and reliable operation. Failure to manage air pressure appropriately will lead to compromised work quality, increased material waste, and potential tool damage.
4. Sequential firing
Sequential firing, a critical operational mode in pneumatic finishing tools, significantly impacts both the safety and precision of fastener placement. In the context of a Ridgid finish nailer, this mechanism necessitates the nosepiece to be fully depressed against the work surface before the trigger is activated, thereby preventing unintentional fastener discharge. This deliberate two-step process serves as a safety measure, minimizing the risk of accidental firing and potential injury. For instance, when installing delicate trim work where precise nail placement is crucial, sequential firing allows the operator to carefully position the tool before driving each fastener, ensuring accuracy and minimizing material damage.
The alternative firing mode, contact or bump firing, allows for rapid fastener deployment by maintaining trigger activation while bumping the tool’s nosepiece against the work. While this increases speed, it compromises precision and poses a higher safety risk, especially in confined spaces or when working with irregular surfaces. For example, using bump firing to install crown molding along an uneven ceiling line greatly increases the likelihood of misfires, crooked fastener placement, and potential damage to the molding itself. The Ridgid finish nailer’s sequential firing option, therefore, becomes particularly valuable for intricate or high-precision tasks where control and accuracy outweigh speed.
In conclusion, the sequential firing mechanism on a Ridgid finish nailer represents a deliberate trade-off between speed and safety. Its activation promotes controlled, precise fastener placement, minimizing the risk of accidental firing and material damage. While bump firing may be suitable for high-volume applications, sequential firing provides the accuracy and control necessary for achieving professional-grade results in finish carpentry. The choice between these modes underscores the importance of understanding the tool’s capabilities and selecting the appropriate firing method for the specific task at hand. Improper usage can compromise both safety and the quality of the finished product.
5. Maintenance schedule
A regular maintenance schedule is integral to the operational lifespan and consistent performance of a pneumatic fastening instrument, such as a Ridgid finish nailer. Neglecting scheduled maintenance leads to decreased efficiency, potential malfunctions, and increased repair costs. The maintenance schedule, therefore, acts as a proactive measure against tool degradation. A primary example lies in the lubrication of internal components. Without regular oiling, friction increases, resulting in reduced power, increased wear, and eventual seizure of the driving mechanism. This directly impacts the instrument’s ability to consistently drive fasteners to the desired depth, leading to substandard work.
Furthermore, a comprehensive maintenance schedule encompasses the inspection and cleaning of the air filter and exhaust ports. Contaminants in the air supply accumulate within these components, restricting airflow and diminishing performance. Clogged filters can cause the tool to operate erratically, delivering inconsistent power and potentially damaging the internal components. Similarly, inspection of the air hose and fittings for leaks prevents pressure loss, maintaining consistent fastener driving force. Addressing these maintenance items proactively avoids operational inconsistencies and extends the instrument’s useful life.
In summary, adherence to a defined maintenance schedule is not merely an optional practice but a necessity for preserving the functionality and extending the lifespan of a Ridgid finish nailer. Regular lubrication, cleaning, and inspection mitigate the detrimental effects of wear and tear, ensuring consistent performance and minimizing the risk of costly repairs. Implementing and following the recommended maintenance plan contributes directly to the tool’s reliability and the quality of the finished product. Ignoring this critical aspect results in premature tool failure and increased operational expenses.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the operation, maintenance, and selection of this type of pneumatic tool. The information aims to provide clarity and guidance for users seeking to maximize the performance and longevity of their equipment.
Question 1: What is the appropriate air pressure for a Ridgid finish nailer?
The recommended operating pressure varies depending on the specific model and the material being fastened. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications, typically found on a label affixed to the tool or within the user manual. Exceeding the maximum pressure can damage the tool and the workpiece, while insufficient pressure results in incomplete fastener setting.
Question 2: How frequently should a Ridgid finish nailer be lubricated?
Regular lubrication is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. It is generally recommended to apply a few drops of pneumatic tool oil to the air inlet before each use. In high-use environments, more frequent lubrication may be necessary. Refer to the user manual for specific lubrication guidelines.
Question 3: What type of fasteners are compatible with a Ridgid finish nailer?
Compatibility depends on the gauge and length specifications of the tool. A 16-gauge finish nailer, for instance, accepts only 16-gauge finish nails within a specific length range. Using fasteners of the incorrect gauge or length can lead to jams, damage to the tool, and compromised fastening.
Question 4: What causes a Ridgid finish nailer to misfire or jam?
Common causes include insufficient air pressure, incorrect fastener selection, a dirty or damaged nosepiece, and a lack of lubrication. Inspecting and addressing these factors often resolves misfires and jams. Refer to the troubleshooting section of the user manual for detailed instructions.
Question 5: Is it necessary to wear safety glasses when operating a Ridgid finish nailer?
The use of safety glasses is mandatory. The tool propels fasteners at high velocity, and the risk of flying debris or errant fasteners poses a significant hazard to the eyes. Safety glasses provide essential protection against such risks.
Question 6: How should a Ridgid finish nailer be stored when not in use?
Disconnect the tool from the air supply and store it in a clean, dry environment. This prevents corrosion and damage to internal components. Storing the tool in its original case or a designated toolbox provides additional protection.
This FAQ section addresses common inquiries and provides a foundation for understanding the efficient and safe operation of the pneumatic fastening tool. Adhering to these guidelines contributes to prolonged tool life and consistent results.
The subsequent section will delve into advanced operational techniques and discuss troubleshooting more complex issues.
Conclusion
This document has explored critical aspects of the Ridgid finish nailer, encompassing operational guidelines, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting strategies. The information presented underscores the importance of proper air pressure regulation, consistent lubrication, and adherence to the manufacturer’s specifications for optimal performance and longevity. Furthermore, the document emphasized the significance of selecting appropriate fastener gauges, utilizing the depth adjustment mechanism effectively, and implementing a regular maintenance schedule.
Understanding the operational nuances of the Ridgid finish nailer is paramount for achieving professional-grade results in finish carpentry applications. Diligent adherence to the recommendations outlined herein will contribute to enhanced tool performance, minimized downtime, and a reduction in potential workplace injuries. Continued vigilance in maintaining this equipment remains essential for its sustained utility and consistent reliability.