
Words ending in ‘j’ are relatively rare in the English language. Most are loanwords, primarily originating from languages like Arabic, Persian, and Hebrew. A common example is “haj,” the pilgrimage to Mecca... Read more »
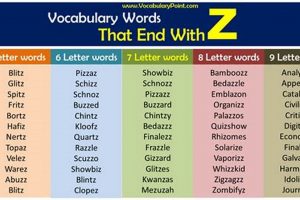
Lexical units concluding with the letter ‘z’ constitute a small but interesting subset of the English vocabulary. Examples include words like “quiz,” “buzz,” “fizz,” and “waltz.” The grammatical function these serve varies;... Read more »
Terms ending in the letter “a” are prevalent across numerous languages and disciplines. These lexical items can represent a wide array of concepts, ranging from concrete objects to abstract ideas. Examples include... Read more »

Words ending in ‘-able’ typically function as adjectives. They denote the capacity, suitability, or worthiness of something to be acted upon. Examples include “readable,” signifying the ease with which something can be... Read more »

Lexical units concluding with the grapheme ‘c’ constitute a specific subset of the English vocabulary. These words, diverse in origin and application, span various parts of speech. For example, “music” functions as... Read more »
Terms ending with the letter ‘f’ constitute a subset of the English lexicon. These terms can represent diverse parts of speech, including nouns (e.g., scarf), verbs (e.g., scoff), and adjectives (e.g., brief).... Read more »
The suffix “-tion” is a common derivational morpheme in the English language, typically transforming verbs into nouns. This process, known as nominalization, creates abstract nouns that often represent actions, processes, states, or... Read more »

Lexemes terminating in the sixth letter of the English alphabet exhibit diverse grammatical functions. These words can represent concrete entities (e.g., loaf, scarf), abstract concepts (e.g., belief, grief), or actions (e.g., waft,... Read more »

Verbal forms ending in “ing” function in multiple grammatical roles. These forms, derived from verbs, can operate as nouns (gerunds), adjectives (participles), or parts of continuous verb tenses. For instance, “swimming” can... Read more »
Lexical items concluding with the grapheme “x” constitute a subset of the English vocabulary. Examples include “box,” “fox,” “wax,” “index,” “matrix,” and “complex.” These words originate from various linguistic sources, including Latin,... Read more »


