An entity operating in the industrial sector, this organization specializes in enhancing the properties and appearance of metallic components. Through processes such as plating, coating, and polishing, the firm transforms raw or semi-finished metal parts, improving their resistance to corrosion, wear, and abrasion. As an example, they might apply a protective zinc coating to steel fasteners used in construction, ensuring longevity and structural integrity.
The existence of such organizations is vital to numerous industries. By extending the lifespan of metal products and optimizing their performance, these companies contribute to resource conservation and reduced maintenance costs. Historically, the development of advanced finishing techniques has paralleled advancements in manufacturing, enabling the production of more durable and reliable goods across sectors ranging from automotive to aerospace.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific finishing methods employed, quality control measures implemented, and the overall impact this type of operation has on the global supply chain. Discussions will also cover the various certifications and standards to which these businesses adhere, ensuring consistent and reliable outcomes for their clientele.
Enhancing Metal Product Durability
Achieving optimal performance and longevity of metal components requires careful attention to surface treatment. The following guidelines highlight crucial factors for ensuring superior results in metal finishing applications.
Tip 1: Material Selection: Prioritize the use of base metals compatible with the intended finishing process. Incompatible materials can lead to adhesion failures, corrosion, or other performance deficits. For instance, certain aluminum alloys exhibit superior anodization characteristics compared to others.
Tip 2: Surface Preparation: Proper pre-treatment is paramount. This includes rigorous cleaning to remove oils, scale, and other contaminants. Failure to adequately prepare the surface will compromise the effectiveness of subsequent finishing steps. Consider mechanical or chemical etching for improved adhesion.
Tip 3: Process Control: Maintain strict control over process parameters, such as temperature, pH levels, and chemical concentrations. Deviations from established protocols can result in inconsistent coating thicknesses, color variations, or compromised protective properties. Continuous monitoring is essential.
Tip 4: Thickness Management: Specify appropriate coating thicknesses based on the application requirements. Insufficient thickness may provide inadequate protection, while excessive thickness can lead to cracking or peeling. Precision measurement techniques, such as X-ray fluorescence, should be employed.
Tip 5: Corrosion Resistance: Select finishing processes that offer the required level of corrosion protection for the intended environment. Salt spray testing, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and other methods can be used to evaluate corrosion performance. Consider duplex systems for enhanced protection in harsh conditions.
Tip 6: Adhesion Testing: Verify the adhesion of the finished coating to the substrate. Techniques such as pull-off testing and scratch testing can be used to assess bond strength. Adequate adhesion is critical for ensuring long-term performance.
Tip 7: Quality Assurance: Implement a comprehensive quality assurance program that includes regular inspections, process audits, and data analysis. Proactive monitoring can identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing defects.
Tip 8: Environmental Compliance: Adhere to all applicable environmental regulations regarding waste disposal and emissions control. Select environmentally friendly finishing processes and materials whenever possible. Sustainable practices are essential for responsible operations.
Adherence to these principles promotes enhanced durability, performance, and aesthetic appeal in metal products, ultimately contributing to increased customer satisfaction and reduced lifecycle costs.
The subsequent discussion will address recent innovations in metal finishing technologies and their implications for various industries.
1. Precision
In the realm of quality metal finishing, precision is not merely a desirable attribute; it is a fundamental requirement. It dictates the consistency, reliability, and ultimately, the performance of the finished product. Organizations offering such services must prioritize accuracy across all operational stages to meet the stringent demands of various industries.
- Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy pertains to achieving specified measurements and tolerances in the finished metal parts. For instance, in aerospace applications, even minute deviations from design specifications can compromise the structural integrity of components. Precision ensures that coatings are applied uniformly, adhering to designated thicknesses within a micrometer range. This facet minimizes the risk of failures and optimizes performance.
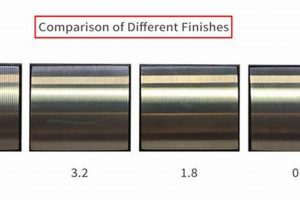
- Surface Finish Control
Surface finish directly influences properties such as friction, wear resistance, and adhesion. Precision in surface preparation, coating application, and polishing processes enables the creation of controlled surface profiles. Examples include achieving specific roughness values for optimal lubricant retention in engine components or creating ultra-smooth surfaces for optical instruments. Precise control ensures desired functional characteristics are achieved.
- Chemical Composition Control
Maintaining precise chemical composition is crucial for achieving desired corrosion resistance, hardness, and other material properties. Precision involves accurate monitoring and control of plating bath chemistries, alloy compositions in coatings, and diffusion treatments. Deviations in chemical composition can lead to compromised performance and premature failure, making accurate control essential.
- Process Parameter Management
Optimal results necessitate meticulous management of process parameters such as temperature, current density, pressure, and immersion time. Precision demands that these parameters be consistently maintained within prescribed ranges. Fluctuations can lead to inconsistencies in coating thickness, adhesion strength, and color uniformity. Implementing closed-loop control systems and rigorous monitoring protocols is essential for process stability.
The aspects of precision discussed above highlight its indispensable role in quality metal finishing. By prioritizing dimensional accuracy, surface finish control, chemical composition control, and process parameter management, these businesses can deliver products that meet or exceed customer expectations. The result is enhanced performance, increased longevity, and reduced risk of failure in demanding operational environments, reinforcing the importance of precision in achieving quality outcomes.
2. Durability
Durability, in the context of metal components, refers to their ability to withstand wear, corrosion, and other forms of degradation over extended periods. The connection between durability and a quality metal finishing corporation is causal: the application of appropriate finishing techniques directly enhances the lifespan and performance of metal parts. This enhancement is achieved through protective layers, altered surface properties, or both. For instance, applying a chromium coating increases hardness and corrosion resistance, allowing components to operate in harsh environments for longer durations. This ability to improve the inherent endurance of metals is central to a quality metal finishing corporation’s value proposition.
The importance of durability as a component of a quality metal finishing corporation is evident in various applications. In the automotive industry, parts like brake rotors and exhaust systems are exposed to high temperatures, road salts, and mechanical stress. Without proper finishing, these components would degrade rapidly, leading to frequent replacements and increased vehicle maintenance costs. A quality metal finishing corporation offers treatments such as thermal spray coatings or specialized plating to extend the service life of these parts, reducing the burden on both manufacturers and consumers. Similarly, in the oil and gas sector, components used in drilling and extraction face extreme pressures, corrosive chemicals, and abrasive particles. Finishing techniques such as ceramic coatings or hard chrome plating can mitigate these effects, preventing premature failure and costly downtime.
In summary, the correlation between durability and a quality metal finishing corporation is critical. Durability, attained through quality finishing processes, is a key attribute enhancing performance and longevity of metal components across various industries. Challenges persist in selecting the optimal finishing technique for specific applications and ensuring consistent quality control. However, organizations prioritizing durability by investing in the right processes and expertise directly contribute to resource efficiency, cost savings, and overall product reliability.
3. Innovation
Innovation serves as a vital catalyst for advancement within the metal finishing sector. A quality metal finishing corporation embraces research and development to enhance existing techniques and pioneer new methodologies. This commitment to progress directly impacts process efficiency, material performance, and environmental responsibility. For instance, the development of trivalent chromium plating as a substitute for hexavalent chromium reflects an innovative response to environmental concerns and stricter regulations.
The importance of innovation within this industry is multifaceted. New coating materials with superior corrosion resistance extend the lifespan of finished products, reducing the frequency of replacements. Advanced application methods, such as pulse plating or vapor deposition, yield coatings with improved uniformity and density, enhancing functional performance. Furthermore, innovative surface preparation techniques, including laser ablation, enable precise control over surface topography, optimizing adhesion and performance characteristics. As an example, the aerospace industry relies on innovative surface treatments to enhance the fatigue life and corrosion resistance of critical components, ensuring aircraft safety and reliability. Similarly, the electronics industry benefits from innovative plating processes that enable the creation of miniaturized and high-performance electronic devices.
In conclusion, innovation is not merely a desirable attribute for a quality metal finishing corporation; it is an essential driver of competitiveness and sustainability. Ongoing research, development, and adoption of new technologies translate into superior product quality, enhanced environmental stewardship, and the ability to meet the evolving needs of diverse industries. While challenges exist in implementing and scaling new technologies, the long-term benefits of embracing innovation are substantial, positioning organizations for sustained success within the dynamic metal finishing landscape.
4. Compliance
Compliance constitutes a foundational element of a quality metal finishing corporation. The connection between operational practices and adherence to regulatory standards is not merely correlative, but causational: stringent compliance protocols directly influence product quality, worker safety, and environmental protection. A metal finishing corporation’s commitment to fulfilling all relevant regulatory requirements reflects its dedication to responsible and sustainable business practices. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, legal ramifications, and reputational damage, undermining the corporation’s long-term viability. Examples of relevant regulations include the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards, each imposing specific requirements related to emissions control, waste management, and workplace safety.
The practical implications of compliance are far-reaching. For instance, strict adherence to waste disposal regulations, such as proper handling and treatment of spent plating solutions, mitigates the risk of environmental contamination. Implementing comprehensive ventilation systems and providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) ensures worker safety by minimizing exposure to hazardous chemicals. Consistent monitoring and reporting of emissions data enables early detection of potential environmental impacts and facilitates proactive corrective actions. Failure to comply with these requirements can lead to substantial fines, facility shutdowns, and even criminal charges, jeopardizing the corporation’s operational continuity and stakeholder trust. As a result, quality metal finishing corporations prioritize the development and implementation of robust compliance programs that encompass all aspects of their operations.
In conclusion, compliance serves as a critical pillar underpinning the success of a quality metal finishing corporation. Adherence to regulatory standards directly enhances product integrity, minimizes environmental impact, and safeguards worker well-being. While challenges exist in navigating the complex and evolving regulatory landscape, organizations that prioritize compliance demonstrate a commitment to ethical business practices and long-term sustainability. The proactive integration of compliance into core operational strategies is thus essential for ensuring both regulatory adherence and sustained competitive advantage.
5. Sustainability
Sustainability has emerged as a central tenet for responsible industrial operations. Within the metal finishing sector, it represents a multifaceted commitment to minimizing environmental impact, conserving resources, and promoting long-term ecological well-being. A quality metal finishing corporation integrates sustainable practices throughout its value chain to mitigate its environmental footprint and contribute to a more circular economy.
- Waste Reduction and Management
Metal finishing processes generate various waste streams, including spent plating solutions, rinse water, and sludge. Sustainable practices emphasize minimizing waste generation through process optimization, recycling, and the implementation of closed-loop systems. For instance, ion exchange technology can be used to recover valuable metals from rinse water, reducing waste volume and reclaiming resources. Proper waste characterization, treatment, and disposal are also crucial for preventing environmental contamination. By actively minimizing waste, a quality metal finishing corporation reduces its environmental burden and conserves valuable resources.
- Resource Conservation
Metal finishing operations consume significant quantities of water, energy, and raw materials. Sustainable practices focus on conserving these resources through efficient process design, water reuse, and the use of energy-efficient equipment. Examples include implementing counter-current rinsing systems to reduce water consumption, utilizing solar energy to power facility operations, and sourcing raw materials from sustainable suppliers. Resource conservation not only reduces environmental impact but also enhances operational efficiency and cost savings for the metal finishing corporation.
- Reduced Use of Hazardous Materials
Traditional metal finishing processes often rely on hazardous chemicals, such as hexavalent chromium and cyanide. Sustainable practices emphasize the substitution of these chemicals with less toxic alternatives, such as trivalent chromium and organic acids. The use of safer chemicals reduces the risk of worker exposure, minimizes environmental contamination, and simplifies waste management. Furthermore, the adoption of environmentally friendly coating technologies, such as powder coating and electrodeposition, can further reduce the reliance on hazardous materials. By minimizing the use of hazardous substances, a quality metal finishing corporation protects human health and the environment.
- Life Cycle Assessment
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a comprehensive methodology for evaluating the environmental impacts of a product or process throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. A quality metal finishing corporation utilizes LCA to identify environmental hotspots within its operations and develop strategies for improvement. By considering the environmental impacts of all stages of the metal finishing process, from energy consumption to waste generation, LCA enables informed decision-making and promotes continuous improvement in sustainability performance.
These interconnected facets underscore sustainability as an indispensable component of a quality metal finishing corporation. Through waste reduction, resource conservation, reduced use of hazardous materials, and life cycle assessment, organizations can minimize their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. A proactive commitment to sustainability not only benefits the environment but also enhances corporate reputation, improves stakeholder relations, and drives long-term business value.
6. Expertise
Expertise serves as the cornerstone of a quality metal finishing corporation. It is the causal factor influencing the efficacy, consistency, and reliability of finished products. The application of specialized knowledge and skills by trained professionals directly translates to superior surface treatments and enhanced material performance. Without proficient personnel adept in chemistry, metallurgy, and engineering principles, the potential benefits of advanced finishing technologies cannot be fully realized. The quality of the final product is directly proportional to the level of expertise applied throughout the process. Examples include the selection of appropriate plating chemistries, precise control of process parameters, and accurate execution of surface preparation techniques, all requiring in-depth understanding and practical experience.
The practical significance of expertise manifests across various operational facets. For instance, in addressing corrosion resistance requirements, a metallurgist’s expertise is crucial in determining the optimal alloy composition and coating thickness to meet specific environmental demands. Similarly, chemical engineers ensure proper bath maintenance and waste treatment, minimizing environmental impact and maintaining regulatory compliance. In troubleshooting, experienced technicians diagnose issues with coating adhesion or uniformity, implementing corrective actions based on their understanding of underlying chemical and physical processes. Therefore, expertise is essential in resolving technical challenges and achieving consistent quality standards.
In summary, expertise is not merely an asset but a fundamental prerequisite for a quality metal finishing corporation. It ensures optimal utilization of resources, minimizes defects, and maximizes the performance of finished products. While challenges exist in attracting and retaining skilled personnel, organizations that prioritize expertise by investing in training, development, and knowledge sharing will invariably achieve a competitive advantage and deliver superior results. This directly contributes to sustained customer satisfaction and long-term business success, solidifying expertise as the bedrock of quality in metal finishing.
7. Reliability
The correlation between a metal finishing corporation’s reliability and its perceived quality is a direct and critical one. Reliability, in this context, encompasses consistency in meeting promised deadlines, adherence to specified quality standards, and dependable performance of the finished product. A quality metal finishing corporation recognizes that its reputation hinges on its ability to consistently deliver results that meet or exceed customer expectations. This reliability translates into customer trust and fosters long-term business relationships. The consistent application of plating, coating, or other finishing processes, delivered on time and within budget, establishes a predictable outcome for clients, reducing the risks associated with production schedules and product performance.
Consider, for instance, an automotive manufacturer requiring a specific anti-corrosion coating for brake components. A reliable metal finishing corporation will ensure the coating meets established standards for salt spray resistance and adhesion, providing assurance the brake components will withstand harsh environmental conditions and function as intended throughout their operational lifespan. Similarly, in the aerospace industry, precision and reliability are paramount. A reliable metal finishing corporation will meticulously follow procedures and provide appropriate documentation confirming processes are executed flawlessly. This is of upmost importance because components that require corrosion resistance in certain products need to fulfill the specifications in their products. In both of these instances, reliability directly contributes to the safety, performance, and longevity of the final product.
In summary, reliability is not merely a desirable attribute but an essential characteristic of a quality metal finishing corporation. Consistent delivery, adherence to standards, and dependable performance establish trust and foster long-term partnerships. Challenges persist in maintaining reliability across fluctuating market demands and evolving technologies. However, organizations prioritizing reliability through rigorous process control, robust quality management systems, and a commitment to customer satisfaction will consistently deliver superior results and secure a competitive advantage within the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the services and processes provided by organizations specializing in surface treatment for metallic components. The objective is to provide clarity and promote informed decision-making.
Question 1: What constitutes “quality” in metal finishing?
Quality in metal finishing encompasses several key characteristics: adherence to specified tolerances, uniformity of coating thickness, optimal adhesion to the substrate material, and resistance to degradation under anticipated operating conditions. Achieving these characteristics requires stringent process control, qualified personnel, and validated testing procedures.
Question 2: What industries benefit most from these services?
A wide range of industries rely on metal finishing services to enhance the performance and longevity of their products. Prominent examples include the automotive, aerospace, medical device, electronics, and construction sectors, all of which require specialized surface treatments to meet specific performance or regulatory demands.
Question 3: What are the primary benefits of using a metal finishing corporation?
Engaging a specialized organization offers several benefits. These include access to advanced technologies and expertise, consistent product quality through established processes, reduced risk of defects or failures, and improved resource efficiency through optimized operations. Furthermore, working with a reputable firm ensures compliance with relevant environmental and safety regulations.
Question 4: How are different finishing methods selected for specific applications?
The selection process involves considering several factors. These include the base material’s composition, the intended operating environment, required performance characteristics (e.g., corrosion resistance, hardness), and any applicable regulatory constraints. Consulting with a qualified engineer or metallurgist is essential to determine the most appropriate finishing method.
Question 5: What quality control measures are typically implemented?
Comprehensive quality control programs incorporate a variety of measures. These include incoming material inspection, in-process monitoring of critical parameters (e.g., bath chemistry, temperature), non-destructive testing techniques (e.g., X-ray fluorescence), and destructive testing procedures (e.g., adhesion testing, corrosion testing). Statistical process control is often employed to ensure process stability and consistency.
Question 6: How can environmental impact be minimized?
Minimizing environmental impact involves several strategies. These include utilizing environmentally friendly chemicals, implementing closed-loop water recycling systems, optimizing energy consumption, and properly managing waste streams. Adherence to relevant environmental regulations and the implementation of sustainable practices are essential for responsible operations.
In summary, a thorough understanding of these aspects contributes to effective collaboration and mutually beneficial outcomes when engaging specialized metal finishing services.
The subsequent article segment will explore recent technological advancements in the field.
Quality Metal Finishing Corporation
Throughout this exploration, the multifaceted nature of a quality metal finishing corporation has been examined. Precision, durability enhancement, innovation, regulatory compliance, sustainability initiatives, specialized expertise, and unwavering reliability were identified as crucial components underpinning the success of these entities. The interplay of these factors ensures the provision of superior surface treatments, extending the lifespan and enhancing the performance of metal components across diverse industrial sectors.
The ongoing pursuit of advancements in materials science, process optimization, and environmental stewardship remains paramount for these corporations. A continued focus on these areas will not only drive innovation but also secure a competitive edge in an evolving global marketplace. Future success hinges on a commitment to excellence and the consistent delivery of value to clients seeking reliable and sustainable metal finishing solutions.