This entity operates within the specialized field of enhancing metallic surfaces. Through application of various techniques, the organization aims to improve the aesthetic appeal, durability, and functionality of metal components. These processes often involve cleaning, coating, and polishing to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as corrosion resistance or increased hardness. For example, components used in aerospace or automotive industries may undergo treatments to meet stringent industry standards.
The value of such operations lies in extending the lifespan of metal products, reducing maintenance costs, and improving overall product performance. Historically, these processes have evolved from rudimentary manual techniques to sophisticated automated systems, reflecting advancements in materials science and engineering. These advancements have enabled the delivery of highly precise and consistent results, meeting the diverse needs of various manufacturing sectors.
The following discussion will explore various facets of the metal finishing industry, including specific processes, material considerations, quality control measures, and environmental compliance. These aspects are crucial for understanding the complexities and importance of achieving high-quality metal finishes for diverse applications.
Guidance on Optimal Metal Surface Preparation
The effectiveness of any metal finishing process is intrinsically linked to the initial state of the substrate. Meticulous attention to preparation significantly enhances the final product’s performance and longevity.
Tip 1: Implement Rigorous Cleaning Protocols: Prior to any surface treatment, the removal of contaminants such as oils, grease, oxides, and scale is paramount. Employ appropriate cleaning methods like solvent degreasing, alkaline cleaning, or abrasive blasting based on the nature of the contaminant and the substrate material. Incomplete cleaning can lead to adhesion failures and compromised corrosion resistance.
Tip 2: Select the Appropriate Abrasive Blasting Media: The choice of abrasive blasting media directly influences surface profile and cleanliness. Consider the material being treated and the desired surface finish. Aluminum oxide is suitable for general cleaning and etching, while glass beads are preferred for delicate surfaces requiring minimal profile alteration. Selection should consider the potential for media embedment and its impact on subsequent finishing processes.
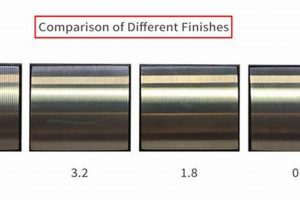
Tip 3: Control Surface Roughness: Surface roughness plays a crucial role in coating adhesion. Optimizing surface roughness involves balancing the need for sufficient mechanical interlocking with the avoidance of excessive roughness that can lead to coating defects or reduced corrosion resistance. Specify and monitor surface roughness parameters using appropriate measurement techniques.
Tip 4: Employ Chemical Pre-Treatments Strategically: Chemical pre-treatments, such as conversion coatings (e.g., chromate conversion or phosphate conversion), are often necessary to enhance corrosion resistance and provide an improved bonding surface for subsequent coatings. The selection of the appropriate pre-treatment should be based on the metal substrate and the specific performance requirements of the finished product.
Tip 5: Maintain Tight Process Controls: Consistent results demand meticulous control of all process parameters, including temperature, pressure, immersion time, and chemical concentrations. Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential to ensure process stability and minimize variability in the final product.
Tip 6: Ensure Adequate Rinsing: After each cleaning or pre-treatment step, thorough rinsing is crucial to remove residual chemicals that can interfere with subsequent processes or lead to corrosion. Employ multiple rinse stages and monitor rinse water quality to ensure complete removal of contaminants.
Tip 7: Implement Stringent Quality Control: Quality control should be integrated into every stage of the finishing process. Employ appropriate testing methods to verify surface cleanliness, roughness, coating thickness, and adhesion. Regular inspection and documentation help identify and address potential problems early, minimizing rework and ensuring consistent quality.
Adherence to these guidelines will lead to enhanced coating adhesion, improved corrosion resistance, and extended service life of the finished metal components. This commitment to quality translates to tangible benefits in terms of product performance and reduced life-cycle costs.
The subsequent section will delve into specific metal finishing techniques, providing a detailed overview of the various options available and their respective applications.
1. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Enhanced corrosion resistance represents a primary objective and a tangible outcome frequently sought through specialized metal finishing processes. It is a critical component within the scope of services, and frequently a key motivator for engaging such services. The detrimental effects of corrosion, ranging from aesthetic degradation to structural failure, necessitate effective protective measures. For instance, marine applications involving metal components require robust resistance to saltwater corrosion, achievable through processes like galvanizing or specialized coatings.
Metal finishing techniques designed to impart enhanced corrosion resistance involve creating a barrier between the base metal and the corrosive environment. This barrier can take the form of a sacrificial coating, such as zinc in galvanizing, which corrodes preferentially to protect the underlying steel. Alternatively, it may involve a passive layer, like the chromium oxide film formed in stainless steel passivation. The effectiveness of these methods depends on factors such as the coating material, thickness, application technique, and the severity of the corrosive environment. The selection of the appropriate process requires a thorough understanding of the application’s specific needs.
The provision of enhanced corrosion resistance through metal finishing translates to significant practical benefits, including extended component lifespan, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved safety and reliability in critical applications. It constitutes a core value proposition, aligning with the overarching goal of improving the performance and longevity of metal products, making it a crucial determinant of the metal finishing service. Ongoing research and development continue to refine existing techniques and explore new materials and methods for achieving even greater levels of corrosion protection.
2. Aesthetic Surface Enhancement
Aesthetic surface enhancement represents a critical aspect of metal finishing, directly impacting the perceived value and market appeal of manufactured goods. This pursuit of visual refinement aligns closely with the capabilities offered by organizations dedicated to superior metal finishing, as it necessitates precise control over surface characteristics and the application of specialized techniques.
- Achieving Desired Reflectivity
The attainment of specific reflectivity levels constitutes a primary goal in many aesthetic finishing applications. Processes such as polishing, buffing, and electropolishing can produce surfaces ranging from matte to mirror-like. In the automotive industry, for example, bright chrome finishes on trim components contribute significantly to the vehicle’s overall aesthetic. An organization specializing in metal finishing must possess the expertise and equipment to consistently achieve and maintain the specified reflectivity standards, crucial for brand image and customer satisfaction.
- Color Consistency and Uniformity
The consistent application of color, whether through painting, powder coating, or anodizing, is paramount for achieving a visually appealing and uniform surface. Variations in color or finish can detract from the product’s perceived quality and value. In architectural applications, consistent color across large metal panels ensures a cohesive and visually pleasing building facade. Achieving this consistency requires precise control over process parameters, material selection, and application techniques, highlighting the importance of expertise.
- Textural Refinement and Decorative Effects
Beyond color and reflectivity, surface texture plays a significant role in aesthetic appeal. Techniques such as brushing, etching, or laser engraving can create unique textures that enhance the tactile and visual experience. In consumer electronics, brushed metal surfaces offer a premium feel and visual interest. Metal finishing capabilities should extend beyond simple coating application to encompass the creation of intricate textures and decorative effects, providing greater design flexibility.
- Defect Minimization and Surface Integrity
The pursuit of aesthetic excellence necessitates the elimination of surface defects such as scratches, dents, or blemishes. Imperfections detract from the overall appearance and can compromise the product’s perceived quality. Stringent quality control measures, meticulous handling procedures, and skilled craftsmanship are essential for minimizing defects and maintaining surface integrity. The ability to consistently deliver defect-free surfaces is a hallmark of reputable organizations specializing in metal finishing.
The diverse range of techniques employed to achieve aesthetic surface enhancement underscores the complexity and sophistication inherent in the metal finishing industry. The pursuit of visual refinement is not merely about applying a coating; it requires a holistic approach encompassing material selection, process control, quality assurance, and skilled craftsmanship. Companies specializing in superior metal finishing must possess the capabilities and expertise to meet these demands, delivering surfaces that are not only visually appealing but also durable and functional.
3. Improved Wear Properties
Enhancing the resistance of metal components to wear represents a significant objective within the domain of metal finishing. It directly influences the longevity, reliability, and performance of parts subjected to frictional forces, abrasion, erosion, or adhesive wear. Consequently, services targeted at imparting improved wear properties are of paramount importance across numerous industries.
- Hard Chrome Plating for Wear Resistance
Hard chrome plating exemplifies a widely employed technique for enhancing wear resistance. The process involves electrodepositing a thick layer of chromium onto the substrate, resulting in a surface characterized by exceptional hardness and low friction coefficient. Applications span various sectors, including hydraulic cylinders, piston rings, and tooling components, where surfaces are constantly subjected to sliding contact and abrasive wear. Superior metal finishing processes that deliver consistent and uniform hard chrome coatings contribute directly to the extended service life and operational efficiency of these components.
- Nitriding for Surface Hardening
Nitriding, a case-hardening process, introduces nitrogen into the surface of a metal component, forming a hard and wear-resistant layer. This technique is particularly effective for enhancing the wear properties of steel components, such as gears, crankshafts, and valve components. Nitriding processes can be tailored to achieve specific case depths and hardness profiles, optimizing wear resistance for different applications. Metal finishing organizations employing advanced nitriding technologies enable manufacturers to produce components with superior wear performance, reducing the likelihood of premature failure and extending service intervals.
- Thermal Spray Coatings for Abrasion Resistance
Thermal spray coatings involve depositing a layer of molten or semi-molten material onto a substrate, creating a wear-resistant surface. A wide range of materials, including ceramics, carbides, and metals, can be applied using thermal spray techniques, allowing for the customization of coatings to meet specific wear requirements. Thermal spray coatings find application in industries such as aerospace, where components are exposed to extreme temperatures and abrasive environments. Superior metal finishing practices employing thermal spray technologies contribute to the enhanced durability and reliability of these critical components.
- Surface Texturing for Friction Reduction
Surface texturing, often achieved through laser etching or other controlled abrasion techniques, can be employed to modify the surface topography of metal components, reducing friction and improving wear resistance. By creating micro-dimples or other surface features, textured surfaces can trap lubricants, reduce contact area, and minimize adhesive wear. This approach is particularly relevant in applications involving sliding or rotating components, such as bearings and seals. Metal finishing services that incorporate surface texturing techniques offer a means of optimizing friction characteristics and extending the lifespan of moving parts.
The application of these techniques by organizations specializing in metal finishing translates to tangible benefits for manufacturers and end-users alike. Enhanced wear properties result in extended component lifespan, reduced maintenance costs, improved operational efficiency, and increased overall product reliability. The ability to provide tailored solutions that address specific wear challenges is a hallmark of a provider focused on delivering superior metal finishing services.
4. Precise Application Techniques
The delivery of consistently high-quality metal finishes necessitates the employment of precise application techniques. The connection between these techniques and organizations purporting to offer superior services stems from the fundamental understanding that the final properties of a finished metal surface are directly dependent on the accuracy and control exercised during each stage of the finishing process. A deviation from established parameters, such as coating thickness, temperature, or chemical concentration, can result in compromised performance, aesthetic defects, or reduced lifespan.
The implementation of precise application techniques is not merely an operational preference; it is a critical component of achieving demonstrably superior results. In the aerospace industry, for example, coatings applied to turbine blades must adhere to strict thickness tolerances to ensure optimal thermal barrier protection. Imprecise application can lead to hot spots, accelerated wear, and potentially catastrophic engine failure. Similarly, in the medical device industry, the biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of implanted devices rely heavily on the uniform and controlled application of specialized coatings. Any variation in coating thickness or composition can compromise the device’s safety and efficacy.
The ability to execute metal finishing processes with precision often necessitates significant investment in advanced equipment, rigorous training programs, and comprehensive quality control systems. Organizations committed to delivering superior services typically prioritize these investments, recognizing that they are essential for achieving consistently high-quality results and maintaining a competitive advantage. Furthermore, meticulous documentation and traceability are critical for identifying and addressing any deviations from established process parameters. These measures ensure that the final product meets the specified requirements and that any potential issues can be quickly resolved. The reliance on and mastery of precise application techniques thus serve as a defining characteristic and a core competency of those providing truly superior metal finishing services.
5. Industry Standard Compliance
Industry standard compliance constitutes a foundational element for any organization seeking to establish itself as a provider of superior metal finishing services. Adherence to established standards, such as those set by ISO, ASTM, or industry-specific regulatory bodies, serves as objective validation of process control, quality assurance, and environmental responsibility. For instance, compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality management, influencing process execution from material selection to final inspection. This adherence is not merely a formality; it is a crucial indicator of an organization’s ability to consistently deliver services that meet defined requirements and specifications.
The practical significance of industry standard compliance extends beyond the operational realm. It provides customers with assurance that the metal finishing processes employed are subject to rigorous scrutiny and meet accepted benchmarks for performance, safety, and environmental impact. In sectors such as aerospace and automotive, adherence to industry-specific standards is often a prerequisite for participation in the supply chain. Failure to comply can result in disqualification from bidding on projects or supplying components, effectively limiting market access. Real-world examples include the requirement for NADCAP accreditation for suppliers of aerospace metal finishing services, highlighting the critical role of compliance in maintaining a competitive position. Moreover, compliance often necessitates ongoing investment in training, equipment upgrades, and process optimization, driving continuous improvement and fostering a culture of excellence within the organization.
In conclusion, industry standard compliance is an inseparable component of superior metal finishing. It serves as both a validation of quality and a driver of continuous improvement. Organizations that prioritize compliance demonstrate a commitment to meeting customer expectations, adhering to regulatory requirements, and maintaining a competitive edge in the marketplace. Challenges remain in navigating the complex landscape of industry standards and adapting to evolving regulatory requirements. However, the benefits of compliance, including enhanced reputation, improved operational efficiency, and expanded market access, far outweigh the associated costs. The adherence to these standards and requirements are what separates a average company to a superior one.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries concerning specialized metal surface treatments. This aims to provide clarity and dispel potential misconceptions.
Question 1: What distinguishes processes from standard coating applications?
These processes involve intricate surface preparation, controlled application environments, and rigorous quality control measures exceeding those typically associated with standard coating procedures. The focus lies on achieving specific performance characteristics rather than solely aesthetic enhancement.
Question 2: How is corrosion resistance optimized for marine environments?
Optimization involves employing sacrificial coatings, such as galvanizing, or specialized barrier coatings designed to withstand prolonged exposure to saltwater. Material selection and coating thickness are critical considerations based on the specific marine conditions.
Question 3: What factors influence the selection of a specific metal finishing technique?
Selection depends on various factors, including the base metal, the desired performance characteristics (e.g., wear resistance, corrosion protection), the application environment, and cost considerations. A comprehensive evaluation is essential to determine the most appropriate technique.
Question 4: What quality control measures are implemented to ensure consistency and reliability?
Quality control involves meticulous monitoring of process parameters, regular inspections, and destructive and non-destructive testing methods to verify coating thickness, adhesion, and other critical properties. Statistical process control is employed to maintain process stability.
Question 5: How is environmental compliance addressed?
Environmental compliance is achieved through adherence to relevant regulations, the use of environmentally friendly materials, and the implementation of waste management and pollution control measures. Continuous monitoring and assessment are essential.
Question 6: What are the typical turnaround times for metal finishing projects?
Turnaround times vary depending on the complexity of the project, the size and quantity of components, and the specific finishing requirements. Project timelines are established based on a thorough assessment of these factors.
Metal finishing provides tangible benefits in terms of performance, longevity, and cost efficiency.
The upcoming section will explore the future trends and innovations shaping the metal finishing industry.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated critical facets associated with specialized metal surface treatments, underlining their importance in enhancing performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. The rigorous processes, precise application techniques, and adherence to industry standards inherent in metal finishing were detailed. The importance of corrosion resistance, wear properties, and aesthetic improvements were also emphasized. The commitment to quality and precision distinguishes providers offering elevated service levels.
The ongoing evolution of materials science and engineering continues to drive innovation within the metal finishing sector. Proactive engagement with these advancements, coupled with a dedication to stringent process control, remains essential for achieving optimal results and meeting the increasingly demanding requirements of diverse industries. Continued investment in research and development is paramount. Metal finishing services hold considerable potential for further enhancing the performance and lifespan of metal products across various industries.