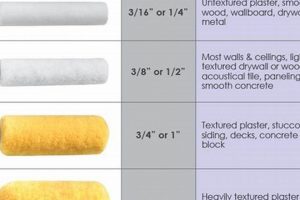
The optimal coating for a door exposed to the elements is one that balances aesthetic appeal with robust protection against weathering. This coating shields the door from moisture, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature fluctuations, preserving its structural integrity and visual quality. For instance, a high-quality acrylic latex paint, when properly applied, creates a durable and attractive barrier.
Selecting an appropriate coating is crucial for extending the lifespan of an exterior door, minimizing maintenance requirements, and enhancing the curb appeal of a property. Historically, oil-based paints were favored for their durability, but advancements in water-based technologies have yielded products that offer comparable or superior performance, along with environmental advantages. The right choice contributes significantly to both the long-term value and the immediate presentation of a building.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific types of coatings suitable for exterior doors, examining their characteristics, application techniques, and relative advantages and disadvantages. Factors such as gloss level, color retention, and ease of maintenance will be discussed to provide a comprehensive guide to selecting the most effective option for a particular application.
Expert Recommendations for Exterior Door Coatings
The following recommendations provide guidance on selecting and applying coatings to ensure long-lasting protection and aesthetic appeal for exterior doors.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to application, thoroughly clean and sand the door surface. Remove any loose paint, dirt, or mildew. A clean, smooth surface ensures optimal adhesion and a uniform appearance. Failing to prepare adequately compromises the longevity of the coating.
Tip 2: Priming is Essential: Apply a high-quality primer specifically formulated for exterior use. Primer seals the wood, provides a uniform base for the topcoat, and enhances adhesion. Use a tinted primer that is close to the finish color to improve coverage and color uniformity.
Tip 3: Select a Durable Coating Type: Acrylic latex coatings are generally recommended for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to fading and cracking. For enhanced durability and resistance to scuffing, consider a hybrid alkyd-acrylic coating. Research product specifications to ensure suitability for exterior use.
Tip 4: Apply Multiple Thin Coats: Avoid applying thick coats, as this can lead to runs, drips, and uneven drying. Multiple thin coats allow for proper curing and provide a more durable finish. Allow each coat to dry completely before applying the next.
Tip 5: Utilize Appropriate Application Tools: Choose high-quality brushes and rollers designed for the specific coating type. For smooth surfaces, a fine-finish foam roller can minimize brush strokes. Proper tools contribute significantly to the overall appearance and durability.
Tip 6: Pay Attention to Environmental Conditions: Apply coatings when the temperature is within the manufacturer’s recommended range. Avoid applying coatings in direct sunlight or during periods of high humidity. Unfavorable conditions can negatively impact drying time and adhesion.
Tip 7: Protect the Door During Drying: Allow the coating to dry completely before exposing the door to the elements. Protect the door from rain, direct sunlight, and excessive dust. Proper drying is essential for achieving a durable and long-lasting finish.
Implementing these recommendations will contribute to a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting coating that effectively protects exterior doors from the damaging effects of weather.
The subsequent sections will discuss specific product recommendations and advanced coating techniques for achieving optimal results.
1. Durability
Durability is a cornerstone attribute of an effective coating. The capacity of a door finish to withstand environmental stressors directly determines its service life and aesthetic integrity. A durable surface resists scratching, chipping, and fading, maintaining its appearance over extended periods. The selection of a coating possessing inherent durability characteristics is, therefore, paramount in achieving a long-lasting and visually appealing result. For example, consider the impact of direct sunlight on a south-facing door: a coating lacking adequate UV resistance will prematurely fade, necessitating frequent reapplication and associated costs.
The relationship between material selection and durability is also significant. Coatings formulated with high-quality resins and pigments exhibit superior resistance to wear and tear compared to those utilizing lower-grade components. Alkyd-modified acrylic paints, for instance, are frequently specified for exterior applications due to their enhanced hardness and abrasion resistance. Furthermore, proper application techniques, including thorough surface preparation and the application of multiple thin coats, contribute substantially to the overall durability of the coating system. Incorrect application can compromise even the most durable material.
In conclusion, durability is an indispensable element. Selecting a coating solely based on aesthetic considerations, while neglecting its ability to endure environmental challenges, inevitably leads to premature failure and increased maintenance expenses. Prioritizing durability at the outset ensures long-term performance, reduces lifecycle costs, and preserves the visual appeal of the entryway.
2. Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is a critical determinant in selecting a suitable coating for exterior doors. The coating must act as a robust barrier against diverse environmental factors to preserve the door’s structural integrity and aesthetic appearance over time. The ability of the chosen finish to withstand these elements directly impacts its longevity and performance.
- Moisture Protection
Coatings must prevent water penetration to avoid wood rot, swelling, and eventual structural damage. Finishes with low permeability ratings are preferred in climates with high rainfall or humidity. For instance, a water-based acrylic latex coating, properly applied, creates a flexible barrier that repels moisture and minimizes the risk of water damage to the underlying wood.
- UV Radiation Resistance
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause coatings to fade, chalk, and degrade. Finishes with UV absorbers or pigments known for their color stability are essential for maintaining the aesthetic appearance of the door. A door painted with a dark color, such as black or dark blue, will heat up more than a door painted with a white or light color. Select a coating with high UV resistance.
- Temperature Fluctuation Tolerance
Exterior doors are subjected to wide temperature swings that can cause expansion and contraction. Coatings must be flexible enough to accommodate these movements without cracking or peeling. Rigid finishes are more prone to failure in environments with significant temperature variations. A flexible acrylic latex coating can expand and contract better than a rigid oil-based enamel coating.
- Resistance to Biological Growth
In humid environments, mold and mildew can proliferate on exterior surfaces. Coatings with mildewcides or inherent resistance to fungal growth are desirable to prevent unsightly staining and potential health hazards. Regularly cleaning the door’s surface also will help resist biological growth.
The aforementioned facets of weather resistance are crucial for determining the long-term viability of any exterior door coating. Selecting a product that effectively addresses these challenges ensures extended protection, reduces maintenance requirements, and preserves the door’s aesthetic appeal. A coating’s ability to effectively mitigate the impact of weather is, therefore, a primary consideration when selecting the best coating. Prioritize coatings designed for superior defense against these environmental forces.
3. Color Retention
Color retention is a critical attribute in determining the suitability of a coating. An exterior door finish should maintain its intended hue and vibrancy despite prolonged exposure to environmental stressors. Deterioration of color impacts not only the door’s visual appeal but also reflects the overall quality and protective capabilities of the coating.
- Pigment Quality and Stability
The type and quality of pigments used in a coating formulation directly influence its resistance to fading. Inorganic pigments, such as iron oxides and titanium dioxide, typically exhibit superior color stability compared to organic pigments. Choosing a coating with a high concentration of lightfast pigments ensures minimal color shift over time, especially in areas with intense sunlight exposure. For example, a door painted with a coating utilizing high-grade titanium dioxide will retain its white color much longer than one painted with a coating using a lower-grade pigment.
- Binder Chemistry
The binder, or resin, in a coating formulation serves as the vehicle for the pigments and determines the coating’s overall durability and resistance to environmental factors. Acrylic latex binders are known for their excellent color retention properties, as they are less prone to yellowing or discoloration compared to alkyd or oil-based binders. A coating formulated with a high-quality acrylic binder will maintain its color integrity even after prolonged exposure to UV radiation and moisture.
- UV Resistance Additives
Incorporating UV absorbers or stabilizers into a coating formulation can significantly enhance its color retention capabilities. These additives act by absorbing or reflecting harmful UV radiation, preventing it from degrading the pigments and binder. Exterior coatings designed for high-exposure environments often contain a blend of UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to provide maximum protection against color fading and chalking. A coating containing these additives will exhibit superior color retention compared to one that does not, particularly in regions with intense sunlight.
- Topcoat Application
The application of a clear topcoat can provide an additional layer of protection against color fading and degradation. A clear topcoat acts as a barrier, shielding the colored basecoat from direct exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and abrasion. This technique is particularly effective for preserving vibrant or dark colors, which are more susceptible to fading. For instance, a dark red door with a clear UV-resistant topcoat will maintain its rich color longer than a door painted with the same red coating alone.
The interplay of pigment selection, binder chemistry, UV resistance, and proper application techniques collectively determines the color retention of an exterior door finish. Selecting a coating that addresses all these factors ensures that the door maintains its aesthetic appeal and protective qualities over time. Prioritizing long-term color stability is crucial for minimizing maintenance requirements and preserving the overall value of the property.
4. Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is a non-negotiable prerequisite for achieving the most effective coating on an exterior door. Irrespective of the coating’s inherent qualities, suboptimal surface preparation will invariably compromise its performance, longevity, and aesthetic result. This stage forms the foundation upon which the entire coating system rests.
- Cleaning and Degreasing
Removal of dirt, grime, and any existing contaminants is essential for ensuring proper adhesion. Residual contaminants act as a barrier, preventing the coating from bonding effectively with the substrate. For instance, a door exposed to road salt during winter will likely have a film of salt residue. Failure to remove this residue will result in premature coating failure. Appropriate cleaning agents and techniques must be employed to achieve a pristine surface.
- Sanding and Smoothing
Sanding creates a uniform surface texture, promoting mechanical adhesion of the coating. It also removes any loose or flaking material, preventing it from undermining the integrity of the new finish. An example is a previously painted door with minor imperfections; sanding smooths these imperfections and creates a “tooth” for the new coating to grip. The grit of sandpaper used should be appropriate for the door material and the existing condition of the surface.
- Repairing Imperfections
Addressing imperfections such as cracks, dents, or gouges is crucial for a flawless result. These imperfections not only detract from the door’s appearance but also provide entry points for moisture, accelerating deterioration. For instance, a small crack in a wooden door can allow water to penetrate, leading to rot and eventual structural damage. Appropriate fillers and patching compounds should be used to repair these imperfections, ensuring a smooth and uniform surface.
- Priming
Priming serves multiple functions, including sealing the substrate, promoting adhesion, and providing a uniform base for the finish coating. Primer seals porous surfaces, preventing them from absorbing excessive amounts of finish coating. It also provides a consistent color base, enhancing the hiding power of the topcoat. For example, applying a primer tinted to match the finish coating can improve color uniformity and reduce the number of coats required. The selection of an appropriate primer formulated for exterior use is paramount.
The quality of surface preparation directly correlates with the durability and visual appeal of the final coating. Neglecting this critical step inevitably leads to compromised results, regardless of the quality of the chosen coating. Diligent and thorough surface preparation ensures optimal adhesion, uniform coverage, and extended service life, contributing directly to achieving the most effective coating for an exterior door.
5. Application Technique
The execution of coating application directly influences the ultimate quality and longevity achieved with any exterior door finish. Irrespective of the coating’s formulation or the meticulousness of surface preparation, improper application techniques can negate these efforts, resulting in a compromised final outcome.
- Brush Selection and Handling
The choice of brush, its bristle type, and the technique employed during application significantly impact the finish’s smoothness and uniformity. Using an inappropriate brush can lead to visible brush strokes, uneven coverage, and trapped air bubbles. For example, applying a water-based acrylic coating with a natural-bristle brush, which absorbs water and becomes limp, results in poor paint distribution and a textured surface. Proper brush handling involves maintaining a wet edge, applying consistent pressure, and using appropriate stroke patterns to achieve a smooth, even layer.
- Spray Application Parameters
When spray application is employed, factors such as nozzle size, spray pressure, and distance from the surface are critical. Incorrect settings can lead to issues such as orange peel texture (caused by excessive pressure or improper atomization), runs and sags (caused by applying too much coating in one pass), or dry spray (caused by spraying from too far away, resulting in a gritty finish). For instance, if applying a coating with an airless sprayer, failing to properly adjust the pressure results in an uneven distribution and a textured finish rather than a smooth, uniform coat. Precise control over these parameters is vital for achieving a professional-quality sprayed finish.
- Environmental Conditions During Application
Ambient temperature, humidity, and direct sunlight exposure during application profoundly affect the coating’s drying and curing process. Applying a coating in excessively hot or humid conditions can lead to blistering, wrinkling, or slow drying, while application in direct sunlight can cause premature drying and poor adhesion. As an example, applying a water-based coating on a hot, sunny day can lead to rapid evaporation, preventing the coating from properly leveling and adhering to the surface. Maintaining optimal environmental conditions within the manufacturer’s recommended range is essential for ensuring proper film formation and long-term performance.
- Layer Thickness and Number of Coats
The thickness of each coat and the total number of coats applied significantly influence the coating’s durability, coverage, and overall appearance. Applying coats that are too thick can lead to runs, sags, or trapped solvents, while insufficient coating thickness results in poor coverage and reduced protection. A real-world example is applying a single, thick coat of coating in an attempt to save time; this often leads to an uneven, poorly cured finish that is prone to cracking and peeling. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended film thickness and applying multiple thin coats, as opposed to a single thick coat, ensures proper curing, optimal protection, and a uniform appearance.
These facets of application technique, encompassing brush or spray execution, environmental management, and adherence to recommended application parameters, collectively determine the realization of the coating’s potential. Mastery and mindful implementation of these techniques are imperative to translating a carefully selected coating into a lasting and aesthetically pleasing shield for an exterior door. The expertise applied in these steps is as significant as the material choice itself in achieving the “best paint finish for exterior door”.
Frequently Asked Questions About Exterior Door Coatings
The following addresses common inquiries regarding selecting and applying the optimal coating, designed to provide clarity and guide informed decision-making.
Question 1: What type of coating provides the most comprehensive protection for an exterior door?
Acrylic latex coatings generally offer a favorable balance of durability, weather resistance, and ease of application. They exhibit good flexibility, minimizing cracking and peeling, and are relatively low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to improved air quality.
Question 2: How critical is surface preparation before applying a new coating?
Surface preparation is paramount. Failure to adequately clean, sand, and prime the door’s surface will compromise the adhesion and longevity of the coating, regardless of its inherent quality. Thorough preparation ensures optimal bonding and a uniform finish.
Question 3: Is priming necessary when recoating an exterior door?
Priming is generally recommended, especially when changing color or when the existing finish is damaged or uneven. Primer seals the surface, promotes adhesion, and provides a uniform base for the topcoat, enhancing coverage and color uniformity.
Question 4: What gloss level is most appropriate for an exterior door coating?
The selection of gloss level is primarily a matter of aesthetic preference, but higher gloss levels tend to be more durable and easier to clean. Semi-gloss or gloss finishes are often favored for their durability and resistance to dirt and moisture.
Question 5: How can color fading be minimized on an exterior door?
Select coatings formulated with high-quality, lightfast pigments and UV absorbers. Darker colors tend to fade more quickly than lighter colors, so consider this factor when making a color selection. Applying a clear, UV-resistant topcoat can also enhance color retention.
Question 6: How frequently should an exterior door be recoated?
The frequency of recoating depends on factors such as the climate, the door’s exposure to the elements, and the quality of the initial coating. Generally, exterior doors should be inspected annually and recoated every 3-5 years, or as needed, to maintain protection and aesthetic appeal.
In conclusion, careful consideration of coating type, surface preparation, application technique, and environmental factors are essential for achieving a durable, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing finish on an exterior door.
The subsequent sections will explore specific product recommendations and case studies to further illustrate the principles discussed herein.
In Conclusion
The preceding discourse has delineated the multifaceted considerations inherent in selecting the optimal barrier for an exterior door. Factors spanning durability, weather resistance, color retention, meticulous surface preparation, and refined application techniques have been explored. The comprehensive analysis underscores the interconnectedness of these elements in achieving a lasting and visually compelling outcome. The ideal product represents a confluence of robust protective qualities and aesthetic suitability, tailored to the specific environmental challenges and architectural nuances of its location.
Therefore, an informed decision necessitates a thorough evaluation of the door’s material, exposure conditions, and desired aesthetic. Prioritizing longevity and protection yields dividends in reduced maintenance and sustained visual appeal, thus safeguarding the investment and enhancing the property’s value. The appropriate application, diligently executed, serves not merely as a cosmetic enhancement but as a bulwark against degradation, ensuring the enduring integrity of the entrance.