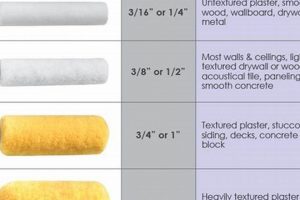
Selecting the appropriate coating sheen for doors significantly impacts both aesthetics and durability. Different levels of gloss affect how light is reflected and how well the surface resists wear and tear. For instance, a higher sheen, such as gloss or semi-gloss, offers greater resilience against scuffs and stains, making it suitable for high-traffic areas.
The choice of sheen is important for several reasons. It influences the perceived cleanliness of the door, as smoother, glossier surfaces are easier to wipe clean. Historically, higher gloss levels were favored for their ability to withstand the rigors of daily use, particularly in homes with children or pets. This decision blends practicality with visual appeal, affecting the overall ambiance of the space.
The following sections will delve into specific sheen options, outlining their respective characteristics and recommending appropriate applications for interior and exterior doors. Considerations such as room type, door style, and desired level of maintenance will be discussed to facilitate informed decision-making.
Considerations for Door Coating Selection
This section provides key considerations when selecting a coating for doors, focusing on aspects that affect longevity and visual impact.
Tip 1: Assess Traffic Levels: High-traffic areas necessitate durable, easily cleanable coatings. Opt for semi-gloss or gloss finishes in hallways and kitchens where frequent contact is expected. These surfaces resist scuffs and stains more effectively than matte or eggshell options.
Tip 2: Evaluate Door Style: The architectural style of the door influences the appropriate sheen level. Traditional doors with intricate moldings often benefit from a satin or semi-gloss finish to accentuate details. Modern, minimalist doors may appear more striking with a matte or eggshell coating that minimizes light reflection.
Tip 3: Account for Room Ambiance: The desired mood of a room should inform the coating selection. Matte finishes create a softer, more muted atmosphere, suitable for bedrooms and studies. Glossier coatings enhance brightness and reflectivity, ideal for smaller or darker spaces.
Tip 4: Prioritize Cleanability: Kitchen and bathroom doors require coatings that withstand frequent cleaning. Semi-gloss and gloss finishes offer superior stain resistance and are easily wiped clean, preventing the buildup of grime and mildew.
Tip 5: Consider Light Exposure: Exterior doors exposed to direct sunlight benefit from UV-resistant coatings to prevent fading and degradation. Select coatings specifically formulated for exterior use to ensure long-term color retention and protection against weather damage.
Tip 6: Test Before Committing: Apply sample coatings to a small, inconspicuous area of the door to assess the appearance under different lighting conditions. This step ensures that the selected sheen complements the surrounding environment and meets expectations.
Tip 7: Prepare the Surface Properly: Adequate surface preparation is crucial for optimal coating adhesion and longevity. Sanding, priming, and cleaning the door before applying the final coating ensures a smooth, uniform finish that resists peeling and chipping.
Selecting the appropriate door coating requires a balanced consideration of durability, aesthetics, and practical maintenance. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can achieve a long-lasting and visually appealing result.
The subsequent discussion will explore the application techniques and tools necessary to achieve a professional-quality finish.
1. Durability
The durability of a door’s surface coating is intrinsically linked to its long-term performance and aesthetic appeal. The choice of coating directly influences its ability to withstand physical impacts, moisture exposure, and the rigors of daily use. For instance, a high-gloss enamel coating, often chosen for its hardness, offers superior resistance to scratches and scuffs in high-traffic areas. Conversely, a matte finish, while aesthetically pleasing in certain applications, is generally more susceptible to damage and requires more frequent maintenance.
The selection process must consider the door’s environment. Exterior doors demand greater protection against weathering, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. In such cases, coatings formulated with specialized resins, designed to resist cracking and fading, are essential. The failure to prioritize durability can result in premature degradation of the surface, requiring costly repairs or replacements. Consider the example of a front door finished with an interior-grade coating; it is likely to exhibit signs of peeling and discoloration within a relatively short period due to exposure to the elements.
In summary, durability is a critical component in the selection of a surface coating for doors. The intended use, environmental conditions, and anticipated level of wear should all factor into the decision-making process. While aesthetic preferences are important, prioritizing a durable coating ultimately leads to increased longevity, reduced maintenance costs, and sustained visual appeal.
2. Cleanability
The ease with which a door’s surface can be cleaned is a crucial factor when selecting the appropriate coating. The choice significantly impacts maintenance requirements and the long-term appearance of the door, particularly in high-traffic areas or environments prone to dirt and grime accumulation.
- Sheen Level and Porosity
Higher sheen coatings, such as semi-gloss or gloss, generally offer superior cleanability due to their lower porosity. The smooth, non-absorbent surface resists the penetration of dirt and stains, allowing for easy removal with mild cleaning agents. Matte finishes, conversely, possess a higher degree of porosity, making them more susceptible to staining and requiring more rigorous cleaning methods that can potentially damage the coating over time.
- Resistance to Cleaning Agents
Certain coatings exhibit greater resistance to harsh cleaning agents than others. Selecting a coating that can withstand frequent cleaning with common household products without degradation or discoloration is essential, especially in environments where hygiene is paramount, such as kitchens and bathrooms. Epoxy-based coatings, for example, are known for their durability and resistance to a wide range of chemicals.
- Surface Texture and Profile
The texture of the coating also influences cleanability. Smooth surfaces are easier to wipe clean than textured surfaces, which can trap dirt and debris in their irregularities. Coatings with a fine, even surface profile minimize the accumulation of contaminants and simplify the cleaning process. The choice of application method, such as spraying or brushing, can also affect the final surface texture and, consequently, its cleanability.
- Environmental Factors
The surrounding environment significantly affects the rate and type of soiling a door surface experiences. Doors in kitchens are prone to grease and food splatters, while those in bathrooms are susceptible to water stains and mildew growth. Understanding these environmental factors helps determine the necessary level of cleanability and informs the selection of a coating that can effectively resist specific types of contamination.
Ultimately, the selection of a door coating should prioritize cleanability, especially in environments where frequent maintenance is required. Balancing the desired aesthetic with the practical considerations of stain resistance, ease of cleaning, and resistance to cleaning agents ensures a long-lasting and visually appealing result.
3. Aesthetics
Aesthetics plays a pivotal role in the selection of coatings for doors, influencing the overall perception and ambiance of a space. The visual impact of a door is significantly determined by its finish, which contributes to the cohesive design of an environment.
- Color Selection and Coordination
Color choice directly impacts the aesthetic appeal of a door. Harmonious color schemes enhance visual unity, while contrasting colors create focal points. The selected hue should complement the surrounding walls, trim, and furnishings to achieve a balanced and intentional design. Considerations include the room’s natural lighting and the psychological effect of different colors.
- Sheen Level and Light Reflection
The sheen level affects how light is reflected, influencing the perceived texture and depth of the door. High-gloss finishes create a reflective surface, enhancing brightness but potentially highlighting imperfections. Matte finishes offer a softer, more subdued appearance, concealing surface flaws but potentially appearing less vibrant. The appropriate sheen level should align with the desired aesthetic and the functional requirements of the space.
- Texture and Surface Detail
The surface texture and detail of a door coating contribute to its tactile and visual appeal. Smooth finishes offer a sleek, modern aesthetic, while textured finishes add depth and character. Decorative techniques, such as faux finishes or stenciling, can further enhance the visual interest of the door. The chosen texture should complement the architectural style of the building and the overall design scheme.
- Architectural Style and Design Coherence
The coating selection should align with the architectural style of the building and the intended design aesthetic. Traditional homes often benefit from classic colors and finishes, while modern spaces may call for bolder colors and more contemporary textures. Coherence between the door’s coating and the overall design scheme enhances the visual harmony and strengthens the aesthetic impact of the space.
The interplay of color, sheen, texture, and architectural style dictates the ultimate aesthetic impact of a door. Thoughtful consideration of these elements ensures that the selected coating not only protects the door but also enhances the visual appeal of the surrounding environment. The aesthetic value of the door contributes significantly to the overall design narrative and functional appeal of the space.
4. Light Reflection
Light reflection is a critical characteristic directly influenced by the coating selected for doors. The degree to which a surface reflects light impacts visual perception, room brightness, and the perceived texture of the door itself. This consideration is paramount when determining the suitable coating for a specific environment.
- Sheen Level and Ambient Brightness
The sheen level of a coating, ranging from matte to gloss, dictates the amount of light reflected. High-gloss coatings maximize light reflection, enhancing brightness in dimly lit spaces. Conversely, matte coatings absorb more light, creating a softer, less reflective environment. The choice between these options depends on the desired ambient brightness and the room’s natural light exposure. Doors in hallways or rooms lacking natural light often benefit from higher sheen finishes.
- Color Saturation and Light Dispersion
The color saturation of a coating interacts with light reflection, influencing the perceived vibrancy of the door. Highly saturated colors reflect a greater proportion of their specific wavelengths, enhancing their visual intensity. Lighter colors generally reflect more light overall, contributing to a brighter space. Darker colors absorb more light, potentially requiring higher sheen levels to compensate for reduced reflectivity. The interplay between color and sheen dictates the final visual impact of the door.
- Surface Texture and Specular Reflection
Surface texture influences the nature of light reflection. Smooth surfaces promote specular reflection, characterized by a clear, mirror-like image. Textured surfaces diffuse light, scattering it in multiple directions. Coatings with a fine texture can reduce glare and create a more uniform appearance. The choice between smooth and textured finishes depends on the desired aesthetic and the need to minimize unwanted reflections.
- Room Size and Perceived Spaciousness
Light reflection significantly affects the perceived size of a room. High-gloss coatings can create the illusion of greater space by reflecting light and expanding the perceived boundaries of the room. Matte coatings, by absorbing light, can make a room feel smaller and more intimate. The selection of an appropriate coating can be strategically employed to enhance the perceived spaciousness of a room.
The facets of light reflection, including sheen level, color saturation, surface texture, and their impact on perceived spaciousness, are integral to the selection of a door coating. Understanding these relationships allows for informed decisions that optimize both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the door, ultimately contributing to the overall design and ambiance of the space.
5. Application
The process of applying a surface coating to doors is inextricably linked to the selection of “what paint finish for doors,” with application techniques directly influencing the final appearance, durability, and overall performance of the chosen coating. Inadequate or improper application can negate the benefits of even the highest-quality surface coatings, leading to premature failure, aesthetic deficiencies, and increased maintenance costs. A gloss enamel, selected for its durability and sheen, may exhibit an uneven texture or diminished reflectivity if applied with improper brushing techniques or insufficient surface preparation. The application is not merely a final step but an integral component of the coating system.
Different coating types necessitate distinct application methods. Oil-based coatings, for example, often require careful brushwork to minimize brush strokes and achieve a smooth finish. Water-based coatings may be more forgiving in terms of brush marks but necessitate careful attention to drying times and environmental conditions to prevent issues such as blistering or cracking. Spray application, while capable of producing a uniform finish, requires specialized equipment and techniques to control overspray and ensure proper adhesion. The choice of application method must therefore be aligned with the specific properties of the selected coating. Preparation of the door’s surface is also crucial. Thorough cleaning, sanding, and priming ensure proper adhesion, preventing peeling or chipping that compromises both the aesthetic and protective functions of the coating. An example is a poorly sanded surface creating coating imperfections.
Effective application ensures the selected finish performs as intended. Improper application can undermine the coating’s protective properties, compromising the door’s longevity and requiring costly repairs or premature replacement. Recognizing the interdependent relationship between surface coating selection and its subsequent application is paramount for achieving optimal results. Consideration of the appropriate techniques, tools, and surface preparation methods ensures the selected coating achieves its intended purpose and contributes to the long-term performance and aesthetic appeal of the door.
6. Cost
The selection of a coating for doors is inextricably linked to budgetary considerations. The initial expenditure on materials, including the coating itself, primers, and application tools, constitutes a significant portion of the overall project cost. Different coatings vary substantially in price, influenced by factors such as resin composition, brand reputation, and specialized properties like UV resistance or low volatile organic compounds (VOCs). For example, a high-performance epoxy coating designed for exterior doors exposed to harsh weather conditions will invariably command a higher price point than a standard latex coating intended for interior use. The long-term implications of coating selection on maintenance costs also warrant careful evaluation.
Higher-quality coatings often exhibit superior durability, extending the lifespan of the door and reducing the frequency of re-coating or repairs. The upfront investment in a more expensive coating may ultimately prove more cost-effective over time due to its enhanced resistance to wear, fading, and environmental damage. Conversely, opting for a cheaper coating may result in more frequent maintenance interventions, escalating the total cost of ownership. Consider a scenario in which a homeowner chooses an inexpensive, low-VOC coating for an exterior door. While the initial cost savings are appealing, the coating’s limited weather resistance necessitates reapplication every two years, incurring recurring expenses and labor costs. A higher-quality coating, though initially more expensive, could potentially last five years or more, reducing the long-term financial burden.
Therefore, the cost of a coating for doors should not be evaluated solely on the basis of its initial price tag. A comprehensive cost analysis must encompass the coating’s expected lifespan, maintenance requirements, and the potential for long-term savings resulting from increased durability and reduced re-coating frequency. Making an informed decision requires balancing budgetary constraints with the long-term performance characteristics of different coating options. Failure to adequately consider these factors can lead to false economies and ultimately result in higher overall expenses.
7. Environment
The selection of coatings for doors carries significant environmental implications, extending from the manufacturing process to the disposal of materials. Responsible decision-making necessitates a thorough evaluation of the environmental impact associated with different coating options.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs are emitted during coating application and curing, contributing to air pollution and potential health hazards. Selecting low-VOC or zero-VOC coatings minimizes these emissions, promoting healthier indoor air quality and reducing the environmental footprint. Regulatory standards increasingly restrict VOC content in coatings, driving the development and adoption of more environmentally friendly formulations. An example includes water-based acrylic coatings formulated with minimal VOCs as compared to traditional solvent-based coatings.
- Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
The extraction and processing of raw materials used in coating production can have significant environmental consequences. Opting for coatings derived from sustainable sources reduces the depletion of natural resources and minimizes habitat disruption. Considerations include the use of recycled content, renewable resources, and responsible forestry practices. A contrasting example would be choosing a coating manufactured using petroleum-based solvents versus one utilizing plant-derived alternatives.
- Waste Management and Disposal
The disposal of leftover coatings and used application tools poses environmental challenges. Proper waste management practices, including recycling and responsible disposal methods, are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Extended lifespan of the chosen coating also reduces the frequency of disposal and waste generation. Examples include donating unused coatings to community organizations or utilizing designated hazardous waste disposal facilities.
- Energy Consumption in Manufacturing
The energy required to manufacture coatings contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Selecting coatings produced using energy-efficient manufacturing processes minimizes the environmental impact. Factors include the utilization of renewable energy sources, optimized production techniques, and reduced transportation distances. Comparing the carbon footprint of coatings produced in local facilities versus those imported from distant locations illustrates this point.
These facets directly influence the sustainability of “what paint finish for doors.” Evaluating VOC content, raw material sourcing, waste management, and energy consumption enables informed choices that minimize environmental harm while achieving desired aesthetic and functional outcomes. The environmental considerations are integral to responsible coating selection, ensuring long-term sustainability and minimizing the ecological footprint.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and application of surface coatings for doors. The information provided aims to clarify best practices and dispel misconceptions surrounding this topic.
Question 1: How does the sheen level of a coating affect its durability?
Higher sheen coatings, such as semi-gloss and gloss, generally exhibit greater durability due to their lower porosity and increased resistance to abrasion and impact. Matte coatings, while aesthetically pleasing in certain applications, are typically more susceptible to damage.
Question 2: Is it necessary to prime a door before applying a surface coating?
Priming is highly recommended, especially for bare wood or previously coated surfaces. Primer enhances adhesion of the subsequent coating layers, promotes uniform color distribution, and seals porous surfaces, improving the overall durability and appearance of the final finish.
Question 3: What type of coating is best suited for exterior doors exposed to harsh weather conditions?
Exterior doors require coatings formulated with specialized resins that offer enhanced UV resistance, moisture protection, and flexibility to withstand temperature fluctuations. Acrylic latex paints specifically designed for exterior use or oil-based paints with UV inhibitors are generally recommended.
Question 4: How do I properly clean a door coated with a matte finish?
Matte finishes require gentle cleaning methods to avoid damaging the surface. Use a soft cloth dampened with mild soap and water. Avoid abrasive cleaners or scrubbing, which can alter the texture and appearance of the coating. Spot-test any cleaning solution in an inconspicuous area before applying it to the entire door.
Question 5: Can a roller be used to apply a coating to a door with intricate moldings?
While a roller can be used on flat surfaces, intricate moldings typically require brush application to ensure adequate coverage and prevent paint buildup in recessed areas. A combination of roller and brush techniques may be necessary to achieve a uniform finish.
Question 6: How long should a coated door be allowed to dry before it can be safely closed?
Drying times vary depending on the type of coating, environmental conditions, and application thickness. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific drying times. Generally, allow a minimum of 24 hours for water-based coatings and 48 hours for oil-based coatings before closing the door to prevent sticking or damage to the finish.
Selecting the appropriate coating involves considering the door’s environment, intended use, and desired aesthetic. Consulting coating-specific guidelines for optimal results is paramount.
The subsequent article will explore advanced techniques and problem-solving strategies related to achieving professional-quality surface coating results on doors.
The Significance of “What Paint Finish for Doors”
The preceding discussion underscored the multifaceted considerations inherent in determining “what paint finish for doors” is most appropriate for a given application. From durability and cleanability to aesthetics, light reflection, cost, and environmental impact, each factor plays a crucial role in the long-term performance and visual appeal of the finished product. A systematic approach, encompassing careful evaluation of these elements, is essential for informed decision-making.
The selection and proper application of a door surface coating represent a critical investment in the longevity and aesthetic integrity of the built environment. Continued advancements in coating technology and sustainable practices promise to further enhance the options available, necessitating ongoing education and adaptation within the field. Prioritizing informed selection criteria will ensure both optimal outcomes and minimized environmental impact for years to come.