A category of products applied to wooden surfaces, these materials serve primarily to protect the wood from environmental factors, enhance its aesthetic appeal, and extend its lifespan. Examples include varnishes, lacquers, oils, and paints, each offering varying degrees of protection and visual characteristics.
The application of these surface treatments is crucial in preserving the integrity of wood against moisture, UV radiation, and physical abrasion. Historically, the choice of treatment has reflected both functional needs and prevailing aesthetic preferences, influencing furniture design, architectural elements, and decorative arts across different eras and cultures. The right selection contributes significantly to the wood’s longevity and overall value.
Understanding the diverse range of available treatments is essential for achieving desired outcomes in woodworking projects. The subsequent sections will delve into specific properties, application techniques, and suitability of different categories, allowing for informed decisions based on project requirements and desired aesthetic qualities. These categories are crucial for the quality of project of woodworking.
Application Guidelines for Surface Treatments
Optimal results in woodworking are contingent upon proper selection and application of protective and decorative coatings. The following guidelines provide insights into achieving professional-grade results.
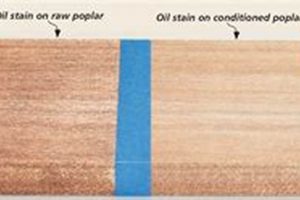
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount. Prior to applying any coating, ensure the wood surface is clean, dry, and free from dust, grease, or existing finishes. Sanding to a smooth, consistent grit is essential for proper adhesion and a uniform appearance.
Tip 2: Understand Product Compatibility. Not all coatings are compatible with each other. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the chosen product is appropriate for the substrate and any existing layers. Failure to do so may result in adhesion issues, discoloration, or premature failure.
Tip 3: Apply Thin, Even Coats. Multiple thin coats are preferable to a single thick coat. This approach minimizes the risk of runs, drips, and uneven drying, resulting in a smoother, more durable finish.
Tip 4: Consider Environmental Factors. Temperature and humidity significantly impact drying times and the final appearance. Apply coatings within the recommended temperature range and avoid application in excessively humid conditions.
Tip 5: Allow Adequate Drying Time. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended drying times between coats and before use is critical. Rushing the drying process can compromise the integrity of the final finish.
Tip 6: Use Appropriate Application Tools. The choice of brush, roller, or sprayer will influence the final appearance. Select tools designed for the specific product being applied and maintain them in good condition.
Tip 7: Test on an Inconspicuous Area. Before applying to the entire project, test the chosen treatment on a small, hidden area to ensure compatibility and desired aesthetic outcome.
Consistent adherence to these application guidelines will significantly enhance the durability, aesthetics, and overall quality of woodworking projects. Proper application ensures long-lasting protection and visual appeal.
These principles provide a foundation for informed decision-making and skillful execution, contributing to superior results in diverse woodworking applications. The subsequent sections will explore advanced techniques and specialized applications for surface coatings.
1. Durability
Durability stands as a critical factor in the selection of wood surface treatments. It represents the ability of the treatment to withstand wear, abrasion, chemical exposure, and environmental stressors over an extended period. The choice directly impacts the longevity and aesthetic integrity of the underlying wood.
- Resistance to Abrasion and Impact
A key aspect of durability is the coating’s capacity to resist scratches, scuffs, and impact damage. For instance, polyurethane finishes exhibit superior resistance to abrasion compared to shellac, making them suitable for high-traffic areas such as flooring or tabletops. Resistance directly affects how well the wood retains its appearance.
- Chemical Resistance
Certain wood surface treatments offer resistance to chemicals, including household cleaners, solvents, and acids. Epoxy resins, for example, are commonly used in laboratory settings due to their inertness and resistance to chemical degradation. A failure to resist may lead to discoloration or compromise structural integrity.
- UV Protection
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause fading, discoloration, and degradation of wood and the applied surface treatment. Varnishes containing UV absorbers or stabilizers are often used on exterior applications to mitigate these effects. Without UV protection, wood is susceptible to accelerated aging.
- Water Resistance and Moisture Permeability
The ability to repel water and resist moisture penetration is essential for preventing rot, warping, and swelling in wood. Oil-based products create a water-repellent barrier, while breathable treatments allow for moisture vapor transmission, preventing moisture buildup within the wood. Effective water resistance is vital for outdoor furniture and marine applications.
Considering these facets of durability is paramount when choosing a wood surface treatment. The selected product should align with the intended use of the wood and the environmental conditions to which it will be exposed. A durable treatment not only extends the lifespan of the wood but also preserves its aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
2. Appearance
The visual characteristics imparted by wood surface treatments exert a substantial influence on the perceived quality and aesthetic value of a finished piece. The selected treatment fundamentally alters the wood’s inherent color, sheen, and grain definition. This alteration is a direct consequence of the treatment’s composition and application, creating an intended aesthetic outcome. For example, a clear polyurethane finish enhances the natural grain pattern while providing a glossy surface, whereas a stain penetrates the wood to impart color without obscuring the grain. The ultimate appearance is thus a synthesis of the wood’s intrinsic properties and the extrinsic properties of the chosen finish.
The importance of appearance extends beyond mere visual appeal; it also contributes to the perceived value and functionality of the wood object. A meticulously applied, aesthetically pleasing surface treatment can significantly increase the market value of furniture or architectural elements. Furthermore, the selected appearance can serve a practical purpose, such as reducing glare or enhancing visibility in specific applications. Consider the use of matte surface treatments in display cases to minimize reflections, or the selection of light-colored, highly reflective coatings in workspaces to improve illumination. These practical applications highlight the inherent connection between appearance and the intended use of the object.
In conclusion, the connection between appearance and wood surface treatments is characterized by a direct cause-and-effect relationship. The selection of a particular treatment dictates the final aesthetic outcome, influencing both the perceived quality and functional utility of the finished piece. Challenges arise in achieving consistent and predictable results, requiring careful consideration of wood species, surface preparation, and application techniques. This interplay underscores the practical significance of understanding the diverse range of surface treatments and their corresponding visual characteristics, ultimately shaping the overall aesthetic and functional value of the treated wood.
3. Application Method
The efficacy of any wood surface treatment is intrinsically linked to its application method. The technique employed directly impacts the treatment’s adherence, uniformity, and ultimately, its performance. Certain surface treatments necessitate specific application methods to achieve the desired outcome, making the method a crucial component. For instance, spraying lacquer requires specialized equipment and precise technique to ensure even coverage and prevent runs or drips. Conversely, applying oil-based treatments typically involves brushing or wiping, followed by careful removal of excess to avoid a sticky or uneven surface. This direct dependency underscores the importance of understanding the properties of both the surface treatment and the appropriate application method.
The practical significance of this understanding is evident in numerous woodworking applications. Consider the restoration of antique furniture. Applying a modern surface treatment using an inappropriate method could irreversibly damage the piece. Instead, employing traditional techniques such as French polishing, which involves multiple thin layers of shellac applied with a specialized pad, preserves the wood’s character and maintains its historical value. Similarly, in large-scale industrial applications like flooring, automated spraying systems are used to apply durable polyurethane coatings, ensuring consistent and efficient coverage across vast areas. The choice of method is, therefore, dictated by the treatment’s properties, the scale of the project, and the desired level of control over the final result.
Challenges arise when the application method is mismatched with the surface treatment. For example, attempting to brush a fast-drying lacquer can lead to brush marks and an uneven finish. Similarly, applying a thick coat of varnish, regardless of the method, can result in blistering or prolonged drying times. In summary, the selection and execution of the application method are integral to achieving the intended performance and aesthetic qualities of any wood surface treatment. Careful consideration of both elements is essential for successful woodworking outcomes.
4. Wood Compatibility
Wood compatibility, in the context of surface treatments, refers to the interaction between the wood substrate and the applied product. This interaction influences adhesion, absorption, color, and long-term performance. The chemical composition and physical properties of both the wood species and the surface treatment dictate compatibility. Softwoods, such as pine, exhibit greater porosity compared to hardwoods like maple, leading to increased absorption of certain finishes. This variability necessitates careful product selection to prevent issues like uneven staining, excessive penetration, or compromised adhesion. Failure to consider wood compatibility may result in premature failure of the coating, aesthetic imperfections, or structural damage to the wood itself. For instance, using an oil-based product on a resinous wood like teak can hinder proper drying and lead to a perpetually tacky surface. This highlights the direct causal relationship between wood selection, finish selection, and the resultant outcome.
The practical significance of understanding wood compatibility is evident in various woodworking applications. In furniture making, where aesthetic appeal is paramount, the choice of surface treatment is often dictated by the wood species. For example, a clear, non-yellowing finish is typically preferred for light-colored woods like ash or birch to preserve their natural appearance. Conversely, darker woods like walnut may benefit from a finish that enhances their richness and depth. In exterior applications, such as decking or siding, the combination of wood species and surface treatment must withstand environmental stressors like moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. Using a water-based stain on a dimensionally unstable wood can lead to cracking, peeling, and subsequent wood rot. Therefore, a systems-based approach is crucial, considering both the wood’s inherent properties and the demands of the intended environment. Ignoring these factors can substantially reduce the lifespan of the treated wood.
In conclusion, wood compatibility represents a foundational element in achieving successful and durable surface treatments. The selection of a product must be informed by the specific characteristics of the wood species, its intended use, and the prevailing environmental conditions. Challenges arise in accurately assessing compatibility, particularly with less common wood species or novel surface treatments. Ongoing research and practical experience are essential for refining understanding and mitigating potential issues. Ultimately, a comprehensive awareness of wood compatibility ensures optimal performance, aesthetic integrity, and long-term preservation of wood surfaces.
5. Level of Protection
The extent to which a wood surface treatment safeguards the substrate from environmental and mechanical stressors constitutes its level of protection. This parameter is paramount in determining the long-term integrity and aesthetic value of the wood, and it is directly contingent on the selection of the appropriate finish type.
- Moisture Resistance
The capacity to impede water absorption is fundamental. Exterior finishes, such as marine-grade varnishes, are formulated to withstand prolonged exposure to moisture, preventing rot, swelling, and warping. Interior applications may necessitate less stringent moisture resistance, but finishes must still protect against spills and humidity. Failure to adequately address moisture intrusion leads to structural compromise.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Shielding
Prolonged exposure to UV light causes degradation of both the wood and the surface treatment. Exterior finishes incorporating UV absorbers or stabilizers mitigate this damage, preventing fading, discoloration, and embrittlement. Interior finishes, while less critical in this regard, may still benefit from UV protection to preserve color and integrity. Insufficient UV shielding accelerates the aging process.
- Abrasion Resistance
The ability to withstand scratching, scuffing, and wear is essential for high-traffic surfaces like flooring and tabletops. Polyurethane finishes exhibit superior abrasion resistance compared to softer finishes such as wax or shellac. Industrial applications may require specialized coatings with enhanced abrasion resistance to endure heavy use. Inadequate abrasion resistance leads to premature wear and necessitates frequent refinishing.
- Chemical Resistance
Protection against chemical spills, cleaning agents, and solvents is critical in laboratory, kitchen, and industrial settings. Epoxy and certain catalyzed finishes offer robust chemical resistance, preventing staining, etching, and degradation. The specific chemicals encountered dictate the required level of resistance. Compromised chemical resistance results in unsightly damage and potential structural weakening.
The preceding facets highlight the critical interplay between the desired level of protection and the appropriate choice of wood surface treatment. Each finish type offers a unique combination of protective properties, and selection should be guided by the specific environmental and mechanical demands of the application. A thorough understanding of these relationships is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of any woodworking project.
Frequently Asked Questions about Wood Surface Treatments
This section addresses common inquiries concerning wood surface treatments, offering concise explanations and insights.
Question 1: What distinguishes a varnish from a lacquer?
Varnishes are typically oil-based or resin-based and cure through oxidation or polymerization, offering durable protection against moisture and abrasion. Lacquers are solvent-based and dry rapidly through evaporation, providing a hard, smooth finish that is less resistant to moisture but easier to repair.
Question 2: How does the selection of a surface treatment impact the appearance of different wood species?
Different wood species exhibit varying levels of porosity and color. Lighter woods may require non-yellowing finishes to maintain their natural tone, while darker woods can benefit from treatments that enhance their depth. Porous woods may necessitate a sealer before applying a finish to prevent uneven absorption.
Question 3: What are the key considerations when choosing a surface treatment for outdoor wood applications?
Outdoor applications require finishes with high UV resistance, moisture protection, and flexibility to accommodate wood movement. Marine-grade varnishes, penetrating oils, and certain exterior-grade paints are suitable choices.
Question 4: Is it necessary to sand wood before applying a surface treatment?
Sanding is generally essential for preparing wood surfaces. It removes imperfections, creates a smooth substrate, and enhances adhesion. The appropriate sanding grit depends on the wood species and the desired finish. Always sand in the direction of the grain.
Question 5: What are the potential risks associated with improper application of wood surface treatments?
Improper application can lead to various issues, including uneven coverage, runs, drips, bubbles, poor adhesion, and prolonged drying times. These issues compromise the aesthetic appeal and protective properties of the finish. Following manufacturer guidelines and practicing proper techniques are crucial.
Question 6: How does one determine if a surface treatment is compatible with an existing finish?
Compatibility testing is recommended. Apply the new finish to a small, inconspicuous area and observe for any adverse reactions, such as lifting, wrinkling, or discoloration. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility guidelines.
Understanding the properties, application, and compatibility of various surface treatments is vital for achieving optimal results in woodworking. Careful selection and execution are essential for long-lasting protection and aesthetic appeal.
The subsequent section will address advanced techniques and specialized applications.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has illuminated the diverse characteristics and applications of various wood surface treatments. From the protective capabilities of varnishes to the aesthetic nuances of stains, each finish presents a unique set of properties dictating its suitability for specific projects. Considerations such as durability, appearance, application method, wood compatibility, and the requisite level of protection collectively inform the decision-making process, impacting the longevity and visual appeal of finished wood surfaces.
A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for all involved in woodworking, from hobbyists to professional artisans and industrial manufacturers. The selection of the appropriate finish extends beyond mere aesthetics; it is a crucial determinant of the material’s resilience and enduring value. Further research and experimentation remain vital for advancing the knowledge base and optimizing the utilization of materials, ensuring the continued appreciation and preservation of wood for generations to come.