The selection of a protective coating for wooden surfaces intended for dining or work purposes requires careful consideration of the material’s resistance to wear, impact, and chemical exposure. The selected coating significantly influences the longevity and aesthetic appeal of the piece. For example, a surface frequently subjected to spills, scratches, and heat necessitates a robust barrier against these elements.
A robust surface treatment provides crucial protection against everyday damage, preserving the underlying wood’s integrity and beauty. Historically, achieving this level of protection involved traditional methods and materials, but modern advancements in chemistry and manufacturing have yielded more resilient and long-lasting solutions. These improved finishes can significantly extend the lifespan of furniture and reduce maintenance requirements.
Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the various types of protective coatings available, their application processes, and their relative strengths and weaknesses is essential for making informed decisions regarding the optimal treatment for wood tables. Subsequent sections will delve into specific types of coatings, outlining their characteristics and suitability for different use cases.
Enhancing Longevity
The following recommendations offer guidance on achieving a robust and enduring finish for wood tables, focusing on preparation, material selection, and application techniques that contribute to long-term durability.
Tip 1: Prioritize Surface Preparation: Thorough sanding is paramount. Begin with coarser grits to remove imperfections, gradually progressing to finer grits for a smooth, uniform surface. This ensures optimal adhesion of the protective coating.
Tip 2: Select Appropriate Coating Material: Consider the intended use of the table and environmental factors. Polyurethane, conversion varnish, and epoxy resins offer varying degrees of resistance to scratches, chemicals, and moisture. Evaluate each option based on specific needs.
Tip 3: Employ Multiple Thin Coats: Instead of applying a single thick layer, opt for several thin, even coats. This method minimizes the risk of runs, drips, and air bubbles, resulting in a more uniform and durable protective layer.
Tip 4: Ensure Adequate Drying Time: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended drying times between coats and before subjecting the table to regular use. Insufficient drying can compromise the integrity and durability of the cured coating.
Tip 5: Control Environmental Conditions: Apply coatings in a well-ventilated area with moderate temperature and humidity levels. Extreme conditions can negatively impact the curing process and the final finish quality.
Tip 6: Consider a Sealer or Primer: Applying a compatible sealer or primer before the protective coating can enhance adhesion and prevent the finish from being absorbed into the wood, resulting in a more uniform and durable surface.
Tip 7: Evaluate Catalyzed Finishes: For high-use surfaces, catalyzed finishes, such as conversion varnish, provide superior durability and chemical resistance compared to non-catalyzed options. However, they require specialized equipment and knowledge for proper application.
Implementing these strategies promotes the creation of a resilient surface, extending the lifespan of wood tables and preserving their aesthetic appeal. Selecting the appropriate protective coating and employing correct application techniques is paramount for achieving optimal long-term results.
The subsequent section will address maintenance strategies for preserving the integrity of a durable wood table finish and mitigating potential damage.
1. Polyurethane Resilience
Polyurethane’s durability is a key factor when evaluating finishes for wood tables, influencing the furniture’s capacity to withstand daily use and environmental stressors. Its protective qualities directly affect the longevity and aesthetic appeal of the table.
- Abrasion Resistance
Polyurethane coatings exhibit high resistance to abrasion, protecting the wood surface from scratches and wear caused by everyday objects. A dining table, frequently subjected to the friction of plates, cutlery, and other items, benefits significantly from this property. High abrasion resistance preserves the table’s visual appeal and reduces the need for frequent refinishing.
- Chemical Resistance
Spills of liquids, including water, coffee, and household cleaners, pose a threat to wood tables. Polyurethane’s resistance to chemicals prevents staining, discoloration, and degradation of the wood. This resistance is particularly crucial in kitchens or dining areas where exposure to various substances is common.
- Impact Resistance
The potential for impacts from dropped objects or accidental collisions necessitates a finish with good impact resistance. Polyurethane’s flexible nature allows it to absorb some of the force from impacts, minimizing the risk of dents or cracks in the wood. A durable surface prevents structural damage to the wood, contributing to the table’s extended lifespan.
- Water Resistance
Exposure to moisture can cause warping, swelling, and eventual decay in wood. Polyurethane creates a barrier against water penetration, preventing these issues. This property is vital for tables in environments with high humidity or frequent exposure to spills.
The multifaceted resilience of polyurethane, encompassing abrasion, chemical, impact, and water resistance, establishes it as a strong contender for achieving a robust protective layer on wood tables. The selection of polyurethane, based on its specific formulation and application technique, plays a vital role in maximizing the table’s longevity and preserving its aesthetic qualities. Other considerations, such as catalyzed varnish, offer a potentially higher level of protection, but polyurethane often presents a balanced combination of durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of application.
2. Catalyzed Varnishes
Catalyzed varnishes represent a class of wood finishes prized for their enhanced durability and resistance to various forms of damage, positioning them as a significant contender in the search for a protective coating. Their chemical composition and curing process contribute to performance characteristics that distinguish them from traditional varnishes.
- Enhanced Chemical Resistance
Catalyzed varnishes exhibit superior resistance to a wider range of chemicals, including solvents, acids, and alkalis. This property is particularly important for wood tables used in environments where spills are likely, such as dining rooms and laboratories. For instance, catalyzed varnishes can withstand exposure to common household cleaners without experiencing discoloration or degradation, thereby preserving the surface’s integrity.
- Increased Hardness and Abrasion Resistance
The catalyzed curing process results in a significantly harder and more abrasion-resistant surface compared to non-catalyzed varnishes. This characteristic reduces the susceptibility to scratches and wear from daily use, extending the lifespan of the finish and minimizing the need for frequent refinishing. Wood tables finished with catalyzed varnish can better withstand the abrasive effects of objects being placed on them, maintaining their aesthetic appeal over time.
- Improved Moisture Resistance
Catalyzed varnishes offer enhanced resistance to moisture penetration, protecting the wood substrate from warping, swelling, and other forms of water damage. This property is crucial for tables located in humid environments or those prone to occasional spills. A table coated with catalyzed varnish is less likely to develop water rings or other moisture-related imperfections, ensuring its long-term stability.
- Cross-Linking Polymer Structure
The addition of a catalyst promotes cross-linking of the varnish polymers during the curing process. This cross-linking creates a tighter, more robust molecular network, resulting in a finish with exceptional durability and resistance to cracking and chipping. This structural characteristic is the key factor underpinning the enhanced performance of catalyzed varnishes, contributing significantly to their ability to withstand the stresses of everyday use.
The enhanced chemical, abrasion, and moisture resistance of catalyzed varnishes, stemming from their unique cross-linking polymer structure, positions them as a viable solution when prioritizing longevity and protection. While other finishes may offer certain advantages in terms of cost or ease of application, catalyzed varnishes frequently represent a compelling choice for wood tables demanding the highest levels of durability. For instance, a kitchen table subjected to frequent use and spills would greatly benefit from the protective qualities of a catalyzed varnish.
3. Epoxy Hardness
Epoxy’s inherent hardness is a primary determinant of its suitability as a protective coating for wood tables. Hardness, in this context, refers to the material’s resistance to indentation, scratching, and abrasion. This attribute is crucial for surfaces subjected to daily use, as it directly impacts the finish’s capacity to maintain its structural and aesthetic integrity over time. For example, a dining table finished with a high-hardness epoxy is less likely to exhibit scratches from cutlery or indentations from dropped objects than a table finished with a softer material. The relationship is causal: increased epoxy hardness directly correlates with a more resilient and durable table surface.
The practical significance of understanding epoxy hardness lies in its ability to inform material selection for specific applications. In environments with high traffic or potential for abrasive contact, such as restaurants or workshops, the selection of a high-hardness epoxy is paramount. Conversely, for tables intended for purely decorative purposes with minimal physical contact, a less robust finish may suffice. The ability to match finish characteristics with the intended application optimizes cost-effectiveness and ensures appropriate protection. Furthermore, specialized epoxy formulations can incorporate fillers or additives to further enhance hardness and resistance to specific environmental factors, such as UV radiation or chemical exposure.
In summary, epoxy hardness is a critical component in achieving a durable finish on wood tables. Its resistance to scratching, indentation, and abrasion directly contributes to the longevity and aesthetic preservation of the surface. Understanding this relationship allows for informed material selection based on the intended use environment and anticipated wear and tear. While hardness is a significant factor, other properties such as flexibility, chemical resistance, and ease of application should also be considered to achieve an optimal balance of performance characteristics in a wood table finish.
4. Application Technique
The durability of a wood table finish is inextricably linked to the method by which it is applied. Regardless of the inherent properties of the chosen coating, improper application will compromise its protective qualities and reduce its lifespan. The execution of the finishing process dictates the ultimate resilience of the surface.
- Surface Preparation Methods
Adequate surface preparation is foundational to a durable finish. This includes thorough sanding to create a smooth, uniform substrate, the removal of dust and contaminants, and the application of a compatible primer or sealer. For example, failure to properly sand a surface may result in poor adhesion of the finish, leading to premature peeling or chipping. Proper preparation ensures that the finish bonds effectively with the wood, maximizing its protective capabilities.
- Environmental Control During Application
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity significantly influence the curing process of wood finishes. Applying a finish in excessively humid conditions can inhibit proper drying and lead to clouding or blistering. Similarly, applying a finish in extremely cold temperatures can slow the curing process and compromise its hardness. Maintaining optimal environmental conditions, typically within the manufacturer’s recommended range, is essential for achieving a durable and uniform finish.
- Application Method and Tool Selection
The choice of application method, whether brushing, spraying, or wiping, and the selection of appropriate tools (brushes, spray guns, applicators) directly impact the quality and durability of the finish. For example, using an unsuitable brush can result in uneven application, brush marks, and air bubbles. Spraying typically provides a more uniform finish, but requires specialized equipment and skill. Selecting the appropriate method and using high-quality tools ensures consistent and even coverage, contributing to a more resilient protective layer.
- Number and Thickness of Coats
The number and thickness of coats applied are critical to achieving the desired level of protection. Applying too few coats may result in insufficient protection against wear and tear. Conversely, applying excessively thick coats can lead to runs, drips, and uneven curing. Applying multiple thin, even coats allows for proper curing and maximizes the build-up of a durable protective layer. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding the number and thickness of coats is paramount.
In conclusion, the application technique is not merely a procedural step, but an integral component in achieving a durable wood table finish. Meticulous surface preparation, environmental control, appropriate method and tool selection, and careful attention to coat thickness collectively determine the resilience and longevity of the protective layer. While the inherent qualities of the finish material are important, the execution of the application process ultimately dictates its effectiveness in safeguarding the wood table from damage.
5. Surface Preparation
Surface preparation constitutes a foundational element in achieving a durable finish on wood tables. The quality of preparation directly influences the adhesion, uniformity, and overall performance of the applied coating. A properly prepared surface maximizes the protective capabilities of even the most advanced finishing products.
- Sanding and Smoothing
Sanding removes imperfections, scratches, and existing finishes, creating a smooth and uniform substrate. Progressing through progressively finer grits ensures the absence of deep scratches that could compromise the integrity of the subsequent finish. For instance, a failure to adequately sand a table before applying a polyurethane coating may result in visible swirl marks and uneven sheen, diminishing both the aesthetic and protective qualities of the finish.
- Cleaning and Degreasing
The removal of dust, dirt, grease, and other contaminants is crucial for promoting proper adhesion of the finish. Residues can interfere with the bonding process, leading to peeling, blistering, or cracking of the coating. The selection of appropriate cleaning agents, such as mineral spirits or specialized wood cleaners, ensures the removal of contaminants without damaging the wood surface. For example, oily residues from handling the wood can prevent proper bonding of the finish, resulting in localized areas of weakness and premature failure.
- Filling Imperfections
Addressing imperfections such as cracks, dents, and open grain is essential for creating a uniform and durable finish. Wood fillers, epoxy resins, or grain fillers can be used to repair these defects, providing a smooth and level surface for the finish to adhere to. Properly filling imperfections prevents the absorption of the finish into the wood, which can lead to uneven coloration and reduced protection in those areas. A table with unfilled cracks, for instance, may allow moisture to penetrate the wood, leading to warping or decay beneath the finish.
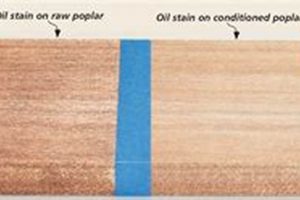
- Priming or Sealing
The application of a primer or sealer can enhance the adhesion of the finish, prevent excessive absorption into the wood, and improve the overall uniformity of the coating. Primers create a stable base for the finish to bond to, while sealers minimize the porosity of the wood, preventing the finish from soaking in unevenly. For example, applying a sealer to a porous wood species like oak before applying a stain can prevent blotchiness and ensure a consistent color throughout the surface, ultimately contributing to a more durable and aesthetically pleasing finish.
These facets of surface preparation collectively contribute to the realization of a finish that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also resilient to the challenges of daily use. Failure to adequately address any of these steps can compromise the durability of the finish, regardless of the quality of the coating itself. Therefore, thorough surface preparation is a critical investment in the long-term performance and value of wood tables.
6. Maintenance Protocols
Maintenance protocols directly affect the longevity and appearance of wood table finishes, regardless of their initial durability. Even surfaces treated with resilient materials are susceptible to degradation if proper care is neglected. Maintenance encompasses a range of practices designed to minimize wear, prevent damage, and preserve the integrity of the protective coating. The implementation of these protocols is paramount in realizing the full potential of a durable finish.
The absence of appropriate maintenance accelerates the deterioration of a wood table’s surface. For example, failure to promptly clean spills can lead to staining or etching, compromising the finish’s protective barrier. Regular dusting prevents the accumulation of abrasive particles that cause scratches over time. The use of coasters and placemats mitigates heat and moisture damage, preventing warping and discoloration. Specialized cleaning products, designed for wood finishes, avoid harsh chemicals that can strip away the protective layer. These specific actions illustrate how consistent maintenance directly preserves the initial properties of the surface coating.
The practical significance of understanding the symbiotic relationship between durable finishes and maintenance protocols lies in optimizing the lifecycle cost and aesthetic appeal of wood tables. While a premium finish represents a significant upfront investment, consistent adherence to proper maintenance procedures maximizes the return on that investment by minimizing the need for repairs or refinishing. In essence, a highly durable finish coupled with rigorous maintenance ensures the long-term preservation of the table, preserving its value and utility for years to come.
7. Environmental Factors
The environment in which a wood table is situated exerts a profound influence on the longevity and performance of its finish. The selection of an appropriate protective coating necessitates a thorough consideration of prevailing environmental conditions to ensure optimal durability.
- Humidity Levels
High humidity levels can induce moisture absorption in wood, leading to swelling, warping, and eventual deterioration of the finish. Conversely, low humidity can cause wood to dry out, resulting in cracking and separation of the finish. The ideal finish should possess inherent moisture resistance and be capable of accommodating dimensional changes in the wood caused by fluctuating humidity levels. For instance, a table located in a coastal region with high humidity would benefit from a finish with superior moisture-blocking properties, such as a catalyzed varnish or marine-grade epoxy.
- Temperature Fluctuations
Rapid or extreme temperature variations can stress wood finishes, causing them to expand and contract at different rates than the underlying wood. This differential expansion can lead to cracking, blistering, and delamination of the finish. A finish with sufficient elasticity and flexibility is crucial for withstanding these temperature-induced stresses. For example, a table placed near a heating vent or in direct sunlight may experience significant temperature fluctuations, necessitating a finish that can accommodate these changes without compromising its integrity.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Exposure
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight can degrade many wood finishes, causing them to fade, yellow, or become brittle. UV radiation breaks down the chemical bonds in the finish, reducing its protective capabilities and aesthetic appeal. Finishes containing UV absorbers or stabilizers are recommended for tables exposed to direct sunlight. A table positioned near a window or on a patio would require a UV-resistant finish to prevent premature fading and degradation.
- Chemical Exposure
Exposure to various chemicals, such as cleaning agents, solvents, and food spills, can damage wood finishes. Some chemicals can dissolve or react with the finish, causing discoloration, staining, or softening. A finish with good chemical resistance is essential for tables used in environments where chemical exposure is likely. For instance, a kitchen table would benefit from a finish that can withstand spills of acidic or alkaline substances without experiencing damage.
These environmental factors collectively underscore the importance of selecting a finish that is not only durable in terms of physical resistance but also resilient to the specific environmental challenges it will face. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and preserving the aesthetic quality of wood tables.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and application of resilient finishes for wood tables, providing insights into factors influencing their longevity and performance.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary determinant of a wood table finish’s durability?
The primary determinant is the finish’s inherent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, impact, and moisture. A coating exhibiting high resistance to these elements will demonstrably extend the lifespan of the table.
Question 2: Are certain wood species inherently more conducive to durable finishes than others?
Yes, wood species with denser grain patterns, such as maple or oak, generally provide a more stable and uniform surface for finishes to adhere to, resulting in enhanced durability. Softer woods may require additional preparation or specialized finishes.
Question 3: Does the application technique exert a significant influence on the finish’s overall durability?
Unequivocally, the application technique is critical. Meticulous surface preparation, proper environmental control, and the use of appropriate application methods are essential for achieving a durable and long-lasting finish. Improper application can compromise even the most robust coating.
Question 4: What are the comparative advantages of polyurethane, catalyzed varnish, and epoxy finishes?
Polyurethane offers a balance of durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of application. Catalyzed varnish provides superior chemical and abrasion resistance. Epoxy resins offer exceptional hardness and moisture resistance, but often require specialized application techniques.
Question 5: Is maintenance a relevant consideration for tables with durable finishes?
Indeed, maintenance is crucial. Consistent cleaning, protection from heat and moisture, and prompt removal of spills are essential for preserving the integrity and extending the lifespan of even the most durable finish.
Question 6: How does environmental exposure impact the long-term performance of a wood table finish?
Exposure to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and humidity can significantly degrade wood finishes. Selecting a finish formulated to withstand these specific environmental stressors is crucial for maximizing its longevity.
In summary, achieving a genuinely durable finish for wood tables requires a holistic approach encompassing material selection, application technique, ongoing maintenance, and environmental considerations.
The subsequent section will explore case studies illustrating the application of different durable finishes in diverse environments.
Most Durable Finish for Wood Table
The preceding discussion has explored various facets pertinent to the selection and implementation of a robust surface treatment for wood tables. Considerations encompassing material properties, application methodologies, maintenance protocols, and environmental factors all contribute to the ultimate longevity and preservation of the finish. The objective is to balance resistance to physical abrasion, chemical exposure, moisture permeation, and ultraviolet radiation, ensuring the sustained integrity and aesthetic value of the underlying substrate.
Ultimately, the informed selection and diligent application of techniques aligned with a durable finish represents a crucial investment. This process protects the wood table and embodies a commitment to enduring quality, ensuring its continued utility and aesthetic contribution for years to come. Further research and innovation will likely yield even more resilient and environmentally conscious options, continuing to refine the pursuit of the ideal surface treatment.





![Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] | Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing](https://bestfinaltouch.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-301-300x200.jpg)
