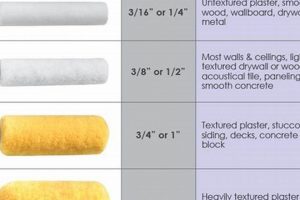
The optimal coating type for outside surfaces significantly impacts a structure’s aesthetic appeal and resilience against environmental factors. Selection hinges on factors such as climate, substrate material, and desired visual effect. Different types offer varying degrees of protection against moisture, UV radiation, and physical wear, affecting the longevity and maintenance requirements of the painted surface. For example, a high-gloss option might be suitable for trim work where durability and ease of cleaning are paramount, while a matte option could be preferred for broad wall surfaces to minimize glare and hide imperfections.
Careful consideration of exterior coating selection provides both immediate and long-term advantages. Appropriate choices enhance curb appeal and property value. Moreover, effective surface protection minimizes the need for frequent repainting, translating into reduced costs and resource consumption over time. The evolution of exterior coatings has witnessed advancements in durability, color retention, and environmental friendliness, reflecting a growing emphasis on sustainable building practices and reducing lifecycle costs.
Subsequently, the following will delve into specific coating categories, analyzing their attributes, appropriate applications, and limitations. The discussion will encompass considerations for surface preparation, application techniques, and maintenance strategies to ensure optimal performance and prolonged lifespan.
Expert Guidance on Exterior Coating Selection
The following guidance facilitates informed decisions concerning exterior coatings, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Tip 1: Thoroughly assess the substrate. Identify the material (wood, metal, stucco, etc.) and any existing coatings. Proper identification dictates appropriate preparation methods and coating compatibility.
Tip 2: Evaluate the local climate. Consider factors such as average rainfall, temperature fluctuations, and UV exposure. Certain coatings exhibit superior performance in specific environmental conditions.
Tip 3: Prioritize surface preparation. Cleaning, scraping, and priming are crucial for adhesion and durability. Neglecting these steps compromises the integrity of the entire coating system.
Tip 4: Select a high-quality primer. A primer enhances adhesion, seals porous surfaces, and provides a uniform base for the topcoat. Choose a primer compatible with both the substrate and the intended topcoat.
Tip 5: Opt for a durable topcoat. Consider acrylic latex, alkyd, or specialty coatings formulated for exterior use. Research the product’s resistance to fading, cracking, and mildew.
Tip 6: Apply multiple thin coats. Multiple thin coats provide better coverage, adhesion, and durability than a single thick coat. Allow adequate drying time between coats as specified by the manufacturer.
Tip 7: Maintain consistent application techniques. Use consistent brushstrokes, roller pressure, or spray patterns to achieve a uniform finish. Avoid excessive build-up in corners and crevices.
Tip 8: Regularly inspect and maintain the coated surface. Promptly address any signs of damage, such as cracking, peeling, or fading, to prevent further deterioration.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes optimal adhesion, durability, and aesthetic appeal, safeguarding the structure against environmental stressors.
Subsequently, the conclusion will synthesize the preceding information, offering a holistic perspective on achieving exceptional exterior coating results.
1. Durability
Durability is a paramount consideration when determining the optimal coating type for outside surfaces. The ability of a coating to withstand environmental stressors and physical wear directly impacts its lifespan and the protection it affords to the underlying substrate. Inadequate durability results in premature degradation, increased maintenance costs, and potential structural damage.
- Resistance to UV Radiation
Ultraviolet radiation degrades coatings, causing fading, chalking, and embrittlement. Coatings formulated with UV inhibitors mitigate these effects, preserving color integrity and extending the coating’s lifespan. Acrylic latex and specialized polyurethane coatings often exhibit superior UV resistance compared to alkyd-based formulations. The geographic location and orientation of the coated surface significantly influence UV exposure levels and, consequently, the required degree of UV protection.
- Resistance to Moisture and Temperature Fluctuations
Exterior coatings must withstand constant exposure to moisture, whether from rain, humidity, or condensation. Repeated cycles of freezing and thawing can cause coatings to crack and peel, particularly if they lack sufficient elasticity. Coatings with good water resistance and flexibility can better accommodate these fluctuations, maintaining adhesion and preventing water infiltration. Elastomeric coatings are specifically designed to expand and contract with temperature changes, making them suitable for climates with extreme temperature variations.
- Resistance to Abrasion and Impact
Coatings on exterior surfaces are susceptible to abrasion from wind-borne debris, physical contact, and cleaning processes. Coatings with high abrasion resistance maintain their aesthetic appearance and protective properties longer. High-gloss and semi-gloss options generally offer greater abrasion resistance than matte types due to their harder surfaces. However, specialized matte options incorporating ceramic or other reinforcing additives can also provide enhanced abrasion resistance.
- Resistance to Chemical Degradation
Exposure to pollutants, acid rain, and cleaning agents can degrade exterior coatings over time. Coatings formulated with chemical-resistant polymers offer enhanced protection against these corrosive substances. The specific chemicals present in the environment should be considered when selecting a coating. For example, structures located near industrial areas or highways may require coatings with greater resistance to acid rain and exhaust fumes.
The inherent ability to endure environmental stressors and physical wear profoundly affects a coating’s ability to safeguard the underlying surface and preserve its intended aesthetic appeal. Therefore, a rigorous evaluation of these durability-related aspects is essential when selecting the appropriate protective finish. Prioritizing durability reduces maintenance requirements, minimizes long-term costs, and maximizes the lifespan of the coated structure.
2. Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is an essential attribute of any external surface coating. Its performance directly impacts the longevity and protective capabilities of the application. The selection of a finish necessitates a careful consideration of the climatic conditions to which it will be exposed. The ability to withstand a spectrum of weather-related challenges determines its ultimate efficacy.
- Moisture Permeability and Blistering
The capacity of a coating to resist water penetration is crucial. Excessive moisture absorption can lead to blistering, peeling, and substrate degradation. Hydrophobic coatings, or those with low water permeability, provide enhanced protection. Examples include acrylic latex formulations engineered for superior water repellency. Conversely, oil-based coatings, while offering good initial water resistance, may become brittle over time, increasing the risk of cracking and water ingress. The choice of coating dictates the structural integrity of the substrate in environments prone to high humidity or frequent precipitation.
- UV Degradation and Color Fading
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation causes chemical changes in coatings, leading to fading, chalking, and a reduction in overall durability. Coatings with UV-resistant pigments and additives offer enhanced protection against these effects. For instance, coatings formulated with titanium dioxide are known for their superior UV resistance. Darker colors tend to absorb more heat and UV radiation, accelerating degradation; therefore, lighter shades are often recommended for areas with intense sunlight. Failure to mitigate UV degradation results in aesthetic decline and compromised protective properties.
- Temperature Fluctuations and Cracking
Expansion and contraction due to temperature fluctuations place stress on coatings, potentially leading to cracking and loss of adhesion. Elastomeric coatings, designed with high flexibility, can better accommodate these movements. These are particularly suited for regions experiencing significant temperature swings. Rigid coatings, on the other hand, may become brittle and prone to cracking under thermal stress. Proper surface preparation, including priming, helps to improve adhesion and reduce the risk of cracking. The material properties of the substrate also influence the choice of a coating that can withstand temperature-induced stresses.
- Wind-Driven Debris and Erosion
Coatings are subjected to abrasion from wind-blown particles, such as sand, dust, and ice. Those with high abrasion resistance maintain their integrity longer in windy or coastal environments. Durable coatings with a smooth, hard finish tend to resist erosion better than softer, more porous alternatives. Application of multiple thin coats, rather than a single thick coat, can improve abrasion resistance. Regular cleaning and maintenance help to remove accumulated debris and prevent accelerated erosion. The selection of coating should consider the prevalence of abrasive elements in the surrounding environment.
These interlinked facets of weather resistance underscore the pivotal role of protective coatings. Formulations must be carefully matched to prevailing conditions to guarantee sustained performance. This meticulous approach ensures enduring beauty, structural stability, and an extended lifespan for exterior surfaces. Selecting coatings with appropriate weather resistance is, therefore, integral to ensuring the long-term integrity of structures.
3. Appearance
A coating’s visual characteristic is inextricably linked to its suitability as an external finish. Aesthetic considerations are central to property value and curb appeal, necessitating careful evaluation of how different options contribute to the overall visual impact of a structure.
- Gloss Level and Light Reflectance
The quantity of light reflected by a coating profoundly influences its perceived appearance. High-gloss options offer a reflective sheen, enhancing vibrancy and highlighting architectural details, but also accentuating surface imperfections. Matte alternatives minimize glare and conceal blemishes, providing a softer, more uniform look. The appropriate choice depends on the desired effect and the condition of the substrate. For instance, high-gloss coatings are often utilized on trim and doors, while matte options are preferred for broad wall surfaces.
- Color and Pigmentation Stability
The chosen color and its ability to retain its original hue over time are critical factors. High-quality coatings utilize pigments that resist fading and chalking under prolonged exposure to sunlight and environmental elements. Pigment instability leads to discoloration and a degraded appearance, necessitating premature recoating. Lightfastness, the resistance of a pigment to fading, should be a primary consideration, particularly in regions with intense sunlight. Utilizing premium paints with durable pigments can extend the lifespan of the color and reduce maintenance requirements.
- Texture and Surface Smoothness
The surface texture of a coating contributes to its overall aesthetic impact. Smooth finishes provide a sleek, modern look, while textured alternatives add visual interest and can mask surface irregularities. Coatings with a textured finish, such as stucco or aggregate-based options, are often employed to create a rustic or traditional aesthetic. The selection of texture should be aligned with the architectural style of the building and the desired visual effect. Application techniques also play a crucial role in achieving the intended texture and surface smoothness.
- Uniformity of Finish and Application Marks
The consistency of the coating across the entire surface area is essential for a professional appearance. Streaks, brush marks, and uneven coverage detract from the overall visual quality. Proper application techniques, including the use of appropriate tools and methods, are critical for achieving a uniform finish. Spray application, for example, typically results in a smoother, more even coating compared to brush or roller application. Careful attention to detail during the application process ensures a visually appealing and consistent finish.
These elements underscore the importance of appearance when selecting the optimal coating type for exterior surfaces. A comprehensive evaluation of gloss level, color stability, texture, and application uniformity is essential for achieving a desired aesthetic outcome. Prioritizing these aesthetic considerations enhances property value, improves curb appeal, and contributes to the overall visual harmony of the built environment.
4. Substrate Compatibility
Substrate compatibility constitutes a foundational principle in selecting any exterior surface finish. Mismatched coating and substrate pairings invite premature failure, undermining both aesthetic aspirations and protective functionality. A thorough understanding of substrate properties is therefore essential for ensuring optimal coating performance.
- Adhesion and Surface Preparation
Adhesion relies on the coating’s ability to form a strong bond with the substrate. Surface contaminants, existing coatings, or inherent substrate characteristics can impede adhesion. For instance, glossy surfaces necessitate abrasion to create a mechanical key for the coating. Porous substrates may require priming to prevent excessive coating absorption and promote uniform adhesion. Failure to adequately prepare the surface often results in peeling, blistering, or cracking of the coating. Proper preparation is thus indispensable for achieving a durable and long-lasting finish.
- Porosity and Coating Absorption
Substrate porosity directly influences coating absorption and, consequently, the uniformity of the finish. Highly porous materials, such as unsealed wood or masonry, absorb coatings unevenly, leading to variations in color and sheen. Primers designed for porous substrates mitigate this issue by sealing the surface and creating a uniform base for the topcoat. Conversely, non-porous surfaces may require coatings with enhanced adhesion properties to ensure proper bonding. Selecting a coating that complements the substrate’s porosity is crucial for achieving a consistent and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
- Chemical Compatibility and Reactivity
Chemical interactions between the coating and the substrate can compromise the integrity of both. Certain coatings may react with specific substrate materials, causing discoloration, degradation, or loss of adhesion. For instance, alkyd coatings are generally incompatible with alkaline substrates, such as fresh concrete, due to saponification. Similarly, some coatings may contain solvents that can damage or dissolve certain plastic or synthetic materials. Careful consideration of chemical compatibility is essential for preventing adverse reactions and ensuring the longevity of the coating system.
- Flexibility and Thermal Expansion
Differences in the flexibility and thermal expansion rates of the coating and the substrate can lead to stress and eventual failure. Coatings applied to substrates that undergo significant expansion and contraction due to temperature fluctuations must possess sufficient flexibility to accommodate these movements. Elastomeric coatings, designed with high flexibility, are often employed on substrates prone to thermal stress. Rigid coatings applied to flexible substrates may crack or delaminate over time. Matching the coating’s flexibility to the substrate’s thermal behavior is crucial for maintaining long-term adhesion and preventing coating failure.
These interconnected aspects of substrate compatibility underscore the importance of informed coating selection. A comprehensive understanding of substrate properties, proper surface preparation, and careful matching of coating characteristics are essential for achieving a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting external surface finish. Prioritizing substrate compatibility minimizes the risk of premature failure and maximizes the return on investment in the coating system.
5. Ease of Application
The practicality of applying an exterior surface coating is intrinsically linked to its overall efficacy and suitability. The selected protective finish must not only offer superior durability and aesthetic appeal but also be manageable within the constraints of available resources and skill levels. Undue complexity in application can lead to suboptimal results, increased labor costs, and compromised long-term performance.
- Viscosity and Flow Properties
A coating’s viscosity dictates its flow and leveling characteristics. Coatings with appropriate viscosity spread evenly and minimize brush marks or roller stipple. Excessive thickness hinders application, requiring more force and potentially leading to uneven coverage. Conversely, overly thin options run easily, necessitating multiple coats. Suitable viscosity streamlines the application process, reduces the likelihood of errors, and contributes to a smoother, more professional finish. This is paramount when selecting the optimal external coating, ensuring efficient use and minimal rework.
- Drying Time and Recoating Intervals
The duration required for a coating to dry influences the overall project timeline and labor requirements. Prolonged drying times expose the coated surface to potential contaminants and weather-related damage. Conversely, excessively rapid drying can impede proper leveling and adhesion. Well-formulated exterior coatings balance drying time with workability, allowing for efficient application and timely recoating. The ability to apply multiple coats within a reasonable timeframe is essential for achieving adequate film thickness and optimal protection. Shorter recoating intervals translate to reduced labor costs and accelerated project completion.
- Application Method Compatibility
Exterior coatings can be applied using various methods, including brushing, rolling, and spraying. The selected finish must be compatible with the chosen application technique to ensure proper atomization, coverage, and finish quality. Certain coatings are formulated for brush application, offering excellent leveling and minimal spattering. Others are designed for spray application, providing a smooth, uniform finish with minimal effort. Selecting a finish that aligns with available equipment and applicator skill levels optimizes the application process and minimizes the risk of defects. Compatibility with different application methods offers flexibility and adaptability, accommodating varying project requirements and site conditions.
- Clean-Up and Maintenance Requirements
The ease with which application equipment can be cleaned and maintained impacts overall project efficiency and cost. Coatings that require harsh solvents for clean-up pose environmental and safety concerns, while those that can be cleaned with water offer a more convenient and eco-friendly alternative. The ability to easily clean brushes, rollers, and spray equipment reduces downtime, minimizes waste, and simplifies the application process. Furthermore, the maintenance requirements of the applied coating contribute to its long-term cost-effectiveness. Finishes that are easy to clean and require minimal upkeep reduce the burden on property owners and ensure continued aesthetic appeal.
The interplay between these factors underscores the significance of ease of application in selecting an optimal finish for external surfaces. While durability, weather resistance, and appearance are paramount, the practicality of applying the coating is equally critical. Coatings that are easy to apply, dry quickly, and clean up efficiently contribute to a more streamlined and cost-effective project, ultimately enhancing the long-term performance and aesthetic value of the coated structure.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
Cost-effectiveness, in the context of exterior surface coatings, transcends the initial purchase price. The optimal finish represents a balance between upfront expenditure and long-term financial implications. A seemingly inexpensive coating may necessitate more frequent reapplication due to inferior durability, ultimately incurring greater overall costs. Conversely, a higher-priced product, exhibiting superior weather resistance and longevity, can yield long-term savings by minimizing maintenance and extending the recoating interval. For example, an acrylic latex paint, while potentially more expensive initially than an oil-based alternative, often demonstrates better color retention and resistance to cracking, resulting in fewer repainting cycles and a lower total cost of ownership. The selection process must, therefore, consider the lifecycle costs associated with different coating options.
Furthermore, the cost of labor associated with surface preparation and application significantly influences the overall cost-effectiveness equation. Coatings requiring extensive surface preparation, such as those necessitating complete removal of existing finishes, introduce additional labor expenses. Similarly, complex application processes, such as multi-coat systems or specialized techniques, can increase labor hours and associated costs. Examples of cost savings in this area include the use of self-priming coatings or those designed for easy application via spraying, which can reduce both material and labor requirements. The integration of these application considerations into the initial selection process can significantly impact the overall project budget.
In summary, determining the finish that maximizes cost-effectiveness demands a holistic evaluation. It necessitates a comparison of initial costs, projected maintenance requirements, labor expenses, and anticipated lifespan. Factors such as climate conditions, substrate material, and desired aesthetic outcomes should be integrated into the analysis. While selecting the least expensive option may appear prudent in the short term, a comprehensive lifecycle cost assessment often reveals that a higher-quality, more durable coating represents the most financially responsible choice for exterior surfaces. The inherent challenge lies in accurately projecting long-term performance and associated costs, requiring careful research and informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding exterior coating types, aiming to provide clarity and informed decision-making.
Question 1: What coating types offer the best protection against UV radiation?
Acrylic latex and specialized polyurethane coatings exhibit superior UV resistance compared to alkyd-based formulations. These options incorporate UV inhibitors that mitigate fading, chalking, and embrittlement caused by prolonged sun exposure.
Question 2: How does substrate porosity affect coating performance?
Substrate porosity influences coating absorption and the uniformity of the finish. Highly porous materials require priming to prevent uneven absorption, while non-porous surfaces may need coatings with enhanced adhesion properties.
Question 3: What are the key factors in assessing the cost-effectiveness of an exterior coating?
Cost-effectiveness evaluation includes initial costs, projected maintenance requirements, labor expenses, and the anticipated lifespan of the coating. A holistic lifecycle cost assessment is essential for making informed decisions.
Question 4: How does temperature fluctuation impact exterior coating selection?
Temperature fluctuations cause expansion and contraction, placing stress on coatings. Elastomeric coatings, designed with high flexibility, accommodate these movements, preventing cracking and loss of adhesion.
Question 5: Is high-gloss always the most durable choice?
High-gloss coatings generally offer greater abrasion resistance but may highlight imperfections. The optimal selection depends on the desired aesthetic and the condition of the substrate.
Question 6: What role does surface preparation play in achieving long-lasting results?
Surface preparation, including cleaning, scraping, and priming, is crucial for adhesion and durability. Neglecting these steps compromises the integrity of the entire coating system.
Selecting appropriate external coatings demands a thorough consideration of factors ranging from UV resistance to substrate compatibility. A meticulous approach ensures lasting performance and aesthetic satisfaction.
Subsequently, the conclusion will synthesize the preceding information, offering a holistic perspective on achieving exceptional exterior coating results.
Best Paint Finish for Exterior
The foregoing exploration has illuminated the multifaceted considerations inherent in selecting a superior coating type for external surfaces. Durability, weather resistance, appearance, substrate compatibility, ease of application, and cost-effectiveness all contribute to the ultimate performance and longevity of the chosen finish. No single product universally excels across all parameters; rather, the optimal selection depends on a careful assessment of specific project requirements and environmental conditions. Adherence to best practices in surface preparation and application remains critical, irrespective of the coating type employed.
The long-term implications of an informed decision extend beyond immediate aesthetic improvements. A meticulously chosen and properly applied coating safeguards structural integrity, minimizes maintenance costs, and maximizes the lifespan of exterior surfaces. Continued advancements in coating technology promise even greater durability, weather resistance, and environmental friendliness. Therefore, thorough research and careful consideration should precede any coating endeavor to ensure lasting value and protection for the structure.