Coatings designed for application on interior concrete surfaces offer a decorative and protective layer. These products, often referred to as specialized paints, are formulated to adhere to concrete’s porous nature while providing a durable, aesthetically pleasing finish. An example includes an epoxy-based covering used in residential basements to prevent dusting and enhance visual appeal.
The implementation of such surface treatments improves the longevity of concrete structures and contributes to healthier indoor environments. By sealing the substrate, these materials can mitigate moisture intrusion, inhibit mold growth, and reduce the release of concrete dust particles into the air. Historically, these treatments were primarily utilitarian; however, advancements in chemical formulations have led to a wide range of colors, textures, and performance characteristics, elevating their use in contemporary design.
The subsequent sections will delve into the various types of these coatings, appropriate surface preparation techniques, application methods, and considerations for specific environmental conditions. This will equip readers with the knowledge necessary to select and apply the optimal covering for their interior concrete projects.
Application Insights
Achieving a successful application requires meticulous planning and execution. The following guidelines enhance the likelihood of a durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to application, thoroughly clean the concrete surface. Remove any existing coatings, dirt, grease, or efflorescence. A clean, porous surface ensures proper adhesion.
Tip 2: Conduct Moisture Testing: Concrete’s moisture content significantly impacts coating performance. Perform a calcium chloride test or utilize a moisture meter to verify moisture levels are within the coating manufacturer’s recommended range. High moisture can lead to blistering and failure.
Tip 3: Select the Appropriate Product: Different formulations offer varying levels of durability, chemical resistance, and aesthetic properties. Consider the intended use of the space and the desired finish when making a selection. Epoxy coatings provide excellent abrasion resistance, while acrylics offer superior UV resistance.
Tip 4: Primer Application is Often Essential: Applying a primer specifically designed for concrete surfaces can improve adhesion and promote a uniform finish. Select a primer compatible with the chosen topcoat.
Tip 5: Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended application rates, mixing ratios, and curing times. Deviations can compromise the coating’s performance.
Tip 6: Apply in Multiple Thin Coats: Applying several thin coats, rather than one thick coat, minimizes the risk of runs, sags, and air entrapment. Allow each coat to dry completely before applying the next.
Tip 7: Ensure Adequate Ventilation: Many coatings contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Adequate ventilation is crucial during application and curing to minimize health risks and ensure proper curing.
Proper execution, including scrupulous preparation and informed product selection, is necessary for realizing the full potential of these coating systems. The advantages of durability and aesthetics are contingent upon adherence to these principles.
The subsequent section will address specific product types and their ideal applications, providing a deeper understanding of available options.
1. Durability
Durability, in the context of coatings for interior concrete, refers to the coating’s ability to withstand wear, tear, and degradation over time while maintaining its protective and aesthetic properties. It’s a critical performance characteristic that directly influences the long-term value and life-cycle cost of the coating system.
- Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is the ability of a coating to resist damage from friction, rubbing, or scraping. In high-traffic areas like hallways or commercial spaces, coatings with poor abrasion resistance will quickly exhibit scuff marks, scratches, and a loss of finish. Epoxy coatings, known for their hardness, are often selected where high abrasion resistance is paramount. For example, an epoxy coating on a concrete floor in a retail store will better withstand foot traffic and the movement of shopping carts than a standard acrylic latex paint.
- Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance defines a coating’s ability to withstand exposure to various chemicals without degradation. This is particularly important in environments like garages or industrial spaces where spills of oils, solvents, or cleaning agents are likely. A coating with inadequate chemical resistance may soften, discolor, or even dissolve upon exposure to certain chemicals. Polyurethane coatings are often chosen for their superior chemical resistance, providing a barrier against common household and industrial chemicals.
- Impact Resistance
Impact resistance refers to a coating’s capacity to withstand sudden impacts without cracking, chipping, or delaminating from the substrate. This is crucial in areas subject to heavy objects or potential impacts, such as warehouses or workshops. A coating with low impact resistance may fail prematurely, requiring costly repairs. Coatings containing elastomeric properties often exhibit improved impact resistance, absorbing energy and preventing damage to the underlying concrete.
- UV Resistance
While often associated with exterior applications, UV resistance plays a role in interior spaces with significant natural light exposure. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause some coatings to fade, chalk, or yellow over time, diminishing their aesthetic appeal. Acrylic polyurethane coatings offer enhanced UV resistance, maintaining their color and gloss longer than standard acrylics in sunlit environments, for example, a sunroom.
The selection of an appropriate coating system with suitable durability characteristics is paramount for ensuring the long-term performance and visual appeal of interior concrete surfaces. Understanding the specific environmental conditions and potential stressors within the intended space is essential for making an informed decision that maximizes the life-cycle value of the application.
2. Aesthetics
The aesthetic dimension of interior concrete surfaces is fundamentally altered through the application of specialized coatings. These treatments transcend mere protection, acting as a primary determinant of the visual character within a space. The selection of a coating is therefore a deliberate aesthetic choice that influences the perceived value and usability of the environment. The appearance of a concrete floor in a minimalist loft, for example, can be transformed from utilitarian to sophisticated through the application of a glossy epoxy finish, effectively establishing a desired ambiance. This visual transformation directly impacts the perceived value of the property and the overall user experience.
Furthermore, the aesthetic impact extends beyond simple color selection. Texture, sheen level, and the simulated appearance of other materials are all achievable through specific coating formulations and application techniques. Stained concrete finishes, for instance, can mimic the look of natural stone or aged leather, introducing an element of luxury or rustic charm. The ability to customize the appearance to such a degree empowers designers to integrate concrete elements seamlessly into a diverse range of architectural styles. Neglecting the aesthetic potential of these coatings can result in a space that feels unfinished or lacking in visual interest, potentially diminishing the overall appeal and functionality.
In summation, the strategic use of coatings provides a powerful tool for shaping the aesthetic qualities of interior concrete. The deliberate consideration of color, texture, and finish enables the creation of spaces that are not only durable and functional, but also visually compelling and aligned with specific design intentions. The key challenge lies in selecting the appropriate coating system that balances aesthetic objectives with performance requirements, ultimately contributing to a holistic and successful interior design outcome.
3. Surface Preparation
Surface preparation is an indispensable prerequisite for successful “concrete finish paint interior” applications. The condition of the concrete substrate directly influences the adhesion, longevity, and aesthetic outcome of the applied coating. Inadequate preparation inevitably leads to premature coating failure, manifesting as blistering, peeling, or cracking. For instance, the presence of laitance a weak, powdery layer on new concrete acts as a bond breaker, preventing the coating from properly adhering to the underlying solid concrete. Similarly, existing coatings, dirt, grease, or efflorescence (mineral salt deposits) on the surface compromise adhesion and create an uneven finish. Therefore, meticulous surface preparation, typically involving cleaning, profiling (roughening), and patching, is essential to create a sound, receptive surface for coating application. Without the correct preparation, even the highest quality product will not perform as intended.
Various methods exist for concrete surface preparation, each suited to specific conditions and types of contaminants. Mechanical methods, such as grinding, shot blasting, and scarifying, are effective for removing existing coatings and creating a profiled surface that enhances adhesion. Chemical methods, involving the use of acid etching or degreasers, can remove laitance, oil, and grease. Proper cleaning, often involving pressure washing, is necessary to remove loose debris and residual chemicals. The choice of method depends on the condition of the concrete, the type of coating to be applied, and the desired surface profile. For example, a self-leveling epoxy coating requires a smoother, more uniform surface profile than a heavily textured coating. Skipping the profiling step for self-leveling epoxy may cause an uneven surface later. Precise assessment is therefore important.
Ultimately, effective surface preparation is not merely a preliminary step but an integral component of the “concrete finish paint interior” system. It ensures optimal coating adhesion, extends the coating’s lifespan, and enhances its aesthetic qualities. Ignoring or inadequately performing surface preparation results in costly rework and diminished performance. The investment in time and resources for proper preparation yields significant returns in the form of a durable, visually appealing, and long-lasting finish. The significance of this foundational process cannot be overstated, as it directly determines the overall success and value of the interior concrete coating project.
4. Moisture Resistance
The ability of coatings to resist moisture intrusion is paramount in interior concrete applications. Concrete, by its inherent nature, is a porous material susceptible to moisture absorption from various sources, including rising damp, condensation, and spills. This absorbed moisture can lead to a cascade of detrimental effects, such as efflorescence, mold growth, and ultimately, structural degradation. Coatings specifically designed to impede moisture ingress serve as a protective barrier, mitigating these risks and prolonging the lifespan of the concrete substrate. An example of this practical application is the use of epoxy-based coatings in basement environments, where high humidity levels are common. These coatings effectively seal the concrete, preventing moisture from penetrating the surface and creating an environment conducive to mold proliferation.
The effectiveness of a coating’s moisture resistance is contingent upon its chemical composition, application technique, and the condition of the underlying concrete. Permeable coatings allow moisture vapor to pass through, potentially leading to blistering or delamination if the vapor pressure exceeds the coating’s tensile strength. Conversely, impermeable coatings, while providing superior moisture protection, may trap moisture within the concrete if the substrate is not properly dried prior to application. Furthermore, the integrity of the coating is directly affected by the quality of surface preparation. A properly prepared surface ensures optimal adhesion, preventing moisture from seeping beneath the coating and compromising its protective barrier. This is why a thorough surface cleansing and profiling step cannot be skipped.
In summary, moisture resistance constitutes a critical performance attribute for coatings designed for interior concrete environments. The selection of a coating with appropriate moisture-resistant properties, coupled with meticulous surface preparation and application, represents a proactive strategy for preserving the integrity and longevity of concrete structures. While challenges remain in achieving perfect moisture control, a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing moisture transport and coating performance is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and healthy indoor environment.
5. Application Technique
The application technique employed when installing coatings on interior concrete surfaces exerts a substantial influence on the final outcome, impacting both the aesthetic appearance and the long-term durability of the finish. Improper techniques can lead to a range of issues, negating the benefits of even the highest-quality coating materials. Attention to detail and adherence to recommended procedures are therefore crucial for successful “concrete finish paint interior” projects.
- Spray Application
Spray application involves the use of specialized equipment to atomize the coating material and apply it to the concrete surface in a fine mist. This technique is often preferred for large areas or intricate designs, as it allows for rapid and uniform coverage. However, proper spray technique requires careful control of factors such as spray pressure, nozzle size, and spray pattern overlap. Insufficient overlap can result in thin spots or striping, while excessive pressure can cause runs or sags. For instance, when applying a clear sealant to a decorative concrete floor, skilled spray application ensures an even, glossy finish free from imperfections.
- Roller Application
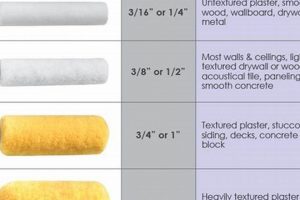
Roller application involves using a roller to transfer the coating material onto the concrete surface. This method is suitable for a variety of coatings and surface textures. The type of roller used (e.g., nap length, material) should be selected based on the specific coating and desired finish. For example, a high-nap roller is often used for textured coatings to ensure complete coverage of the surface irregularities. Consistent roller pressure and overlapping strokes are necessary to achieve a uniform coating thickness and avoid roller marks. Over-application or using an improper roller can lead to an uneven finish and compromised coating performance.
- Brush Application
Brush application involves using a brush to apply the coating material to the concrete surface. This technique is typically used for detailed work, edges, corners, or areas inaccessible to rollers or spray equipment. The type of brush used (e.g., bristle type, size) should be appropriate for the coating being applied. Proper brush technique involves applying the coating in smooth, even strokes, avoiding excessive buildup or brush marks. When applying a stain to a concrete countertop, careful brush application along the edges and corners ensures a consistent and professional finish.
- Self-Leveling Application
Some coatings, particularly epoxy-based systems, are designed to be self-leveling. These coatings are poured onto the concrete surface and allowed to flow and spread, creating a smooth, level finish. The application of self-leveling coatings requires careful attention to surface preparation and proper mixing ratios. The concrete surface must be properly primed and sealed to prevent the coating from absorbing into the substrate. The coating must also be mixed thoroughly to ensure proper curing and prevent inconsistencies in the finish. Skilled application is essential to avoid air entrapment and ensure a uniform thickness across the entire surface.
The selection and execution of the appropriate application technique are essential determinants of success of any “concrete finish paint interior” project. Mastering these techniques requires practice, attention to detail, and a thorough understanding of the properties of the coating materials being used. By carefully considering these factors, professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike can achieve durable, aesthetically pleasing finishes that enhance the value and longevity of interior concrete surfaces.
Frequently Asked Questions About Interior Concrete Surface Coatings
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions regarding the selection and application of coatings for interior concrete surfaces. The information provided aims to offer clarity and guidance for achieving optimal results.
Question 1: What constitutes “concrete finish paint interior?”
It refers to a specialized category of coatings engineered for direct application to interior concrete substrates. These materials provide both decorative and protective attributes, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and durability of concrete surfaces.
Question 2: Is surface preparation truly necessary? Can’t the coating just be applied directly?
Surface preparation is non-negotiable. Direct application without proper preparation compromises adhesion and can lead to premature coating failure, resulting in blistering, peeling, or cracking. Adhering to the specific recommendations for surface preparation of the coating is paramount.
Question 3: How does one choose the appropriate coating type for a specific application?
Selection is driven by multiple factors: the intended use of the space, anticipated traffic levels, exposure to chemicals, and desired aesthetic properties. Consulting manufacturer data sheets and technical specifications is essential for informed decision-making.
Question 4: Are all coatings suitable for use in environments with high moisture levels?
No. Coatings vary significantly in their moisture resistance. In high-moisture environments, such as basements or bathrooms, it is imperative to select coatings specifically formulated to resist moisture penetration and prevent mold growth.
Question 5: What role does application technique play in the success of a coating project?
Application technique is a critical determinant of the final outcome. Improper application can lead to uneven coverage, air entrapment, and diminished performance. Adherence to manufacturer-recommended application methods is essential.
Question 6: How important is it to follow manufacturer’s instructions precisely?
Strict adherence to manufacturer instructions is non-negotiable. Deviations from recommended mixing ratios, application rates, or curing times can compromise the coating’s performance and longevity. The technical data sheet provided by the manufacturer serves as the blueprint for success.
In summary, selecting and applying coatings to interior concrete surfaces requires careful consideration of factors ranging from surface preparation to application technique. A thorough understanding of these aspects is crucial for achieving durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting results.
The subsequent section will provide an overview of available coating types and their specific properties.
Conclusion
This exposition has provided an overview of considerations pertinent to interior concrete surface treatments. The characteristics of the concrete substrate, performance expectations, and aesthetic objectives are all critical determinants in the selection and application process. Factors such as appropriate surface preparation, coating durability, moisture resistance, and precise application techniques directly impact long-term performance. A comprehensive understanding of these variables is necessary for achieving optimal results.
The appropriate implementation of specialized surface coatings offers a viable method for enhancing the durability, functionality, and visual appeal of concrete surfaces within interior environments. Continued advancements in material science and application methodologies promise to yield even more sophisticated solutions in the future. Therefore, ongoing research and professional development are essential for remaining abreast of emerging best practices in this dynamic field.