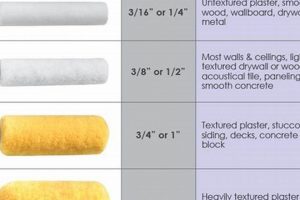
A surface coating’s sheen level significantly impacts both aesthetics and performance. Two common options for outside applications include minimal and moderate reflectance characteristics. The former, also known as matte, absorbs light, minimizing imperfections on surfaces. The latter offers a subtle radiance, providing increased durability and easier cleaning compared to its less reflective counterpart.
Selecting the appropriate sheen level is critical for long-term protection and visual appeal. Lower reflectance options are often preferred for hiding flaws on siding and masonry, offering a uniform appearance. Higher reflectance alternatives are frequently chosen for trim and doors, due to their enhanced resistance to dirt and moisture, and their ability to highlight architectural details. The choice represents a balance between desired visual effect and practical considerations such as maintainability and resistance to environmental factors.
Understanding the nuances of these different coating options is essential for ensuring a durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome. Subsequent sections will delve into factors influencing the selection process, including substrate type, environmental conditions, and desired aesthetic.
Application Strategies for Exterior Coatings
The selection and application of exterior coatings require careful consideration to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The following tips provide guidance on maximizing the benefits of different sheen levels for exterior surfaces.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Prior to application, ensure the surface is clean, dry, and free from loose paint, dirt, or mildew. Proper preparation enhances adhesion and prolongs the coating’s lifespan.
Tip 2: Consider the Substrate: Porous surfaces like stucco may benefit from coatings with minimal reflectance to minimize imperfections. Smoother surfaces, such as trim, can effectively showcase coatings with subtle radiance.
Tip 3: Environmental Conditions Matter: Avoid applying coatings in direct sunlight or during periods of high humidity. Ideal conditions promote proper drying and curing, resulting in a more durable finish.
Tip 4: Application Techniques Influence Outcome: Employ consistent application techniques, whether brushing, rolling, or spraying, to achieve uniform coverage and minimize inconsistencies in sheen.
Tip 5: Multiple Coats Enhance Protection: Applying two coats of the chosen coating system provides increased durability and resistance to weathering, especially in harsh climates.
Tip 6: Understand Sheen Level Impact on Maintenance: Coatings with subtle radiance are generally easier to clean than their less reflective counterparts. Factor this into the decision-making process, especially for high-traffic areas.
Tip 7: Test Before Committing: Always test a small, inconspicuous area before applying the coating to the entire surface. This allows for verification of color and sheen compatibility with the substrate.
Adhering to these recommendations will optimize the performance and appearance of exterior coatings. The result will be an enhanced level of protection and aesthetic appeal for the structure.
The subsequent section will address the long-term maintenance and care considerations associated with exterior coatings.
1. Hiding Imperfections
The capacity of an exterior coating to obscure surface irregularities is a key determinant in the overall aesthetic quality of a structure. The choice between minimal and moderate reflectance levels significantly impacts this ability. Surfaces with inherent imperfections, such as older siding or masonry, often benefit from coatings with minimal reflectance. The light-absorbing nature of these coatings minimizes shadows and variations in texture, effectively concealing minor blemishes and creating a more uniform appearance. This is particularly evident on stucco or brick surfaces, where the inherent texture can be accentuated by higher reflectance levels, thereby highlighting rather than minimizing imperfections.
Conversely, coatings with subtle radiance, while offering increased durability and ease of cleaning, tend to amplify surface irregularities. The slight sheen reflects light, thereby drawing attention to any dents, scratches, or inconsistencies in the underlying substrate. Therefore, these finishes are generally more suitable for smoother, well-prepared surfaces, such as trim or doors, where the likelihood of significant imperfections is reduced. A real-world example would be applying a moderate sheen coating to previously damaged wood siding; the defects would be noticeably amplified compared to using a minimal sheen finish.
In summary, the selection of an exterior coating based on its ability to hide imperfections requires careful consideration of the substrate’s condition. Minimal reflectance coatings are advantageous for masking flaws on rough or uneven surfaces, whereas subtle radiance coatings are better suited for smooth, well-maintained surfaces. Understanding this relationship is crucial for achieving the desired aesthetic outcome and ensuring a visually appealing building exterior.
2. Durability Variation
The longevity of an exterior coating is directly influenced by its sheen level. Coatings with minimal reflectance, while aesthetically pleasing in their ability to conceal imperfections, generally exhibit lower durability compared to their subtle radiance counterparts. The increased porosity of coatings with minimal reflectance renders them more susceptible to environmental factors such as moisture penetration, UV degradation, and the accumulation of dirt and mildew. This, in turn, leads to a reduced lifespan, requiring more frequent reapplication. For example, an exterior wall coated with a flat finish in a humid climate is likely to show signs of deterioration, such as fading and mildew growth, much sooner than a similar wall coated with a satin finish.
Coatings exhibiting subtle radiance possess a tighter molecular structure, creating a more robust barrier against external elements. This inherent resistance translates to enhanced protection against abrasion, staining, and moisture intrusion. Consequently, surfaces coated with these finishes maintain their aesthetic appeal for a longer duration, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repainting. Consider a front door finished with a satin coating; its surface is better equipped to withstand the constant wear and tear of daily use and exposure to the elements, retaining its color and sheen longer than if it were coated with a flatter finish. The effect of UV rays can be damaging to exterior walls and the satin finish provides more protection.
In conclusion, while minimal reflectance coatings offer advantages in hiding surface imperfections, their inherent vulnerability to environmental factors results in decreased durability. Subtle radiance coatings, on the other hand, provide superior protection and longevity, making them a more practical choice for areas subjected to harsh conditions or frequent use. The selection of an exterior coating, therefore, necessitates a careful evaluation of both aesthetic preferences and long-term performance requirements. It is a critical choice between aesthetics and resistance to the climate elements of the region where the coating is needed.
3. Cleanability Differences
The ease with which exterior surfaces can be cleaned is directly correlated to the sheen level of the coating applied. Surfaces coated with minimal reflectance finishes, due to their porous nature, present challenges in cleaning. The matte texture provides microscopic crevices that readily trap dirt, dust, and other contaminants. This increased surface area makes it difficult to dislodge embedded grime, often necessitating more aggressive cleaning methods. Vigorous scrubbing, while effective, can compromise the coating’s integrity, leading to fading, streaking, or even complete removal. This effect is commonly observed on walls with a matte finish in high-traffic areas, such as near walkways or driveways, where accumulated dirt is difficult to eliminate without damaging the coating.
Conversely, coatings exhibiting subtle radiance offer superior cleanability owing to their smoother, less porous surface. The tighter molecular structure of these finishes creates a barrier that prevents dirt and grime from deeply embedding. Consequently, contaminants can be easily removed with gentle washing, requiring less effort and minimizing the risk of damaging the coating. A practical illustration would be the comparison of cleaning a matte-finished door versus a satin-finished door; the latter can be effortlessly wiped clean, while the former may require repeated scrubbing and specialized cleaning agents. This increased cleanability translates to reduced maintenance costs and an extended lifespan for the coated surface.
In summary, the choice between minimal and moderate reflectance exterior coatings should consider the importance of cleanability. Minimal reflectance coatings, while effective at concealing imperfections, pose cleaning challenges due to their porous nature. Subtle radiance coatings offer superior cleanability, reducing maintenance efforts and prolonging the coating’s lifespan. The selection process must balance aesthetic preferences with practical considerations regarding the long-term upkeep of exterior surfaces. In highly polluted or heavily used areas, a satin finish is often the more judicious choice.
4. Light Reflectance
Light reflectance is a critical property influencing the visual appearance and thermal behavior of exterior coatings. The interaction of light with a surface determines perceived color, depth, and the degree to which the surface absorbs or reflects solar energy. Different levels of light reflectance are characteristic of varying sheen levels commonly employed in exterior applications.
- Specular Reflection and Sheen
Specular reflection, the mirror-like reflection of light, is more pronounced in coatings with subtle radiance. This effect creates a sheen or gloss that enhances the perceived vibrancy of colors and highlights surface textures. However, excessive specular reflection can produce glare, particularly in direct sunlight, potentially causing visual discomfort. Flat finishes, conversely, exhibit minimal specular reflection, resulting in a matte appearance.
- Diffuse Reflection and Color Perception
Diffuse reflection, the scattering of light in multiple directions, is the dominant mode of reflection for coatings with minimal reflectance. This phenomenon contributes to a more uniform color perception, as light is dispersed evenly across the surface, mitigating the effects of shadows and surface irregularities. The absence of strong specular reflection also reduces the perceived intensity of colors, resulting in a softer, more muted aesthetic.
- Total Solar Reflectance (TSR) and Energy Efficiency
Total Solar Reflectance (TSR) measures the percentage of solar energy reflected by a surface. Higher TSR values indicate greater reflectivity and reduced heat absorption. Coatings with subtle radiance tend to have slightly higher TSR values than flat finishes, due to their increased specular reflection. However, the overall difference is often minimal, and the specific pigments used in the coating formulation have a more significant impact on TSR. Choosing lighter colors in either finish type generally results in higher TSR and reduced cooling loads for buildings.
- Impact on Visual Defects
The extent to which surface imperfections are noticeable varies with the light reflectance. Flat paints, because they minimize specular reflection, will de-emphasize these flaws. Satin paints, however, by highlighting light reflection, reveal imperfections more readily. This is an important consideration when determining which paint to use on surfaces known to have defects.
In conclusion, light reflectance is a key factor in determining the visual and thermal properties of exterior coatings. The choice between minimal and moderate reflectance levels involves balancing aesthetic preferences with practical considerations related to glare, color perception, and energy efficiency. The selection ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired characteristics of the finished surface.
5. Application Considerations
The successful application of exterior coatings hinges significantly on several factors related to the application process itself. The choice between minimal and moderate reflectance finishes influences these considerations, affecting the final outcome and longevity of the coating.
- Surface Preparation and Adhesion
Surface preparation is paramount regardless of the chosen sheen level. However, coatings with minimal reflectance, possessing a more porous texture, may require a more thorough preparation to ensure adequate adhesion. Contaminants or loose particles can readily compromise the bond of minimal reflectance coatings, leading to premature failure. Conversely, while still critical, surface preparation for subtle radiance coatings allows for slightly more tolerance, owing to their tighter molecular structure. Regardless, all previous coatings should be carefully removed and the surface cleaned before any new applications are carried out.
- Application Technique and Uniformity
Achieving a uniform finish is crucial for both minimal and moderate reflectance coatings. However, inconsistencies in application are more readily apparent with subtle radiance coatings, which tend to amplify variations in texture and sheen. Therefore, greater care must be taken to ensure consistent film thickness and proper blending of wet edges when applying coatings with subtle radiance. Spray application often yields the most uniform results, particularly for larger surfaces. The right tools always ensure a correct and appropriate application. These techniques are also dependent on the outside weather conditions.
- Environmental Conditions and Drying Time
Ambient temperature and humidity levels significantly impact the drying and curing of exterior coatings. Coatings with minimal reflectance may be more sensitive to unfavorable conditions, potentially leading to prolonged drying times and increased susceptibility to dirt accumulation during the curing process. Furthermore, high humidity can exacerbate the porosity of these coatings, compromising their water resistance. It’s essential to adhere to manufacturer recommendations regarding optimal application temperatures and humidity levels. The weather must be ideal for both drying and adherence.
- Number of Coats and Coverage
The recommended number of coats can vary based on the chosen sheen level and the color being applied. Minimal reflectance coatings often require multiple coats to achieve adequate hiding and uniformity, especially when covering a contrasting color. Subtle radiance coatings, with their enhanced opacity, may achieve the desired coverage with fewer coats. However, proper film thickness is essential regardless of the number of coats applied.
In conclusion, application considerations are inextricably linked to the choice between minimal and moderate reflectance exterior coatings. Factors such as surface preparation, application technique, environmental conditions, and the number of coats applied influence the final appearance and performance of the coating. Careful attention to these details is essential for achieving a durable and aesthetically pleasing result. Understanding the conditions and environment that the coatings will face can help you determine what method of application is best.
6. Substrate Compatibility
The selection of an exterior coating necessitates careful consideration of the substrate to which it will be applied. Compatibility between the coating and the underlying material directly influences adhesion, durability, and overall performance, especially when choosing between minimal and moderate reflectance options.
- Porous Substrates and Minimal Reflectance Coatings
Porous substrates, such as stucco or unsealed concrete, readily absorb moisture. Minimal reflectance coatings, being more permeable, allow for breathability, preventing moisture buildup beneath the coating. This characteristic is crucial for preventing blistering, peeling, and ultimately, coating failure. Applying a moderate reflectance coating to a highly porous substrate can trap moisture, leading to significant damage over time. In areas with high rainfall, this becomes especially important.
- Smooth Substrates and Moderate Reflectance Coatings
Smooth, non-porous substrates, like metal or previously painted surfaces, typically benefit from coatings with subtle radiance. These finishes provide enhanced adhesion to smooth surfaces, forming a durable and protective barrier. The reflective properties of these coatings also enhance the aesthetic appeal of smoother surfaces. Minimal reflectance coatings on these surfaces may not achieve optimal adhesion and can appear dull or lifeless. A well-maintained trim around a window frame showcases the aesthetic when using moderate reflectance coating.
- Wood Substrates and Flexibility Considerations
Wood substrates expand and contract with changes in temperature and humidity. The selected coating must possess sufficient flexibility to accommodate these dimensional changes without cracking or peeling. Both minimal and moderate reflectance coatings can be formulated with flexible resins, but the specific formulation must be appropriate for exterior wood applications. Failure to account for wood movement can result in premature coating failure. Because most wood is porous, an exterior primer is helpful when applying a moderate reflectance coating.
- Previously Coated Substrates and Intercoat Adhesion
When applying a new coating over a previously coated surface, ensuring proper intercoat adhesion is paramount. The existing coating must be thoroughly cleaned, and any loose or flaking material removed. Incompatibility between the new and old coatings can lead to delamination and peeling. It is often advisable to use a primer or bonding agent to promote adhesion, particularly when switching between different coating types or sheen levels. Furthermore, roughing the surface of the previous coating will aid adhesion.
Substrate compatibility is a fundamental consideration when selecting an exterior coating. Choosing the appropriate coating based on the substrate’s porosity, texture, and movement characteristics is essential for achieving long-term performance and aesthetic satisfaction. Failing to do so can lead to costly repairs and premature coating failure, underscoring the importance of proper substrate analysis and coating selection.
7. Environmental Impact
The selection of an exterior coating impacts the environment through various stages of its lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. Minimal and moderate reflectance finishes each present distinct environmental considerations. The production of some coatings involves volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Regulations increasingly restrict VOC content, prompting manufacturers to develop low-VOC or zero-VOC alternatives. The durability of the coating also plays a crucial role; longer-lasting finishes reduce the frequency of repainting, thereby decreasing the demand for new coatings and minimizing waste. For example, a durable satin finish may require replacement less often than a flat finish, resulting in a lower overall environmental footprint. The improper disposal of coatings and cleaning materials introduces further environmental concerns, necessitating responsible waste management practices. Some coatings are disposed of via landfill and contribute to the general carbon footprint of the building.
Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating the environmental impact of different coating options. LCAs consider factors such as energy consumption, water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation throughout the entire lifecycle of the coating. These assessments can inform decision-making by highlighting the environmental trade-offs associated with different choices. For example, an LCA might reveal that a low-VOC flat finish with a shorter lifespan has a higher overall environmental impact than a traditional satin finish with higher VOC content but greater durability. However, it is not only the make-up of the coating that creates an environmental impact, but the proper disposal and recycling of the materials. Using a well-cleaned brush will help to reduce the usage of paint thinners. Proper disposal of these products is essential.
In summary, minimizing the environmental impact of exterior coatings requires a holistic approach encompassing material selection, durability considerations, responsible application practices, and proper waste management. Choosing low-VOC or zero-VOC formulations, opting for durable finishes that extend the repainting cycle, and adhering to environmentally sound disposal methods are essential steps in reducing the ecological footprint. The growing awareness of environmental sustainability is driving innovation in the coatings industry, leading to the development of more eco-friendly products and practices. Continued research and development efforts are needed to further minimize the environmental impact of exterior coatings while maintaining or improving their performance characteristics. Future advancements might explore bio-based coatings or more effective recycling and reuse programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and application of exterior coatings with varying sheen levels, focusing on performance characteristics and best practices.
Question 1: What are the primary differences between exterior coatings characterized as “flat” and those labeled “satin?”
Flat coatings exhibit minimal light reflectance, resulting in a matte appearance that effectively hides surface imperfections. Satin coatings possess a subtle sheen, offering enhanced durability and cleanability compared to flat finishes.
Question 2: Under what circumstances is a flat exterior coating preferred over a satin finish?
Flat coatings are generally preferred for surfaces with significant imperfections, such as older siding or stucco, where their light-absorbing properties minimize the visibility of flaws. The hiding qualities of flat exterior coatings cannot be matched.
Question 3: Conversely, when is a satin exterior coating the more appropriate choice?
Satin coatings are often selected for trim, doors, and other areas subject to frequent contact or exposure to moisture, owing to their increased durability and ease of cleaning. The protective features are important for high-touch points on a building.
Question 4: How does the sheen level of an exterior coating impact its resistance to dirt and mildew?
Satin coatings, with their smoother surface, are inherently more resistant to dirt and mildew accumulation compared to flat coatings, which possess a more porous texture. The cleaning qualities extend the life of the coating and protect the integrity of the building’s exterior.
Question 5: Does the choice of exterior coating sheen level affect the overall cost of the project?
While the material cost of flat and satin coatings may be similar, the increased durability and longevity of satin finishes can result in lower long-term maintenance costs. The investment is well worth the result, especially in climates with harsh weather patterns.
Question 6: Are there specific application techniques recommended for achieving optimal results with different exterior coating sheen levels?
Proper surface preparation is crucial for all exterior coatings. However, satin coatings may require more careful application to avoid inconsistencies in sheen. Using a high-quality brush or sprayer is also recommended.
Selecting the appropriate exterior coating finish represents a balance between aesthetic preferences and practical considerations. Evaluating the substrate, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance requirements is essential for achieving a durable and visually appealing result.
The subsequent section will summarize the key factors influencing the selection of exterior coatings.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis underscores the critical considerations involved in selecting an appropriate exterior paint finish flat or satin. The choice necessitates a comprehensive understanding of substrate characteristics, environmental factors, application techniques, and desired aesthetic outcomes. Flat finishes offer superior concealment of imperfections, while satin finishes provide enhanced durability and ease of maintenance. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully evaluated.
Ultimately, the selection of an exterior coating finish represents a significant investment that directly impacts both the longevity and visual appeal of a structure. Thorough research, meticulous planning, and adherence to best practices are essential for achieving optimal results. Prioritizing informed decision-making will ensure a durable and aesthetically pleasing exterior that withstands the test of time, therefore contributing to a higher resale value of a building in the future.