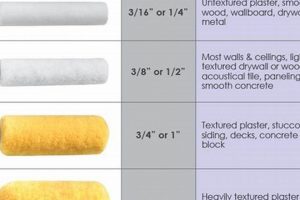
The term refers to a high-quality coating product designed to provide a durable and aesthetically pleasing final layer on various surfaces. It implies a paint that delivers a superior level of appearance, protection, and longevity compared to standard options. For example, a house painter might specify the use of this type of product for exterior walls to ensure resistance to weather elements and lasting color retention.
The selection of such a product is critical for achieving desired visual outcomes and maintaining structural integrity. Its benefits include improved resistance to wear and tear, enhanced color stability over time, and reduced need for frequent repainting. Historically, advancements in coating technology have led to the development of these specialized products, addressing the demand for more robust and lasting solutions in construction and design.
Further considerations will address factors influencing its selection, including surface preparation, application techniques, environmental impact, and cost-effectiveness. An examination of specific product types and their suitability for diverse applications will also be presented.
Tips for Optimal Coating Application
Achieving a professional-grade result requires adherence to specific best practices throughout the coating process. These guidelines ensure longevity, aesthetic appeal, and overall performance.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Thoroughly clean and prepare the substrate prior to application. Remove any loose debris, dirt, or existing coatings. Proper preparation promotes adhesion and prevents premature failure.
Tip 2: Priming Enhances Adhesion and Coverage: Apply a suitable primer compatible with both the substrate and the coating product. Priming seals porous surfaces, improves adhesion, and ensures uniform color distribution.
Tip 3: Temperature and Humidity Control: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended temperature and humidity ranges during application and drying. Extreme conditions can negatively impact the curing process and affect the final finish.
Tip 4: Application Technique Matters: Employ consistent application techniques, such as maintaining a wet edge and using even strokes. Avoid excessive buildup or thin spots, which can lead to uneven appearance and reduced durability.
Tip 5: Multiple Thin Coats are Superior: Apply multiple thin coats rather than a single thick coat. This allows for proper drying and curing, minimizing the risk of runs, sags, and trapped solvents.
Tip 6: Equipment Selection and Maintenance: Utilize high-quality brushes, rollers, or spray equipment designed for the specific product. Regularly clean and maintain equipment to ensure optimal performance and prevent contamination.
Tip 7: Proper Curing Time is Essential: Allow sufficient curing time as specified by the manufacturer before exposing the coated surface to traffic or environmental elements. Premature exposure can compromise the integrity of the finish.
By meticulously following these guidelines, users can maximize the benefits and ensure a durable, aesthetically pleasing outcome. Attention to detail and adherence to recommended practices are crucial for achieving a professional-grade result.
Subsequent sections will address common challenges encountered during coating applications and provide solutions for troubleshooting potential issues.
1. Durability
The property of durability constitutes a fundamental aspect of coatings. It determines the product’s capacity to withstand degradation caused by various environmental and mechanical stressors. In the context of specialized coating products, this attribute signifies resistance to scratching, abrasion, impact, UV radiation, chemical exposure, and moisture ingress. Consequently, the longevity and protective capabilities are directly proportional to its inherent durability. For instance, coatings used in high-traffic areas, such as hospital corridors or school hallways, must exhibit exceptional resistance to abrasion to maintain their aesthetic appearance and protective function over extended periods. The selection of a product lacking adequate durability leads to premature failure, necessitating frequent recoating and increased life-cycle costs.
The durability characteristics are often achieved through the selection of specific raw materials, formulation techniques, and curing processes. For example, two-component epoxy coatings, known for their superior hardness and chemical resistance, are frequently employed in industrial settings where exposure to harsh chemicals or solvents is prevalent. Similarly, polyurethane coatings, prized for their flexibility and abrasion resistance, find application in automotive clear coats and aircraft finishes. The incorporation of UV absorbers and stabilizers in the formulation further enhances durability by mitigating the deleterious effects of sunlight exposure, preventing color fading and film degradation. The use of nanoparticles, such as silica or alumina, can also improve scratch resistance and overall hardness.
In summary, durability is not merely a desirable attribute but an essential requirement. The performance and life-cycle cost-effectiveness is intrinsically linked to its ability to withstand the rigors of its intended environment. A comprehensive understanding of durability characteristics, coupled with careful selection of appropriate coating systems, is crucial for achieving optimal protection, aesthetic appeal, and long-term value. Challenges remain in developing coatings that balance durability with other desirable properties, such as low VOC emissions and sustainable sourcing of raw materials. These challenges drive ongoing research and development efforts within the coating industry.
2. Aesthetics
Aesthetics, as a property, represents a critical performance dimension. It directly influences the perceived value and user satisfaction across diverse applications. In the context of surface coatings, aesthetics encompasses factors such as gloss level, color uniformity, smoothness, and overall visual appeal. A coating may provide exceptional protection and durability, but if it fails to deliver the desired aesthetic qualities, its suitability is compromised. The choice of specialized coating products is frequently driven by the need to achieve a specific aesthetic outcome, aligning with design intent and functional requirements. For instance, architectural coatings applied to building facades must offer both weather resistance and a visually pleasing appearance that complements the architectural style and surrounding environment.
The impact of aesthetics extends beyond purely visual considerations. It also influences tactile perception, light reflectivity, and the overall ambiance of a space. A smooth, glossy coating on furniture not only enhances its visual appeal but also provides a pleasant tactile experience. Similarly, the selection of appropriate colors and gloss levels in interior spaces can significantly impact mood and productivity. In retail environments, carefully chosen coatings can enhance product presentation and influence consumer behavior. Furthermore, coatings play a crucial role in branding and corporate identity, with companies often using specific colors and finishes to convey their brand image. The pursuit of enhanced aesthetics has driven significant innovation in coating technology, leading to the development of specialized pigments, additives, and application techniques.
In conclusion, aesthetics represents an indispensable attribute. It is not merely a cosmetic concern but a fundamental performance criterion that determines the overall success and acceptability. The interplay between aesthetics, durability, and functionality necessitates a holistic approach to coating selection, considering both technical performance and the desired visual and tactile experience. Future advancements in coating technology will likely focus on further enhancing aesthetic properties, while also addressing environmental concerns and promoting sustainable practices.
3. Protection
Protection represents a paramount function provided by a high-caliber coating, forming an integral component of its value proposition. The ability of a product to shield the underlying substrate from environmental and mechanical stressors directly impacts its lifespan and performance.
- Resistance to Moisture Intrusion
The primary function of many coatings is to create a barrier against water penetration. This is particularly crucial in exterior applications, where prolonged exposure to rain, snow, and humidity can lead to corrosion, rot, or structural damage. A product with effective moisture resistance prevents these issues, preserving the integrity of the substrate. For example, coatings applied to metal structures, such as bridges or pipelines, must possess exceptional water-repellent properties to mitigate the risk of corrosion-induced failure.
- Protection from UV Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can cause significant degradation of coating films, leading to discoloration, cracking, and loss of adhesion. High-quality coatings incorporate UV absorbers or stabilizers to mitigate these effects. The incorporation of these elements extends the lifespan of the coating and preserves its aesthetic appearance. Consider automotive clear coats, which rely heavily on UV protection to prevent fading and chalking of the underlying paint layers.
- Chemical Resistance
Many applications require coatings to withstand exposure to various chemicals, such as acids, alkalis, solvents, and oils. This is particularly relevant in industrial settings, where equipment and surfaces are often subjected to harsh chemical environments. Products formulated with appropriate chemical resistance protect the substrate from corrosion, erosion, and other forms of chemical attack. For example, tank linings used to store corrosive liquids must exhibit exceptional chemical resistance to prevent leaks and contamination.
- Abrasion and Impact Resistance
Coatings designed for high-traffic areas or surfaces subject to mechanical stress must possess adequate abrasion and impact resistance. This protects the underlying substrate from damage caused by scratching, scuffing, or impact from objects. Products formulated for flooring, furniture, or machinery often incorporate hardeners or other additives to enhance their resistance to these forms of mechanical wear. The coatings used on aircraft exteriors must withstand the impact of debris and extreme weather conditions during flight.
In summary, the protective capabilities of a specialized coating are multifarious. They encompass resistance to moisture, UV radiation, chemicals, abrasion, and impact. The synergistic combination of these protective attributes guarantees longevity, preservation of structural integrity, and maintenance of aesthetic quality. The selection of a product with appropriate protective properties is crucial for optimizing performance and maximizing the life-cycle value of the coated object.
4. Longevity
The correlation between longevity and a high-caliber coating product is substantial. A primary objective in selecting a specialized coating is to extend the lifespan of the substrate to which it is applied. This extension is achieved through the coating’s ability to protect the substrate from environmental degradation, physical damage, and chemical attack. The selection of a product lacking inherent durability directly diminishes the long-term return on investment, necessitating premature maintenance or replacement. For example, a marine-grade product applied to a ship’s hull is intended to prevent corrosion and fouling, thereby prolonging the vessel’s operational life and reducing the frequency of costly dry-docking procedures. In the absence of such protection, the hull would be susceptible to accelerated deterioration, resulting in structural weakness and increased fuel consumption.
The practical application of this understanding lies in meticulous product selection and proper application techniques. Coatings intended for exterior use must exhibit superior resistance to ultraviolet radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture exposure. Furthermore, surface preparation is critical; a properly prepared surface provides optimal adhesion, thereby maximizing the product’s protective lifespan. The use of compatible primers and sealers further enhances longevity by creating a uniform and stable base for the finish coat. Consider the application of a protective coating to a concrete bridge; inadequate surface preparation or the selection of a product with insufficient resistance to freeze-thaw cycles will lead to cracking and spalling, compromising the structural integrity of the bridge and requiring extensive repairs.
In summary, longevity is a key determinant of its overall value. Its selection should be viewed as a long-term investment, with the goal of minimizing maintenance costs and maximizing the operational life of the coated asset. While initial costs may be higher for specialized products, the extended lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements often result in significant long-term savings. Challenges remain in accurately predicting coating lifespan under varying environmental conditions and in developing sustainable coating solutions that minimize environmental impact without compromising performance. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges and improving the predictive modeling of coating performance.
5. Adhesion
Adhesion represents a critical factor determining the overall performance and longevity when using this type of paint. Proper bonding between the product and the substrate ensures that the protective and aesthetic qualities are maintained over time, preventing premature failure and costly repairs.
- Surface Preparation Influence
Surface preparation directly impacts the extent of adhesion. Contaminants such as dirt, grease, and loose particles interfere with the formation of a strong bond. Mechanical abrasion, chemical cleaning, and priming are techniques used to create a clean, receptive surface that promotes optimal interaction between the coating and the substrate. Failure to adequately prepare the surface typically results in peeling, blistering, or delamination of the coating. An example includes the application of this to a metal surface without first removing rust; the coating will adhere poorly and fail prematurely.
- Compatibility of Materials
The chemical compatibility between the coating and the substrate, as well as any intermediate layers (primers or sealers), is paramount. Incompatible materials can lead to weak bonds and interfacial failures. Manufacturers provide compatibility guidelines to ensure optimal adhesion. For instance, using an oil-based coating over a latex primer without proper preparation can result in poor adhesion and subsequent flaking. Matching the chemical properties of the coating and substrate ensures a stable and durable bond.
- Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions during application and curing significantly affect adhesion. Temperature, humidity, and airflow influence the rate of solvent evaporation and the cross-linking process, which are essential for developing a strong adhesive bond. Deviations from recommended environmental parameters can lead to incomplete curing, reduced adhesion strength, and increased susceptibility to environmental degradation. Applying this type of paint in excessively humid conditions can prevent proper curing and weaken the bond to the substrate.
- Application Techniques
The method of application plays a crucial role in achieving proper adhesion. Consistent and uniform application, using appropriate tools and techniques, ensures adequate contact between the coating and the substrate. Over-application or under-application can both lead to adhesion problems. For example, spraying with incorrect nozzle settings can result in a coating that fails to properly wet the surface, leading to weak adhesion. Proper application techniques ensure complete coverage and optimal bonding.
These factors underscore the multifaceted nature of adhesion in the context of this type of paint. Addressing each aspect surface preparation, material compatibility, environmental control, and application technique is essential for maximizing the benefits and ensuring long-term performance. Neglecting any of these considerations can compromise the integrity and longevity of the protective and aesthetic characteristics.
6. Application
The application process directly determines the ultimate success or failure. Improper application negates the intrinsic benefits of a quality formulation. Factors such as surface preparation, environmental conditions, and application method significantly influence the final result. A poorly executed application, even with a superior product, results in diminished protection, compromised aesthetics, and reduced longevity. Consider the example of a high-performance, corrosion-resistant coating applied to a steel structure; inadequate surface preparation renders the coating vulnerable to premature failure, undermining its protective function.
Application techniques vary depending on the specific product and substrate. Brush, roller, and spray applications each demand unique skills and equipment. Choosing the appropriate method is crucial for achieving uniform coverage and optimal adhesion. For instance, spraying typically provides a smoother, more consistent finish on large surfaces, while brush application offers greater control in intricate areas. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, impact drying and curing times, influencing the final hardness and durability. Failing to adhere to recommended environmental parameters can lead to blistering, cracking, or poor adhesion. The application of a specialized coating in excessively humid conditions can trap moisture, leading to premature deterioration.
Effective application requires meticulous attention to detail and adherence to manufacturer’s specifications. Proper surface preparation, appropriate technique selection, and environmental control are essential elements. A comprehensive understanding of these factors ensures that the specialized coating delivers its intended performance, maximizing protection, aesthetics, and longevity. The challenges lie in consistently executing best practices across diverse application environments and providing adequate training to applicators. Continuous advancements in application technology aim to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve the consistency of results.
7. Cost
The economic dimension is a substantial consideration when evaluating specialized coating options. The initial expenditure for premium-grade products typically surpasses that of conventional alternatives; this differential reflects the incorporation of higher-quality raw materials, advanced formulation techniques, and rigorous testing protocols. However, a myopic focus on immediate cost overlooks the potential for long-term savings derived from enhanced durability, reduced maintenance frequency, and extended service life. The selection of a lower-cost product may necessitate more frequent reapplication, ultimately exceeding the cumulative expenditure associated with a higher-initial-cost, superior-performance option. For instance, consider two protective coatings for an offshore oil platform; a conventional coating with a lower upfront cost may require reapplication every three years, while a product, though more expensive initially, may offer a service life of ten years, reducing downtime and associated labor expenses significantly.
The economic evaluation extends beyond the initial product price to encompass associated labor costs, surface preparation expenses, and potential environmental compliance fees. Surface preparation requirements often vary based on the type of coating; some formulations demand more extensive surface preparation to ensure optimal adhesion and performance, resulting in increased labor costs. Furthermore, the environmental impact of coating products, particularly volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, is subject to regulatory scrutiny, potentially incurring compliance costs. Selecting a product with lower VOC emissions may mitigate these costs, despite a potentially higher initial price. Applying the aforementioned to interior wall paint will reflect a higher premium paint, but it can protect walls and require little to zero work to clean and maintain.
In summation, the integration of a comprehensive life-cycle cost analysis is essential. This analysis considers not only the initial product cost but also the long-term implications of maintenance, repair, and potential environmental liabilities. While the initial investment may be higher, the enhanced durability, reduced maintenance, and potential environmental benefits often render it a more economically prudent choice over the long term. The challenge lies in accurately quantifying these long-term benefits and communicating their value to decision-makers. Continuous advancements in coating technology are aimed at developing cost-effective solutions that balance performance, environmental sustainability, and long-term economic value.
Frequently Asked Questions About Premium Coatings
The following addresses common inquiries regarding high-performance surface coatings. These responses aim to provide clarity on their characteristics, applications, and overall value.
Question 1: What distinguishes this type of coating from standard paint formulations?
It differentiates itself through the incorporation of superior raw materials, advanced formulation techniques, and rigorous testing protocols. These attributes result in enhanced durability, protection, and longevity compared to conventional paints.
Question 2: In what specific applications is this type of coating most beneficial?
Its characteristics make it particularly suitable for environments demanding exceptional performance, such as industrial facilities, marine structures, high-traffic areas, and applications requiring resistance to harsh chemicals or extreme weather conditions.
Question 3: How does surface preparation impact the performance?
Surface preparation represents a critical step in the application process. Proper cleaning, abrasion, and priming ensure optimal adhesion, maximizing the protective and aesthetic properties. Inadequate surface preparation can lead to premature failure and diminished performance.
Question 4: What factors influence the selection of a specific coating formulation?
The selection process should consider the substrate material, environmental conditions, desired aesthetic outcome, and specific performance requirements. Consulting with a coating specialist can aid in identifying the most appropriate product for a given application.
Question 5: What are the long-term cost implications associated with this type of product?
While the initial cost may be higher, the long-term benefits, including reduced maintenance frequency, extended service life, and minimized downtime, often result in significant cost savings compared to conventional alternatives.
Question 6: How can the environmental impact be minimized when using surface coatings?
Selecting low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations, implementing proper application techniques to minimize waste, and adhering to recommended disposal procedures can significantly reduce the environmental footprint.
In conclusion, the product represents a strategic investment when superior performance, durability, and longevity are paramount. Understanding its characteristics and proper application techniques is essential for maximizing its benefits.
The subsequent section will address case studies illustrating successful applications and demonstrating the tangible benefits.
Conclusion Regarding High-Performance Coating Solutions
This exploration of “finish master paint” has illuminated its critical role in achieving durable, aesthetically pleasing, and protective surfaces. The analysis has underscored the importance of material selection, application techniques, and environmental considerations in maximizing the long-term performance of these specialized products. Cost considerations, both initial and life-cycle, have been presented as crucial factors in informed decision-making.
The enduring value of these product solutions lies in their capacity to extend asset lifespans, reduce maintenance burdens, and enhance overall functionality. Continued advancements in coating technology offer further potential for improved performance, sustainability, and economic efficiency. Therefore, meticulous evaluation and diligent implementation are imperative for harnessing the full potential of these coating advancements in any application.