The entity is a business, specifically a corporation, engaged in the provision of specialized surface treatment services for metallic components. These services enhance the durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal of metal parts across diverse industries.
Such organizations play a vital role in manufacturing supply chains. Their services are crucial for extending the lifespan of metal products, improving their performance in harsh environments, and meeting stringent industry standards. The historical context of these operations is rooted in the evolution of materials science and the growing demand for high-quality, long-lasting metal goods.
The following analysis will delve into specific aspects of operations, including service offerings, quality control measures, industry compliance, and potential areas for growth and innovation.
Operational Best Practices
The subsequent guidelines aim to promote efficiency and uphold quality benchmarks within specialized surface treatment operations. These recommendations are intended for implementation by personnel at all levels.
Tip 1: Implement Rigorous Pre-Treatment Protocols. Inadequate surface preparation compromises the adhesion and longevity of applied coatings. Thorough cleaning, degreasing, and etching are essential prerequisites for optimal results.
Tip 2: Maintain Precise Control of Bath Chemistry. Fluctuations in chemical concentrations can significantly impact coating thickness, uniformity, and performance characteristics. Regular monitoring and adjustment of bath parameters are crucial.
Tip 3: Optimize Process Parameters. Factors such as current density, voltage, temperature, and immersion time directly influence the quality of the finished product. Establishing and adhering to validated parameter ranges is paramount.
Tip 4: Employ Regular Equipment Calibration and Maintenance. Properly functioning equipment ensures consistent process control and minimizes the risk of defects. Scheduled maintenance and calibration procedures are indispensable.
Tip 5: Conduct Comprehensive Quality Assurance Inspections. Implementing multi-stage inspections, including visual examination, thickness measurement, and adhesion testing, is vital for identifying and rectifying deficiencies.
Tip 6: Prioritize Employee Training and Certification. Highly skilled personnel are essential for executing complex processes and maintaining quality standards. Comprehensive training programs and industry certifications are highly recommended.
Tip 7: Uphold Stringent Environmental Compliance. Surface treatment processes often involve hazardous materials. Strict adherence to environmental regulations, including waste management protocols, is non-negotiable.
Adherence to these guidelines contributes to enhanced product quality, reduced operational costs, and minimized environmental impact. Continuous improvement through process optimization and employee development remains a critical objective.
The following sections will elaborate on specific industry standards and emerging technologies shaping the future of metal finishing operations.
1. Surface Preparation Quality
Surface preparation quality is a foundational element for entities engaged in specialized surface treatments. This process directly influences the efficacy and longevity of subsequent finishing applications, making it a critical determinant of overall product performance and customer satisfaction. This exploration elucidates key facets that contribute to superior surface preparation.
- Contaminant Removal
Effective removal of contaminants, such as oils, grease, scale, and rust, is paramount. Residual contaminants impede coating adhesion and promote premature failure. Processes like alkaline cleaning, acid etching, and abrasive blasting are employed to achieve a clean substrate. Insufficient contaminant removal leads to blistering, peeling, and compromised corrosion protection.
- Surface Profiling
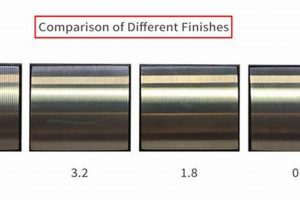
Creating an appropriate surface profile, or roughness, enhances mechanical bonding between the substrate and the coating. Techniques such as grit blasting or chemical etching generate microscopic anchor points for the finish. An inadequate profile results in poor adhesion and reduced durability, while an excessively rough profile can increase coating consumption and create aesthetic imperfections.
- Material Compatibility
Selecting surface preparation methods compatible with the substrate material is crucial. Acid etching, for example, may be suitable for steel but detrimental to aluminum. Similarly, abrasive blasting parameters must be adjusted based on the substrate’s hardness and sensitivity. Incompatible preparation methods can induce surface damage, alter material properties, and compromise the integrity of the finished product.
- Process Control & Monitoring
Maintaining rigorous process control and implementing robust monitoring protocols are essential for consistent surface preparation quality. Monitoring parameters such as bath chemistry, abrasive media size, blast pressure, and cleaning solution temperature ensures that the desired surface characteristics are achieved. Lack of process control leads to variability in surface preparation, resulting in inconsistent coating performance and potential product defects.
These facets underscore the importance of meticulous attention to detail throughout the surface preparation process. The success of specialized surface treatment operations relies heavily on the ability to consistently achieve optimal surface conditions, ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of the finished product.
2. Process Control Precision
Precision in process control is an indispensable attribute for any entity offering specialized surface treatments. In the context of metal finishing, deviations from established parameters during cleaning, coating, or curing phases can yield products failing to meet performance specifications. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: uncontrolled variations in chemical bath concentrations, temperature, voltage, or dwell times result in inconsistent coating thickness, adhesion, or corrosion resistance. Therefore, integrating precise process control mechanisms constitutes a fundamental component of successful metal finishing operations.
The practical significance of this lies in mitigating risks and maximizing efficiency. For example, variations in electroplating bath chemistry, if unchecked, lead to non-uniform deposition and potential substrate embrittlement. Implementing continuous monitoring systems and automated adjustments ensures consistent bath composition. Similarly, in powder coating applications, precise control over oven temperature and conveyor speed is essential for proper curing and achieving the desired finish properties. Real-world examples highlight the costs associated with neglecting process control: rework, scrap, warranty claims, and damage to reputation. Conversely, embracing process control precision contributes to enhanced product quality, reduced material waste, and increased throughput.
In conclusion, process control precision is not merely an operational detail but a strategic imperative. Challenges in achieving this include initial capital investment in advanced monitoring equipment, the need for skilled technicians capable of interpreting data and making adjustments, and the ongoing commitment to process validation and continuous improvement. However, the benefits of consistent product quality, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction outweigh these challenges, solidifying process control precision as a key differentiator in a competitive market.
3. Equipment Maintenance Standards
Adherence to rigorous equipment maintenance standards directly influences the operational efficiency and product quality. Specialized surface treatment processes rely on complex machinery to achieve precise and consistent results. Failure to maintain this equipment adequately results in process variability, increased downtime, and compromised product integrity. The entity’s ability to deliver services that meet industry specifications is inextricably linked to the proactive maintenance of its operational assets. The significance lies in preventing breakdowns, minimizing production disruptions, and ensuring consistent coating quality, essential for industries where component performance is critical.
Consider electroplating lines: a malfunctioning rectifier results in inconsistent current density, leading to variations in coating thickness and adhesion. Similarly, in powder coating operations, poorly maintained spray guns cause uneven powder distribution, resulting in cosmetic defects and compromised corrosion protection. Establishing and adhering to preventive maintenance schedules, including regular inspections, lubrication, component replacements, and performance calibrations, directly mitigates these risks. Real-world application involves integrating a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) to track maintenance activities, schedule preventive tasks, and manage spare parts inventory. This enhances the overall effectiveness of the maintenance program and provides data-driven insights for optimizing maintenance strategies.
In summation, stringent equipment maintenance standards are not merely a cost center but a strategic investment in operational excellence. The challenges lie in balancing the costs of preventive maintenance with the potential costs of equipment failure and production disruption. Overcoming these challenges requires a commitment to proactive maintenance practices, skilled maintenance personnel, and a comprehensive maintenance management system. The long-term benefits of reduced downtime, improved product quality, and enhanced operational efficiency justify the resources invested in maintaining equipment to the highest standards, safeguarding its competitive position.
4. Compliance & Sustainability
Compliance with environmental regulations and a commitment to sustainable practices are inseparable facets of responsible business operation. Regulatory adherence minimizes legal and financial risks while safeguarding public health and environmental integrity. Sustainability efforts, exceeding mere compliance, reduce resource consumption, minimize waste generation, and lower the overall environmental footprint. In the context of surface treatment operations, the selection of less hazardous chemicals, implementation of water conservation measures, and adoption of energy-efficient technologies are examples of sustainable actions. The cause-and-effect relationship is direct: proactive environmental management enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs associated with waste disposal and regulatory penalties, and cultivates a positive brand image. These efforts attract environmentally conscious customers and investors. The importance of environmental stewardship cannot be overstated: it reflects an organizations commitment to ethical business practices and long-term sustainability. Real-life examples showcase organizations that invest in closed-loop water treatment systems, significantly reducing water consumption and wastewater discharge. Others replace hazardous solvents with environmentally friendly alternatives, minimizing worker exposure and air emissions. These actions demonstrate tangible benefits for both the business and the environment. The practical significance lies in the ability to create a more resilient and responsible operation.
Further analysis reveals the economic benefits associated with embracing sustainable practices. Waste minimization programs reduce disposal costs and generate revenue through recycling. Energy-efficient technologies lower energy consumption and utility bills. Furthermore, a strong environmental track record enhances access to capital and strengthens relationships with stakeholders. A company committed to environmental excellence attracts top talent and builds stronger customer loyalty. Practical applications include implementing life cycle assessments to identify environmental hotspots and optimize product design for reduced environmental impact. Collaborating with suppliers to promote sustainable sourcing practices strengthens the supply chain and minimizes environmental risks. Transparent reporting of environmental performance demonstrates accountability and builds trust with stakeholders.
In conclusion, compliance and sustainability are not merely regulatory requirements but core components of responsible and successful enterprise. Challenges in achieving these goals include initial capital investments in cleaner technologies, the need for ongoing employee training, and the complexity of navigating evolving environmental regulations. However, the long-term benefits, including reduced costs, enhanced reputation, and a positive contribution to society, outweigh these challenges. Organizations that prioritize compliance and sustainability demonstrate a commitment to ethical business practices and long-term value creation.
5. Employee Skill Development
Employee skill development represents a critical investment for any organization operating in specialized technical domains. For entities like surface treatment companies, the proficiency of its workforce directly correlates with product quality, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. A robust employee skill development program is essential for ensuring that personnel possess the necessary expertise to execute complex processes, maintain equipment, and adapt to evolving industry standards. The following outlines key facets of this critical area.
- Technical Proficiency in Surface Treatment Processes
This facet emphasizes the acquisition of in-depth knowledge and practical skills related to various surface treatment techniques. Employees require comprehensive training in processes such as electroplating, anodizing, powder coating, and chemical conversion. This training encompasses an understanding of process parameters, chemical interactions, and troubleshooting techniques. For example, technicians must be proficient in adjusting bath chemistry, monitoring voltage and current, and diagnosing coating defects. Organizations commonly implement apprenticeship programs, on-the-job training, and external certifications to enhance technical proficiency. The impact of this training is seen in reduced rework rates, improved coating quality, and enhanced process optimization.
- Equipment Operation and Maintenance Expertise
This element concentrates on the development of skills necessary for operating and maintaining complex surface treatment equipment. Employees must be trained in the proper operation, troubleshooting, and preventative maintenance of equipment such as rectifiers, pumps, spray booths, and curing ovens. This training includes understanding equipment manuals, performing routine inspections, and conducting repairs. A skilled maintenance technician, for instance, can diagnose and repair a malfunctioning pump, preventing a line shutdown and minimizing production delays. Organizations regularly provide equipment-specific training, vendor-led workshops, and certification programs to build equipment operation and maintenance expertise. This expertise directly contributes to reduced equipment downtime, improved operational efficiency, and extended equipment lifespan.
- Quality Control and Inspection Capabilities
This aspect focuses on developing the ability to conduct thorough quality control inspections at various stages of the surface treatment process. Employees must be proficient in using inspection tools such as thickness gauges, adhesion testers, and corrosion testing chambers. They also require a strong understanding of quality standards and acceptance criteria. Quality control inspectors, for example, must be able to accurately measure coating thickness, assess adhesion strength, and identify cosmetic defects. Organizations provide training in quality control methodologies, statistical process control, and relevant industry standards such as ISO 9001. Enhancing quality control capabilities leads to reduced product defects, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced regulatory compliance.
- Environmental Compliance and Safety Awareness
This element focuses on ensuring that employees are knowledgeable about environmental regulations and safety protocols. Employees must be trained in handling hazardous materials, managing waste streams, and responding to emergencies. This training includes understanding regulatory requirements such as those outlined by the EPA and OSHA. Technicians who handle hazardous chemicals, for instance, must be trained in proper handling procedures, personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, and spill response protocols. Organizations provide comprehensive safety training, conduct regular safety audits, and implement environmental management systems. Enhancing environmental compliance and safety awareness minimizes environmental risks, reduces worker injuries, and ensures adherence to regulatory requirements.
These facets collectively underscore the strategic importance of employee skill development. The entity that prioritizes employee skill enhancement realizes improvements across various operational parameters. Continuous investment in employee skill development positions the company for sustained competitiveness and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding processes and capabilities. These questions are intended to provide clarity and inform decision-making.
Question 1: What range of metal substrates can be processed?
The entity possesses the capability to process a diverse range of metal substrates, including but not limited to steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. Each substrate requires tailored pre-treatment and finishing processes to ensure optimal adhesion and performance of the applied coating or treatment.
Question 2: What are the typical turnaround times for projects?
Turnaround times vary depending on project complexity, volume, and specific process requirements. Standard projects typically require a lead time of [X] days. Expedited services are available for urgent requirements, subject to capacity constraints and additional fees. Contacting project management directly allows for accurate assessment and scheduling.
Question 3: What quality control measures are in place?
Stringent quality control measures are implemented throughout the entire surface treatment process. These measures include incoming material inspections, in-process monitoring of chemical bath parameters, and final inspection of finished products. Testing methods include visual inspection, thickness measurement, adhesion testing, and corrosion resistance testing. Certified to ISO 9001.
Question 4: Is compliance with industry-specific standards ensured?
Compliance with relevant industry-specific standards is a fundamental aspect of operation. Processes are designed and executed to meet or exceed requirements outlined in standards such as ASTM, MIL-SPEC, and RoHS. Documentation and certifications are provided to verify compliance with applicable standards.
Question 5: What environmental practices are employed?
Responsible environmental practices are integrated into operational procedures. Measures are taken to minimize waste generation, conserve water, and reduce air emissions. The company adheres to all applicable environmental regulations and continuously seeks opportunities for improvement in its environmental performance.
Question 6: Are custom finishing solutions offered?
Custom finishing solutions are available to meet unique customer requirements. Engineering and technical teams collaborate with clients to develop tailored processes and coatings that address specific performance, aesthetic, and functional needs. Feasibility assessments are conducted to determine the viability of custom finishing solutions.
These responses provide a concise overview of key aspects of our service offerings. More detailed information can be obtained by contacting customer service or consulting technical documentation.
The subsequent article sections will further discuss advanced techniques and emerging trends.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has dissected key operational facets critical to the success of surface treatment entities. This analysis encompassed essential elements such as meticulous surface preparation, rigorous process control, diligent equipment maintenance, unwavering compliance with regulations, and continuous employee skill development. Each of these components contributes directly to the quality, durability, and performance characteristics of finished metallic components, ultimately influencing customer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
Organizations committed to these principles demonstrate a dedication to excellence. The ability to consistently deliver high-quality surface treatment solutions is paramount in a demanding industrial landscape. Future success hinges on embracing innovation, investing in advanced technologies, and maintaining an unwavering commitment to ethical and sustainable business practices. Continued refinement of these operational practices will secure a position as a leader in the field.