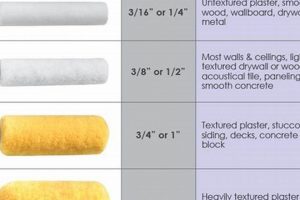
A protective and often decorative coating applied to exterior surfaces, it shields materials from environmental elements. For instance, a residence exposed to harsh sunlight may benefit from a coating formulated with UV-resistant pigments.
Its significance lies in extending the lifespan of substrates by mitigating damage from moisture, temperature fluctuations, and biological growth. Historically, formulations relied on natural oils and pigments, evolving over time with advancements in polymer chemistry to offer enhanced durability and performance.
The subsequent sections will delve into the various types available, application techniques, and factors to consider when selecting the appropriate coating for a specific exterior project.
Tips Regarding Exterior Coating Application
Achieving a long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing exterior coating requires careful planning and execution. The following are several critical considerations for optimal results.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount. All surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned, removing dirt, mildew, loose paint, and any other contaminants. Failure to properly prepare the surface will compromise adhesion and longevity.
Tip 2: Select the Correct Primer. Primer selection should be based on the substrate material and the type of coating being applied. Using an incompatible primer can lead to premature coating failure. For example, bare wood requires a primer designed to seal the porous surface and prevent moisture absorption.
Tip 3: Choose a Coating Appropriate for the Climate. Environmental conditions significantly impact coating performance. Coastal areas require coatings with enhanced salt resistance, while regions with extreme temperature fluctuations necessitate flexible coatings that can withstand expansion and contraction.
Tip 4: Apply Coating in Optimal Weather Conditions. Avoid applying coating in direct sunlight, high humidity, or when rain is imminent. Ideal conditions typically involve moderate temperatures and low humidity, which promote proper drying and curing.
Tip 5: Use High-Quality Application Tools. The quality of brushes, rollers, and spray equipment directly affects the final appearance. Investing in professional-grade tools will ensure a uniform and even application.
Tip 6: Apply Two Thin Coats Rather Than One Thick Coat. Multiple thin coats provide better coverage, adhesion, and durability compared to a single thick coat, which is prone to cracking and sagging.
Tip 7: Allow Adequate Drying Time Between Coats. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended drying times is crucial for proper curing and optimal coating performance. Rushing the process can lead to adhesion problems and a compromised appearance.
Proper execution of these tips will result in a durable and visually appealing exterior coating, enhancing both the protection and aesthetic value of the structure.
The subsequent sections will explore specific coating types and their suitability for various exterior applications.
1. Durability and Resilience
Durability and resilience are paramount considerations when selecting an exterior coating. The external environment presents a continuous barrage of challenges, demanding a coating that can withstand physical stresses and maintain its protective properties over extended periods. A lack of inherent strength leads to premature failure, necessitating frequent and costly recoating.
- Resistance to Abrasion
Exterior surfaces are constantly subjected to abrasion from wind-borne particles, foot traffic (on decks and steps), and contact with objects. A durable coating resists scratching and scuffing, preserving its aesthetic appearance and protective barrier. An example includes coatings on high-traffic areas of commercial buildings needing to withstand frequent cleaning and accidental impacts.
- Impact Resistance
Impact resistance is the ability to withstand sudden blows or impacts without cracking or chipping. This is particularly important in areas prone to hail, falling debris, or accidental contact with equipment. Industrial facilities often specify high-impact coatings to protect against damage from moving equipment and potential collisions.
- Flexibility and Elongation
Exterior substrates, such as wood and metal, expand and contract with temperature and humidity fluctuations. A resilient coating possesses sufficient flexibility and elongation to accommodate these movements without cracking or losing adhesion. Coatings on metal siding, which experiences significant thermal expansion, must exhibit high elongation to prevent stress fractures.
- Chemical Resistance
Exposure to pollutants, acid rain, and cleaning agents can degrade exterior coatings over time. Chemical resistance is the ability to withstand these corrosive substances without experiencing discoloration, blistering, or loss of protective properties. Facilities near industrial areas often require coatings with specialized chemical resistance to withstand airborne pollutants and chemical runoff.
The intertwined attributes of abrasion resistance, impact resistance, flexibility, and chemical resistance collectively define the durability and resilience of an exterior coating. Selecting a product that effectively addresses these challenges is critical for ensuring long-term protection, aesthetic preservation, and reduced maintenance costs. The suitability of a specific coating is determined by the specific demands of the exterior environment and the substrate material.
2. Weather Resistance
Exterior coatings’ ability to withstand environmental elements directly dictates their longevity and performance. Weather resistance, in this context, encompasses a multifaceted defense against moisture, solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, and wind-driven abrasion. The consequences of inadequate weather resistance are manifested through coating failures such as blistering, cracking, fading, and eventual delamination. For example, a coating applied to a coastal property lacking saltwater resistance will likely exhibit accelerated corrosion and degradation compared to a coating specifically formulated for such environments.
Understanding weather resistance facilitates informed selection of coating materials. Formulations incorporating UV absorbers mitigate pigment degradation caused by sunlight, preserving color integrity over time. Similarly, coatings with enhanced flexibility accommodate substrate expansion and contraction resulting from temperature changes, preventing cracking and maintaining adhesion. Application techniques also factor into weather resistance; proper surface preparation ensures optimal bonding, reducing the risk of moisture intrusion and subsequent coating failure. The performance of a house located in Arizona demonstrates this effect. The same coating type applied to a house in Arizona will degrade faster if the pigments aren’t UV-resistant compared to the same coating in a moderate-UV climate.
Ultimately, weather resistance is an indispensable characteristic of any exterior coating, directly influencing its effectiveness in protecting the underlying substrate and preserving aesthetic value. Challenges persist in developing coatings that offer comprehensive protection across diverse climatic conditions. However, advancements in materials science continue to yield solutions that enhance weather resistance, contributing to the long-term performance and sustainability of exterior structures.
3. Surface Adhesion
Surface adhesion is a foundational property directly influencing the longevity and performance of any exterior coating. It represents the measure of the coating’s ability to bind securely to the substrate, resisting separation under various environmental stresses. Inadequate adhesion leads to premature failure, manifested as peeling, blistering, or flaking, which compromises both the aesthetic appeal and the protective function of the exterior coating. A common example is seen with improperly prepared wood surfaces; coatings applied to untreated, weathered wood are prone to early failure due to poor adhesion. This necessitates frequent recoating, increasing maintenance costs and potentially exposing the substrate to damage from moisture and UV radiation.
Achieving optimal surface adhesion requires careful consideration of several factors, including surface preparation, primer selection, and coating compatibility. Thorough cleaning to remove contaminants, such as dirt, grease, and mildew, is essential for creating a receptive surface. Primers act as an intermediary layer, promoting adhesion between the substrate and the coating, while also providing additional benefits, such as sealing porous surfaces or inhibiting corrosion. Selecting a primer compatible with both the substrate and the coating is crucial; incompatibility can lead to adhesion problems. Furthermore, applying the coating under appropriate environmental conditions, such as moderate temperature and low humidity, supports proper curing and bonding.
In conclusion, surface adhesion is an indispensable element of a successful exterior coating application. Its importance stems from its direct impact on the coating’s ability to withstand environmental stresses and provide long-term protection. While challenges remain in achieving consistent adhesion across diverse substrates and environmental conditions, advancements in materials science and application techniques continue to improve coating performance. A meticulous approach to surface preparation, primer selection, and application, combined with an understanding of the underlying principles of adhesion, is paramount for maximizing the service life and effectiveness of any exterior coating.
4. UV Protection
Ultraviolet (UV) protection is a critical attribute of any exterior coating. Solar radiation, particularly in the UV spectrum, induces photochemical degradation in coating components, leading to premature failure. The inclusion of UV-protective additives is therefore vital for maintaining the aesthetic and protective qualities of exterior finishes.
- Pigment Stability
UV radiation degrades pigments, causing fading and color shift. Coatings formulated without adequate UV protection exhibit noticeable color deterioration over time, especially in highly exposed areas. For instance, red and yellow pigments are particularly susceptible to UV degradation, requiring stabilization through the addition of UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS). The use of inorganic pigments, such as iron oxides, offers inherent UV resistance, but may limit color choices.
- Resin Degradation
The polymeric resins that bind the coating together are also vulnerable to UV damage. UV exposure can cause chain scission, leading to embrittlement, cracking, and loss of adhesion. UV absorbers function by absorbing UV radiation and dissipating it as heat, protecting the underlying resin. Clear coatings, lacking pigments to block UV light, rely heavily on UV absorbers to prevent degradation. The durability of a clear coat on a wooden door, for example, depends heavily on its UV protection additives.
- Chalking Resistance
Chalking, the formation of a powdery residue on the coating surface, is a common consequence of UV-induced degradation. As the resin breaks down, pigment particles become unbound and migrate to the surface. Chalking not only detracts from the appearance but also reduces the coating’s thickness and protective capabilities. Coatings with high chalking resistance maintain their integrity and require less frequent maintenance. Consider the difference in appearance between a chalk-resistant coating on a public building versus a standard coating after years of sun exposure.
- Gloss Retention
UV exposure can cause a reduction in gloss, resulting in a dull or matte finish. This is due to surface roughening caused by the degradation of the coating’s top layer. Gloss retention is an important aesthetic consideration, particularly for high-gloss coatings used on doors or trim. Coatings with good UV protection maintain their original sheen longer, preserving the desired aesthetic appearance. The difference in the appearance of a coating on a building’s trim after several years, depending on its UV protection, is a direct reflection of this facet.
UV protection is an essential design element for exterior coatings to provide long-term performance and visual appeal. Selection of quality, UV-resistant components, combined with suitable application methods, ensures that exterior coatings will endure exposure to sunlight and other environmental stresses.
5. Color Retention
Color retention, in the context of exterior coatings, represents the ability of a coating to maintain its original hue and saturation over an extended period of exposure to environmental elements. It is a crucial performance characteristic directly influencing the aesthetic lifespan and perceived value of a coated structure. A failure in color retention manifests as fading, chalking, or discoloration, diminishing the visual appeal and potentially impacting property valuation. For instance, a vibrant red barn, once a focal point of the landscape, gradually turning to a muted pink illustrates the tangible effects of inadequate color retention.
The degradation of color in exterior coatings is primarily driven by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight, which breaks down the chemical bonds within pigment molecules. Higher-quality coatings incorporate UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to mitigate this process, effectively prolonging color vibrancy. Pigment selection also plays a critical role; inorganic pigments such as iron oxides generally exhibit superior UV resistance compared to organic pigments. Furthermore, the binder system, the component holding the pigments together, influences color retention. Binders with poor UV stability can yellow or degrade, affecting the perceived color of the coating. The difference in color fade between a dark-colored house with proper pigments and one with inexpensive pigments after a couple of years shows the importance of UV resistant pigments.
In summary, color retention is a non-negotiable attribute of a quality exterior coating. Its preservation relies on a confluence of factors, including UV protection additives, pigment selection, and binder stability. While achieving perfect color retention is challenging due to the relentless nature of environmental exposure, advancements in coating technology continue to improve performance. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of color degradation and selecting coatings formulated to resist these processes are essential for ensuring long-term aesthetic satisfaction and structural value.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Exterior Coatings
The following addresses common inquiries and clarifies aspects of exterior coatings, providing objective information for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What constitutes the most critical factor in determining the lifespan of an exterior coating?
Surface preparation fundamentally dictates coating longevity. Thorough cleaning and removal of contaminants ensures proper adhesion, preventing premature failure. Ignoring proper preparation compromises the integrity of even the highest-quality coating.
Question 2: How does climate influence the selection of an appropriate coating?
Climatic conditions exert significant stress on coatings. Coastal environments necessitate salt-resistant formulations. Regions with extreme temperature fluctuations require coatings with enhanced flexibility to accommodate expansion and contraction. Matching coating properties to the prevailing climate is crucial.
Question 3: What is the purpose of a primer in an exterior coating system?
Primers serve as an intermediary layer, promoting adhesion between the substrate and the topcoat. They also seal porous surfaces, prevent moisture intrusion, and inhibit corrosion. Selecting a compatible primer is essential for system-wide performance.
Question 4: How does UV radiation affect exterior coatings?
UV radiation degrades coating components, causing fading, chalking, and embrittlement. Coatings formulated with UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) mitigate these effects, preserving color and extending coating life.
Question 5: What is the significance of flexibility in an exterior coating?
Flexibility enables the coating to accommodate substrate movement caused by temperature and humidity changes. Coatings lacking sufficient flexibility are prone to cracking and loss of adhesion, compromising their protective function.
Question 6: How should one determine the appropriate number of coating layers to apply?
Applying two thin coats generally provides better coverage, adhesion, and durability compared to a single thick coat. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended application rates and drying times is crucial for optimal performance.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of exterior coatings is essential for achieving long-term protection and aesthetic satisfaction.
The subsequent section will explore advanced techniques for specialized exterior coating applications.
Conclusion
This exploration has delineated the critical attributes of effective exterior coatings, ranging from durability and weather resistance to UV protection and color retention. Surface preparation, primer selection, and climate considerations have been identified as paramount factors influencing the long-term performance of these systems. The selection and proper application of a suitable “outdoor paint finish” remains a significant undertaking.
The presented information is intended to inform prudent decision-making when specifying and applying exterior coatings. Prioritizing coating characteristics aligned with specific environmental demands and substrate properties will ensure optimal protection, extended aesthetic appeal, and ultimately, a reduction in long-term maintenance costs. Continued advancements in coating technologies promise to further enhance the durability and performance of exterior protection systems.