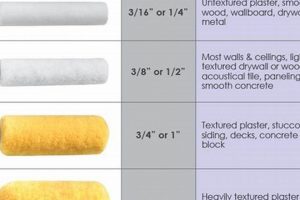
The selection applied to the overhead surface impacts both aesthetic appeal and functional performance. The substance’s texture and sheen influence light reflection and perceived space within a room. For example, a flat option minimizes imperfections and provides a uniform appearance, while a glossier option enhances brightness but can accentuate surface flaws.
Appropriate coating selection offers several advantages, including enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, crucial in areas prone to humidity like bathrooms and kitchens. Historically, coarser, less refined options were employed primarily for utilitarian purposes. Modern formulations provide a wider range of textures and functionalities, allowing for greater design flexibility and improved longevity. These advancements cater to the demands of contemporary architectural and interior design.
The subsequent sections will explore specific characteristics, application techniques, and considerations for selecting the optimal surface application to upper interior surfaces. Factors such as room size, lighting conditions, and desired aesthetic outcomes will be addressed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Application Guidance
Effective application requires careful consideration of several factors to achieve a professional and lasting result.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation: Ensure the surface is clean, dry, and free from dust, grease, or loose particles. Repair any imperfections such as cracks or holes with appropriate patching compound. Failure to adequately prepare the surface will compromise adhesion and the final aesthetic.
Tip 2: Priming: Apply a primer formulated for interior surfaces. Priming enhances adhesion, promotes uniform color, and seals porous surfaces, thereby reducing the amount of topcoat required. The selection of a suitable primer is crucial for optimal results.
Tip 3: Application Method: Employ a roller with a nap appropriate for the texture being used. For smooth applications, use a short-nap roller; for textured applications, a longer nap may be necessary. Maintain consistent pressure and overlap each stroke slightly to avoid streaking.
Tip 4: Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation during and after application. Proper ventilation facilitates drying and minimizes the buildup of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This step is critical for both air quality and safety.
Tip 5: Number of Coats: Apply at least two coats, allowing sufficient drying time between each. Multiple coats provide better coverage, durability, and color uniformity. Follow the manufacturers recommendations regarding drying times.
Tip 6: Cutting In: Before rolling, use a brush to “cut in” along the edges of the surface where it meets walls, trim, or other features. This creates a clean, crisp line and prevents the roller from marking adjacent surfaces.
Tip 7: Lighting Conditions: Evaluate the surface under different lighting conditions during and after application. This allows for the identification and correction of any imperfections or inconsistencies that may not be visible under normal lighting.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes a professional-grade finish, enhancing both the appearance and longevity of the treated surface.
The concluding section will summarize key considerations and provide resources for further exploration.
1. Light Reflectance
Light reflectance, in the context of overhead surface coatings, defines the proportion of light reflected by a given surface. The degree of reflectance directly influences perceived brightness, space, and energy efficiency within an environment. Therefore, selection significantly impacts the ambiance and functionality of a room.
- Light Reflectance Value (LRV)
LRV quantifies the percentage of visible light reflected from a surface, ranging from 0% (absolute black) to 100% (perfect reflector). Higher LRV materials contribute to brighter spaces, reducing the reliance on artificial illumination and potentially lowering energy consumption. In smaller rooms or spaces with limited natural light, selecting coatings with higher LRV is particularly beneficial.
- Sheen Level and Light Diffusion
Sheen level, from flat to gloss, affects light diffusion. Flat options minimize glare and hide imperfections but reflect less light overall. Gloss options, while enhancing brightness, can accentuate surface flaws and create distracting reflections. Selecting the appropriate sheen depends on the room’s intended use and existing architectural features.
- Color Pigmentation and Reflectance
Color pigmentation significantly impacts reflectance. Lighter colors inherently possess higher LRVs, reflecting more light than darker shades. Using lighter colors on overhead surfaces can contribute to a more open and airy feel, particularly in rooms with low ceilings. Conversely, darker colors absorb more light, potentially creating a more intimate and enclosed atmosphere.
- Impact of Texture on Light Scattering
Surface texture affects the way light is scattered. Smooth surfaces tend to reflect light more uniformly, while textured surfaces diffuse light, reducing glare and creating a softer ambiance. Considerations for texture should align with the desired aesthetic and the presence of other reflective surfaces within the room.
The interplay of LRV, sheen level, color pigmentation, and texture dictates the overall light reflectance properties of the application. Selecting the optimal combination maximizes the functional and aesthetic benefits within a specific environment. Careful consideration of these factors ensures that the overhead surface contributes positively to the overall lighting scheme and perceived spatial dimensions.
2. Moisture Resistance
The moisture resistance of a ceiling application is paramount, particularly in environments with elevated humidity levels. Failure to provide adequate moisture resistance can initiate a cascade of detrimental effects, including the growth of mold and mildew, compromising structural integrity, and necessitating costly repairs. For instance, in bathrooms and kitchens, where steam and condensation are prevalent, coatings lacking sufficient moisture barrier properties will allow water vapor to penetrate the substrate, leading to the aforementioned issues. In extreme cases, prolonged exposure can result in ceiling collapse. Choosing a product specifically formulated for high-humidity environments is therefore not merely an aesthetic consideration but a critical factor in preventing long-term structural damage.
The effectiveness of a coating’s moisture resistance is directly related to its chemical composition and application method. Coatings incorporating acrylic or epoxy resins typically exhibit superior moisture-blocking characteristics compared to those based on less robust formulations. Proper surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and the application of a moisture-resistant primer, further enhances the protective barrier. Furthermore, meticulous application, ensuring complete and uniform coverage, minimizes weak points where moisture penetration is likely to occur. Case studies involving improperly sealed ceilings in commercial kitchens have demonstrated the rapid proliferation of mold, leading to health code violations and business closures. These examples underscore the practical significance of selecting and applying products with verified moisture resistance.
In summary, moisture resistance is an indispensable attribute of any coating intended for use on upper interior surfaces, particularly in moisture-prone environments. Neglecting this aspect can lead to substantial structural damage, health hazards, and financial burdens. The careful selection of moisture-resistant products, coupled with proper application techniques, mitigates these risks and ensures the long-term durability and safety of the ceiling. This understanding is crucial not only for building professionals but also for homeowners seeking to maintain the integrity and value of their properties.
3. Surface Imperfections
The presence of surface imperfections on overhead surfaces directly influences the selection and application of coatings. Scratches, dents, nail pops, and uneven textures compromise the uniformity and aesthetic appeal of the intended effect. Coatings, therefore, must be chosen and applied strategically to either minimize the visibility of these flaws or, in some cases, conceal them entirely. The type and extent of the imperfections dictate the required preparation steps and the most suitable product to achieve the desired result. A ceiling with numerous small imperfections, for instance, may benefit from a heavily textured coating, whereas a surface with isolated, larger defects necessitates patching and sanding prior to any coating application.
The relationship is bidirectional: surface imperfections affect coating choice, and the coating itself can either accentuate or diminish these pre-existing conditions. High-gloss options, while offering durability and ease of cleaning, tend to highlight every irregularity, making them less suitable for imperfect surfaces. Conversely, flat options, by diffusing light, mask minor imperfections more effectively. Furthermore, the application technique plays a critical role. Improperly applied coating on an uneven surface can create noticeable inconsistencies, compounding the initial problem. A practical example is the common occurrence of hairline cracks in plaster ceilings of older homes. Simply applying a standard coating will often fail to conceal these cracks adequately. The recommended approach involves patching the cracks with a flexible compound, sanding the area smooth, and then applying a primer and a flat coating to minimize the visibility of any remaining imperfections.
Understanding the interplay between surface imperfections and coating selection is crucial for achieving a satisfactory result on overhead surfaces. Neglecting the initial assessment of the surface condition can lead to wasted materials, unsatisfactory aesthetics, and the need for costly rework. By carefully evaluating the type and severity of imperfections, and by choosing appropriate coatings and application techniques, the visual impact of these flaws can be minimized, resulting in a smoother, more aesthetically pleasing overhead surface. This understanding extends beyond purely aesthetic considerations, as it also influences the longevity and overall performance of the applied treatment, especially in environments prone to moisture or physical stress.
4. Application Method
The chosen application method directly dictates the quality and longevity of the surface treatment. The effectiveness of even the most advanced coatings is contingent upon proper execution during the application process. Inadequate techniques can lead to premature failure, compromised aesthetics, and increased maintenance costs. For overhead surfaces, gravity presents a unique challenge, demanding precision and specialized tools to ensure uniform coverage and prevent sagging or dripping. The selection of brushes, rollers, and spraying equipment, coupled with the applicator’s skill, significantly influences the final outcome. For instance, using an inappropriate roller nap can result in uneven texture and visible roller marks, detracting from the intended finish. A lack of proper surface preparation or inadequate priming will compromise adhesion, leading to peeling and flaking. Real-world examples abound, from commercial buildings with poorly applied coatings exhibiting widespread mold growth to residential properties marred by unsightly streaks and blemishes. These failures underscore the critical importance of mastering proper application methods.
Specific techniques, such as back-rolling, are often employed to ensure even distribution and penetration of the substance into the substrate. Back-rolling involves lightly re-rolling a freshly coated area to eliminate roller marks and improve adhesion. This technique is particularly crucial for textured coatings, where uniform coverage is essential for achieving the desired aesthetic effect. Furthermore, the use of specialized equipment, such as airless sprayers, can provide a smoother, more consistent application, particularly on large or complex surfaces. However, airless spraying requires careful masking and ventilation to prevent overspray and ensure operator safety. The prevailing environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity, also impact the application process. High humidity can slow drying times and promote the growth of mildew, while extreme temperatures can affect the viscosity and flow of the coating, making it more difficult to apply evenly. Adherence to manufacturer guidelines regarding environmental conditions is therefore essential for optimal results.
In conclusion, the application method is an indispensable component of a successful coating outcome. The selection of appropriate tools and techniques, combined with meticulous attention to detail and adherence to manufacturer recommendations, ensures a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting result. Challenges associated with overhead surfaces, such as gravity and limited accessibility, necessitate a higher degree of skill and precision. Recognizing the practical significance of the application method, and investing in proper training and equipment, is paramount for achieving the desired outcome and avoiding costly mistakes. The link between application method and the final result is undeniable, making it a critical consideration for both professionals and homeowners alike.
5. Color Uniformity
Achieving consistent color on overhead surfaces is a critical component of a successful coating application. Variations in color across a ceiling, even subtle ones, can disrupt the visual harmony of a space and draw unwanted attention to the surface itself. Several factors contribute to color variations, including inadequate mixing of the coating prior to application, inconsistent application techniques, and variations in substrate porosity. Substrate porosity plays a significant role, as porous surfaces absorb more coating, leading to a darker shade than non-porous areas. An example can be seen in newly constructed homes where gypsum board seams, if not properly sealed, absorb more coating, resulting in visible color inconsistencies. Color consistency, or lack thereof, directly impacts the perceived quality of the space, with non-uniformity often perceived as a sign of amateur workmanship or low-quality materials. The practical significance lies in its influence on the overall aesthetic and psychological impact of the interior environment.
To mitigate color inconsistencies, several preventative measures are necessary. Thorough mixing of the coating prior to application is paramount to ensure uniform pigment distribution. Furthermore, the application technique must be consistent across the entire surface, maintaining a uniform film thickness. This can be achieved through proper roller selection, even pressure application, and consistent overlapping of strokes. Priming the surface before applying the coating reduces substrate porosity variations and promotes a more consistent color absorption. In situations where color uniformity is of utmost importance, it may be necessary to apply multiple coats of the coating, ensuring sufficient coverage and minimizing the impact of any underlying substrate variations. The coating batch numbers should also be checked. Utilizing different production batch numbers can have a visible color shift.
In summary, color consistency is a crucial attribute of a professionally applied coating on overhead surfaces. Achieved through careful preparation, consistent application, and the use of appropriate materials, color uniformity contributes significantly to the visual appeal and perceived quality of a space. Ignoring this aspect can result in distracting inconsistencies that detract from the overall aesthetic and undermine the intended design. Understanding the factors that influence color consistency and implementing strategies to mitigate variations are essential for achieving a satisfactory result. The challenges associated with achieving uniform color highlight the need for meticulous attention to detail and adherence to best practices throughout the application process.
6. Long-Term Durability
The longevity of a ceiling application is directly contingent upon its inherent resistance to degradation over extended periods. Several factors influence this, including environmental conditions, the quality of the substances used, and the adherence to proper application techniques. A coating that exhibits poor durability will necessitate frequent repairs or reapplication, incurring additional costs and disruptions. Conversely, a durable selection minimizes these maintenance demands, preserving the aesthetic appeal and protecting the underlying substrate for a prolonged duration. The connection is causal: substandard durability leads to accelerated deterioration, while robust durability yields prolonged performance. For instance, coatings in high-humidity environments, such as bathrooms, must withstand persistent moisture exposure to prevent blistering, peeling, and mold growth. Failure to select a durable, moisture-resistant option will inevitably result in premature failure.
Long-term durability is not merely an abstract attribute; it is a critical component of a cost-effective and sustainable solution for overhead surfaces. Considerations extend beyond the initial application. Durable substance reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions over time as less frequent repainting is required. From a practical perspective, a durable substance translates into reduced lifecycle costs for building owners. Consider the example of a commercial office building. A durable ceiling application, resistant to yellowing and staining, reduces the need for disruptive and costly re-coatings, minimizing downtime and preserving the professional appearance of the workspace. Understanding this connection enables informed decision-making, prioritizing long-term value over short-term cost savings.
In conclusion, long-term durability is an indispensable attribute of a high-quality surface treatment. It extends beyond mere aesthetics, encompassing economic and environmental considerations. Selecting and applying durable substances ensures prolonged protection, reduces maintenance requirements, and minimizes lifecycle costs. The challenges associated with achieving long-term durability highlight the importance of proper material selection, meticulous application techniques, and a comprehensive understanding of the environmental factors that can impact coating performance. The ultimate goal is a surface that not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the space but also provides lasting protection and value.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ceiling Surface Applications
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, application, and maintenance of coatings for overhead surfaces. The information provided aims to clarify misconceptions and offer practical guidance for achieving optimal results.
Question 1: What is the optimal texture for residential bathrooms?
For residential bathrooms, a matte or eggshell texture is generally recommended. These textures minimize light reflection, concealing imperfections and reducing glare, which is particularly beneficial in smaller spaces. Furthermore, matte and eggshell surfaces exhibit enhanced moisture resistance compared to flatter options, mitigating the risk of mold and mildew growth.
Question 2: How does substrate preparation influence the outcome?
Proper substrate preparation is paramount to achieving a durable and aesthetically pleasing outcome. Thorough cleaning, patching of imperfections, and application of a primer are essential steps. Failure to adequately prepare the substrate compromises adhesion, promotes uneven color absorption, and reduces the overall lifespan of the application.
Question 3: What type of roller is best suited for smooth finishes?
For smooth finishes, a short-nap roller is typically recommended. Short-nap rollers minimize texture and prevent the creation of unwanted roller marks. Foam rollers can also be used to achieve exceptionally smooth surfaces. The choice of roller nap depends on the desired level of smoothness and the viscosity of the coating being applied.
Question 4: How does ventilation affect drying time and air quality?
Adequate ventilation is crucial for promoting rapid drying and minimizing the buildup of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Proper ventilation reduces the risk of the surface becoming tacky or developing imperfections during the drying process. Furthermore, it safeguards indoor air quality, mitigating potential health risks associated with prolonged exposure to VOCs.
Question 5: Are multiple coats necessary, even with high-quality coatings?
Multiple coats are generally recommended, even when using high-quality coatings. Multiple coats provide enhanced coverage, improved color uniformity, and increased durability. The number of coats required depends on the opacity of the coating and the color contrast between the coating and the underlying substrate.
Question 6: How should one address existing mold or mildew growth prior to re-coating?
Prior to re-coating, any existing mold or mildew growth must be thoroughly eradicated. This typically involves scrubbing the affected area with a bleach solution, followed by rinsing and drying. Failure to remove mold and mildew will result in its continued proliferation beneath the new surface, leading to recurring problems and potential health hazards.
These FAQs provide a foundation for understanding key aspects of ceiling surface treatments. Further research and consultation with professionals are recommended for addressing specific project requirements.
The subsequent section will explore advanced techniques and specialized coatings for unique architectural applications.
Conclusion
This discussion has examined the multifaceted nature of paint finish for ceiling, highlighting its critical role in influencing aesthetics, functionality, and long-term performance. Surface preparation, coating selection, application techniques, and environmental considerations have been addressed as essential factors contributing to a successful outcome. The impact of light reflectance, moisture resistance, and color uniformity on the overall quality and longevity of the treated surface has been emphasized.
The selection and implementation of appropriate treatments demand a comprehensive understanding of the variables involved. As architectural design evolves and material science advances, ongoing research and professional development are crucial for optimizing the performance and sustainability of overhead surfaces. Continued diligence in applying established best practices remains paramount in achieving lasting and visually compelling results.