Surface coatings applied to wooden furnishings, imparting both aesthetic appeal and protective qualities, enhance the substrate’s visual characteristics and longevity. Such treatments involve the application of various pigmented mediums, often including primers, color coats, and sealants, to create durable and visually appealing surfaces. For example, a dresser might undergo a multi-stage process involving sanding, priming, application of acrylic latex paint, and a final layer of polyurethane for enhanced scratch resistance.
The practice offers a method to revitalize older pieces, harmonize furniture with interior design schemes, and safeguard against environmental factors such as moisture and wear. Historically, these applications were often based on natural ingredients like milk and plant oils, while modern formulations leverage synthetic resins and polymers to achieve greater durability and a wider range of visual effects. The selection of appropriate methods and materials is crucial for achieving desired outcomes and ensuring the long-term integrity of the treated furniture.
Consequently, a detailed understanding of preparation techniques, application methods, and coating types is essential for achieving professional-quality results. Subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects such as surface preparation, paint selection criteria, and application techniques to equip readers with the necessary knowledge for successful furniture refinishing projects.
Essential Considerations for Painted Furniture Finishes
Achieving a durable and aesthetically pleasing result requires careful planning and execution. The following tips offer guidance on key aspects of the process.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount. Proper sanding, cleaning, and priming are crucial for adhesion and a smooth final coat. Failure to adequately prepare the surface will result in peeling, chipping, and an uneven appearance. For previously varnished surfaces, thorough sanding or chemical stripping is often necessary.
Tip 2: Select the Appropriate Paint Type. Different paint formulations possess varying characteristics in terms of durability, sheen, and application properties. Acrylic latex paints are commonly used for their ease of application and clean-up, while oil-based paints offer greater hardness and resistance to wear. Consider the intended use of the furniture and the desired aesthetic when making a selection.
Tip 3: Apply Multiple Thin Coats. Applying several thin coats of paint is preferable to a single thick coat, as it minimizes the risk of drips, runs, and uneven drying. Allow each coat to dry completely before applying the next. Light sanding between coats can further improve the smoothness of the final surface.
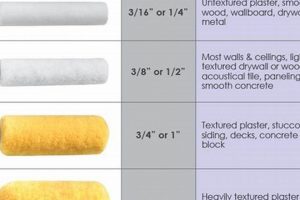
Tip 4: Invest in Quality Brushes and Rollers. The quality of application tools significantly impacts the finish. Opt for brushes with synthetic bristles for water-based paints and natural bristles for oil-based paints. Use a high-density foam roller for large, flat surfaces to minimize brushstrokes.
Tip 5: Control the Environment. Apply finishes in a well-ventilated area with minimal dust and debris. Avoid painting in direct sunlight or extreme temperatures, as these conditions can affect drying time and paint adhesion.
Tip 6: Consider a Protective Topcoat. Applying a clear topcoat, such as polyurethane or varnish, will enhance the durability and longevity. Choose a topcoat that is compatible with the paint type and consider the desired sheen (matte, satin, gloss).
Tip 7: Allow Adequate Curing Time. Allow the finish ample time to fully cure before placing items on the furniture or subjecting it to heavy use. Rushing this process can compromise the integrity of the finish.
These considerations represent critical factors influencing the quality and longevity of applied coatings. Adherence to these practices contributes to a professional, durable, and visually appealing result.
The following sections will address common challenges and troubleshooting techniques related to furniture coatings.
1. Surface Preparation
Surface preparation forms the foundational step in achieving durable and aesthetically pleasing applied furniture coatings. It directly influences the adhesion, smoothness, and overall longevity of the subsequently applied layers. Inadequate preparation inevitably leads to defects such as peeling, blistering, and an uneven texture. The process typically involves cleaning, sanding, and priming the substrate to create an optimal base for the coating. Contaminants such as grease, wax, and dirt must be removed to ensure proper bonding. Sanding creates a mechanical key for the coating, enhancing its adhesion, while priming seals the surface, preventing absorption of the coating and promoting uniform color.
Consider a scenario where an old dresser is to be revitalized. If the existing surface is not thoroughly sanded to remove loose coatings and imperfections, the new layer will likely chip or peel prematurely. Similarly, failing to clean the surface of grease or wax residue will impede the coating’s ability to adhere, resulting in an uneven and potentially compromised surface. The choice of primer is equally significant. Applying an oil-based primer over a latex coating, or vice versa, can lead to adhesion problems and premature failure. Therefore, meticulous surface preparation is not merely a preliminary step but an integral component of the coating process, directly impacting the final outcome.
In summary, the link between surface preparation and successful applied coatings is undeniable. By diligently addressing cleaning, sanding, and priming, practitioners ensure that the subsequent layers can effectively bond, resulting in a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and long-lasting surface. Neglecting this crucial stage compromises the entire project, leading to costly rework and diminished results. The investment in time and effort dedicated to surface preparation yields significant dividends in the quality and longevity of coatings.
2. Paint Selection
The selection of a coating is a critical determinant of the final aesthetic and functional characteristics of furniture. Diverse coating formulations possess distinct properties affecting durability, appearance, and suitability for various applications. Careful evaluation of these properties is essential for achieving desired outcomes and ensuring long-term performance.
- Type of Coating
Coatings are broadly classified into categories based on their chemical composition, such as acrylic latex, alkyd, and epoxy formulations. Acrylic latex coatings are water-based, offering ease of application, low odor, and good color retention. Alkyd coatings, conversely, are oil-based, providing enhanced hardness, durability, and resistance to solvents. Epoxy coatings are characterized by exceptional chemical resistance and adhesion, making them suitable for high-wear applications. The selection of coating type should align with the specific requirements of the project, considering factors such as intended use, environmental conditions, and desired level of protection.
- Sheen Level
Sheen, or gloss level, refers to the degree to which a surface reflects light. Coatings are available in a range of sheens, from matte to high-gloss. Matte finishes offer a non-reflective appearance, concealing imperfections and providing a soft, subtle aesthetic. Satin finishes possess a moderate sheen, offering a balance between durability and visual appeal. Semi-gloss finishes provide increased reflectivity and are easier to clean, making them suitable for surfaces prone to dirt and grime. High-gloss finishes offer the highest level of reflectivity, creating a dramatic visual impact but also accentuating surface imperfections. Sheen selection should be guided by aesthetic preferences, functional requirements, and the desired level of maintenance.
- Color Pigmentation
Color pigmentation significantly impacts the final appearance. The availability of a wide spectrum of colors allows for customization and integration with interior design schemes. Pigments are classified as organic or inorganic, each possessing distinct properties related to color stability, lightfastness, and durability. Inorganic pigments, such as iron oxides and titanium dioxide, tend to be more durable and resistant to fading compared to organic pigments. Color selection should consider factors such as the existing color palette, lighting conditions, and the desired mood or ambiance. Careful attention to color matching and compatibility with other elements in the room is crucial for achieving a cohesive and visually appealing result.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Content
Coatings contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are emitted as the coatings dry. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can pose health risks. Low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations are available, offering a more environmentally friendly option. The selection of coatings with reduced VOC content is increasingly prioritized due to growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations. While low-VOC coatings may exhibit slightly different application properties compared to traditional formulations, advancements in coating technology have minimized these differences, making them a viable alternative for most applications. Consider VOC content to reduce environmental impact and ensure a healthier environment.
In essence, the proper selection contributes significantly to the ultimate success. Aligning the properties of the coating with the intended use, desired aesthetic, and environmental considerations ensures a durable, visually appealing, and sustainable outcome. Careful consideration of these elements is paramount for achieving professional-quality results.
3. Application Technique
The proficiency with which surface coatings are applied to furnishings directly influences the resulting aesthetic appeal, durability, and overall quality. Suboptimal application can negate the benefits of even the highest-grade coatings, resulting in visual imperfections and compromised protective qualities. Therefore, a thorough understanding of application methodologies is paramount.
- Brushwork and Bristle Selection
The choice of brush, and the manner in which it is employed, dictates the smoothness and uniformity of the applied coating. Natural bristle brushes are generally suited for oil-based coatings, while synthetic bristles perform optimally with water-based products. The brushstroke technique, whether employing long, even strokes or short, stippling motions, directly impacts the final texture. For example, improperly loaded brushes can lead to drips and runs, while inconsistent pressure can result in uneven coverage. Careful consideration of bristle type and stroke technique is crucial for achieving a professional result.
- Roller Application
Rollers are typically used for applying coatings to large, flat surfaces. The nap length of the roller cover affects the texture. Short-nap rollers produce smoother finishes, while longer-nap rollers are better suited for textured surfaces or applying thicker coatings. Proper roller technique involves applying even pressure and maintaining a wet edge to avoid lap marks. A common error is over-saturating the roller, leading to drips and uneven distribution of the coating. Skilled roller application results in a uniform layer, minimizing brushstrokes and maximizing efficiency.
- Spray Application
Spraying, whether using compressed air or airless systems, provides a method for achieving exceptionally smooth finishes. However, spray application demands a high degree of skill and control. Factors such as nozzle selection, spray pattern adjustment, and distance from the substrate must be carefully managed to prevent runs, orange peel texture, and overspray. Furthermore, adequate ventilation and personal protective equipment are essential when using spray equipment. Proper spray technique results in an even, consistent coating with minimal surface imperfections. Conversely, improper spraying can lead to significant material waste and rework.
- Environmental Considerations
Ambient temperature, humidity, and airflow exert significant influence on the drying characteristics and overall quality of coatings. Applying coatings in excessively hot or humid conditions can lead to blistering, cracking, and slow drying times. Dust and debris in the environment can contaminate the coating, resulting in surface imperfections. Proper ventilation is crucial for removing solvent vapors and promoting uniform drying. Consideration of environmental factors is integral to achieving optimal application results. For example, planning application during cooler, drier periods can enhance the quality of the final finish.
The efficacy of protective and aesthetic coatings is inherently linked to the application technique. Mastery of brushwork, roller application, and spray methods, coupled with a careful consideration of environmental factors, allows practitioners to maximize the potential of surface coatings, resulting in durable, visually appealing, and long-lasting outcomes. These techniques represent vital skills.
4. Layering Process
The layering process represents a fundamental aspect of achieving high-quality applied coatings on furniture. It involves the sequential application of multiple distinct layers, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing the aesthetic and protective characteristics of the final finish. The proper execution of the layering process is critical to the durability, smoothness, and visual appeal of furniture surfaces. Disregard for correct layering techniques leads to compromised results, including peeling, cracking, and uneven color distribution.
- Primer Application
The initial layer, typically a primer, serves to prepare the substrate for subsequent coatings. Primers promote adhesion, seal porous surfaces, and provide a uniform base for color application. For instance, applying a primer to bare wood prevents excessive absorption of the topcoat, ensuring consistent color and minimizing the risk of blistering. Selecting an appropriate primer compatible with both the substrate and the topcoat is crucial for long-term durability. Failure to prime can result in inadequate adhesion and premature coating failure.
- Color Coating Application
Subsequent layers consist of one or more color coats, each contributing to the final hue and opacity. Multiple thin layers of color provide more uniform coverage and minimize the risk of drips or runs compared to a single thick layer. For example, achieving a deep, saturated color on dark wood might require three or more coats, each applied with careful attention to even distribution and proper drying time. Inconsistent application of color coats results in an uneven finish with visible variations in color intensity.
- Sealer or Topcoat Application
The final layer often involves a clear sealer or topcoat, which provides protection against abrasion, moisture, and UV damage. Topcoats enhance the durability and longevity of coatings, preserving their aesthetic appearance over time. Applying a polyurethane topcoat to a painted tabletop provides a protective barrier against scratches and spills, significantly extending the lifespan of the finish. The choice of topcoat sheenmatte, satin, or glossfurther influences the visual outcome.
- Intermediate Sanding
Sanding between layers, often with fine-grit sandpaper, removes imperfections and creates a smoother surface for subsequent coatings. This process enhances adhesion and contributes to a more refined final finish. For instance, lightly sanding the primer layer before applying the color coat eliminates any raised grain or imperfections, resulting in a perfectly smooth surface. Neglecting intermediate sanding can lead to a textured or uneven finish, detracting from the overall aesthetic appeal.
In summary, the layering process is integral to achieving professional-quality coatings. Each layer, from the initial primer to the final topcoat, contributes specific properties to the overall finish. Proper attention to surface preparation, application technique, and material selection is essential for maximizing the benefits of the layering process and ensuring the durability and beauty of applied furniture coatings.
5. Curing Duration
The time allocated for a coating to fully harden and achieve its intended properties represents a critical, yet often overlooked, element in surface coating applications. The duration of this process profoundly influences the durability, chemical resistance, and overall performance of painted furniture finishes.
- Solvent Evaporation and Polymer Crosslinking
Coatings undergo a transformation from a liquid to a solid state through solvent evaporation and, crucially, polymer crosslinking. The extent of crosslinking directly correlates with the hardness, scratch resistance, and chemical inertness of the coating. Insufficient curing time impedes complete crosslinking, leaving the coating vulnerable to damage. For instance, prematurely placing objects on a freshly coated surface can imprint marks or damage the uncured finish, compromising its integrity.
- Temperature and Humidity Effects
Ambient temperature and humidity exert a significant influence on the curing process. Elevated temperatures generally accelerate curing rates, while low temperatures retard them. High humidity can impede solvent evaporation, prolonging the curing time and potentially leading to a hazy or cloudy finish. The manufacturer’s recommendations regarding optimal temperature and humidity ranges for curing should be strictly adhered to. Deviations from these parameters can significantly affect the final properties of the finish.
- Coating Type Specific Requirements
Different coating chemistries exhibit distinct curing characteristics and time requirements. For example, two-component epoxy coatings typically require a specific mixing ratio and a defined induction time before application to initiate the curing process. Polyurethane coatings may require several days to achieve full hardness and chemical resistance. Adhering to the manufacturer’s specified curing times for each coating type is paramount. Deviations can result in a finish that is either too soft and easily damaged, or excessively brittle and prone to cracking.
- Impact on Long-Term Performance
Adequate curing is not merely a matter of aesthetics; it fundamentally impacts the long-term performance of painted furniture finishes. A properly cured finish provides enhanced resistance to scratches, abrasion, chemicals, and UV degradation. Insufficient curing reduces the lifespan of the coating, necessitating premature refinishing. Properly accounting for this crucial factor results in enhanced longevity. For instance, a table subjected to daily use will exhibit superior resistance to wear and tear if its surface coating has undergone complete and thorough curing.
The relationship between curing duration and the successful application of coatings is inextricable. Neglecting the specified curing times compromises the potential of the applied materials, leading to diminished aesthetic appeal and reduced longevity. A focus on curing duration ensures optimum outcomes, adding significant value to the finished product.
6. Protection Methods
The preservation of painted furniture finishes necessitates the implementation of specific strategies designed to mitigate potential damage and degradation. Protective measures extend the lifespan and maintain the aesthetic integrity of coated surfaces. The selection and application of appropriate methods are crucial for ensuring the longevity of painted furniture.
- Application of Sealants and Topcoats
Sealants and topcoats serve as a sacrificial layer, shielding the underlying painted surface from abrasion, moisture, and chemical exposure. Polyurethane and varnish are commonly employed to provide a durable, transparent barrier. For instance, applying a polyurethane topcoat to a painted kitchen table protects it from spills and scratches, preserving the integrity of the finish. The selection of an appropriate sealant or topcoat depends on the intended use of the furniture and the desired level of protection.
- Use of Furniture Pads and Coasters
Physical barriers, such as furniture pads and coasters, minimize direct contact between the painted surface and potentially damaging objects. Furniture pads placed beneath table lamps and decorative items prevent scratching and scuffing. Coasters protect surfaces from liquid rings and heat damage. These simple precautions significantly reduce the risk of surface damage and prolong the lifespan of the finish. For example, placing a coaster beneath a beverage on a painted coffee table prevents unsightly rings from forming.
- Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Consistent cleaning and maintenance remove accumulated dirt, dust, and grime, preventing these substances from abrading or staining the painted surface. Using a soft cloth and mild detergent solution to clean painted furniture regularly removes contaminants without damaging the finish. Harsh chemicals and abrasive cleaners should be avoided, as they can strip the coating or dull the sheen. Routine maintenance, such as dusting and wiping spills promptly, preserves the appearance and extends the lifespan of the painted surface.
- Environmental Control and UV Protection
Exposure to direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations can accelerate the degradation of painted furniture finishes. Ultraviolet radiation causes fading and discoloration, while temperature variations can lead to cracking and peeling. Placing painted furniture away from direct sunlight and maintaining a stable indoor temperature helps to preserve the finish. UV-resistant coatings can also be applied to mitigate the effects of ultraviolet exposure. This environmental awareness helps ensure longevity.
These protective methods are indispensable for maintaining the integrity and aesthetic appeal of painted furniture. The consistent application of these measures safeguards the investment in painted furniture, ensuring its longevity and continued beauty. The integration of these steps will contribute to the quality of coated furniture.
7. Aesthetic Outcome
The aesthetic outcome represents a primary consideration in the application of painted furniture finishes. The process inherently aims to alter or enhance the visual characteristics of a piece, aligning it with specific design preferences or functional requirements. This outcome is not merely cosmetic; it directly impacts the perceived value, desirability, and integration of the furniture within a broader interior design scheme. A poorly executed finish detracts from the overall aesthetic, regardless of the quality of the furniture itself.
The relationship between the technique and visual characteristics is evident in numerous real-world scenarios. Consider a vintage cabinet intended for a modern kitchen. The selection of a matte, pastel-colored finish transforms the piece, imbuing it with contemporary appeal while retaining its original form. Conversely, a high-gloss, dark finish applied to the same cabinet might evoke a more traditional or formal aesthetic. The choice of paint type, color, sheen, and application method collectively determine the final aesthetic. Furthermore, factors such as surface preparation and the application of decorative techniques, such as distressing or antiquing, contribute significantly to the overall visual impact. For example, deliberately distressing the edges of a painted dresser creates a rustic, aged appearance, enhancing its character and visual interest. Therefore, understanding the interplay between various parameters and final visual result is crucial.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the ability to achieve predictable and desirable results. By carefully considering the desired aesthetic and selecting appropriate techniques, practitioners can transform furniture to meet specific design objectives. This knowledge is essential for furniture refinishers, interior designers, and individuals seeking to personalize their living spaces. Challenges may arise in accurately predicting the final color or sheen due to variations in lighting and substrate characteristics. However, careful planning and testing can mitigate these challenges, ensuring that the application aligns with the intended vision, ultimately validating the link between technique and a valuable finished product.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding coatings applied to furniture. These questions aim to clarify best practices and dispel misconceptions surrounding surface applications.
Question 1: What constitutes adequate surface preparation prior to applying a surface coating?
Adequate surface preparation encompasses cleaning to remove contaminants, sanding to create a mechanical key for adhesion, and priming to seal the substrate. Failure to perform these steps will likely result in compromised adhesion and premature failure.
Question 2: How does one select the appropriate type of coating for a given piece of furniture?
Selection criteria should include the intended use of the furniture, the desired level of durability, the aesthetic preferences, and environmental considerations such as VOC content. Acrylic latex coatings are suitable for general use, while alkyd coatings offer enhanced hardness.
Question 3: What is the optimal method for applying surface coatings to minimize imperfections?
Applying multiple thin coats is preferable to a single thick coat, as it reduces the risk of drips, runs, and uneven drying. Proper brushwork, roller technique, or spray application are essential for achieving a smooth and uniform finish.
Question 4: How does the curing duration influence the quality and longevity of a coating?
Sufficient curing time allows for complete solvent evaporation and polymer crosslinking, enhancing the hardness, chemical resistance, and overall durability. Insufficient curing compromises these properties and shortens the lifespan.
Question 5: What protective measures can be implemented to preserve surface applications?
Applying a clear topcoat, using furniture pads and coasters, regular cleaning and maintenance, and controlling the environment are effective strategies for protecting surface applications from damage and degradation.
Question 6: How can one troubleshoot common problems such as peeling, cracking, or uneven color distribution?
Peeling often results from inadequate surface preparation, cracking from excessive temperature fluctuations or improper curing, and uneven color distribution from inconsistent application or insufficient coats. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause is crucial for remediation.
Proper coating application requires meticulous attention to surface preparation, material selection, application technique, curing duration, and protective measures. Adherence to these principles is critical for achieving durable and aesthetically pleasing outcomes.
The following sections will delve into case studies illustrating the application of surface coatings in various furniture restoration projects.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of painted furniture finishes highlights the multifaceted nature of this subject. From meticulous surface preparation to the careful selection of materials and application techniques, each step contributes significantly to the ultimate aesthetic and functional outcome. The interplay between these elements dictates the durability, longevity, and overall visual appeal of the treated furniture.
A comprehensive understanding of these principles empowers informed decision-making in furniture restoration and enhancement projects. Further research and experimentation are encouraged to expand the knowledge base and refine existing practices within this evolving field, thereby preserving and augmenting the value and beauty of furniture for generations to come.