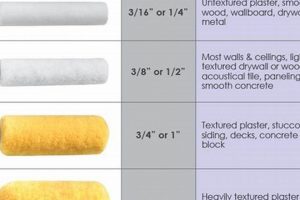
Selecting the appropriate protective coating for wooden surfaces exposed to the elements is crucial for longevity and aesthetic appeal. The ultimate selection hinges on factors such as the specific wood species, climate conditions, and desired visual effect. Different coatings offer varying levels of protection against moisture, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and physical damage. For instance, a high-gloss option might provide enhanced durability and ease of cleaning, while a matte finish could offer a more subtle and natural look.
The correct selection provides numerous advantages, including extended lifespan of the wood, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced curb appeal. Historically, oil-based solutions were favored for their penetration and durability. However, advancements in water-based acrylic technologies have led to formulations that offer comparable, and sometimes superior, performance with lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Proper application techniques, including surface preparation and appropriate drying times, are also critical to maximizing the benefits of the coating.
The following sections will delve into the characteristics of several popular choices, examining their advantages and disadvantages in detail. Factors to be considered will include durability, ease of application, resistance to mildew and fading, and suitability for different types of wood and environmental conditions. This exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence the optimal selection for protecting wooden exteriors.
Exterior Wood Coating Selection Tips
Proper selection and application of a protective coating extends the life and preserves the beauty of exterior wood surfaces. The following guidelines aid in choosing the optimal coating for a given application.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount: Thoroughly clean the wood surface, removing any dirt, mildew, or loose coatings. Sanding promotes adhesion and creates a smooth base for the new coating.
Tip 2: Primer Application is Essential: Apply a high-quality primer specifically formulated for exterior wood. Primer seals the wood, improving adhesion and preventing tannin bleed-through, particularly with redwood and cedar.
Tip 3: Consider the Wood Type: Different wood species have varying levels of porosity and oil content. Select a coating compatible with the specific wood to ensure proper adhesion and longevity. Consult manufacturer recommendations for optimal product selection.
Tip 4: Evaluate Climate Conditions: Regional weather patterns significantly impact coating performance. In areas with high humidity and frequent rainfall, opt for coatings with enhanced mildew resistance and water repellency. Coastal regions necessitate coatings with superior salt spray resistance.
Tip 5: Select an Appropriate Sheen Level: Sheen level impacts both aesthetics and durability. Higher gloss coatings offer better scrubbability and resistance to dirt pickup but can highlight imperfections. Matte finishes provide a softer appearance but may require more frequent cleaning.
Tip 6: Multiple Thin Coats are Superior to One Thick Coat: Applying several thin coats allows for proper drying and curing, resulting in a more durable and resilient finish. Avoid applying coatings too thickly, as this can lead to cracking, peeling, and blistering.
Tip 7: Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere to the coating manufacturer’s instructions regarding application temperatures, drying times, and recommended spreading rates. Deviations from these guidelines can compromise the coating’s performance and longevity.
Proper surface preparation, informed product selection, and meticulous application are vital for achieving a long-lasting and visually appealing finish. Investing time and effort in these steps minimizes maintenance and protects the value of the property.
The next segment will explore the long-term maintenance strategies crucial for maximizing the lifespan of the selected coating and preserving the beauty of the exterior wood surfaces.
1. Durability against Weather
A direct correlation exists between the longevity of exterior wood and the weather resistance offered by its protective coating. The capacity of a coating to withstand environmental stressors, such as precipitation, temperature fluctuations, and solar radiation, is a primary determinant of its overall effectiveness. Coatings that exhibit superior durability against weather conditions inherently contribute to the preservation of the underlying wood structure, mitigating risks associated with rot, decay, and structural compromise. The selection of a high-performance coating becomes a critical investment in safeguarding wood exteriors from premature deterioration.
The impact of weather on wood coatings can be observed in various real-world scenarios. For example, homes located in regions with high humidity and frequent rainfall are particularly vulnerable to the effects of moisture intrusion. In such environments, coatings with excellent water repellency and mildew resistance are essential for preventing fungal growth and wood rot. Similarly, in areas with intense sunlight, coatings with UV inhibitors are crucial for minimizing fading, cracking, and chalking caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Failure to account for these environmental factors when selecting a coating can lead to costly repairs and premature replacement of wood siding or trim. An unsuitable product could exhibit premature peeling, blistering, or degradation, resulting in both aesthetic and structural damage.
Understanding the significance of weather durability in coating selection translates directly into practical benefits for homeowners and building professionals. By prioritizing coatings with proven resistance to specific environmental challenges, one can minimize maintenance requirements, extend the lifespan of exterior wood surfaces, and ultimately enhance the long-term value of the property. The investment in a durable coating provides not only aesthetic enhancement but also essential protection against the destructive forces of nature, ensuring the continued integrity and appearance of wood exteriors.
2. Resistance to Moisture
Moisture infiltration represents a primary threat to the integrity of exterior wood structures. The selection of an appropriate exterior coating is therefore intrinsically linked to its ability to resist moisture penetration. Coatings that effectively impede water absorption mitigate the risk of wood rot, fungal growth, and dimensional instability. These properties are essential components in determining the ideal protective finish. A coating with inadequate moisture resistance will permit water to permeate the wood fibers, leading to swelling, warping, and ultimately, structural damage. Conversely, a coating formulated with water-repellent additives creates a barrier against moisture, extending the lifespan of the wood.
Consider, for example, the application of a water-based acrylic latex coating versus an oil-based coating on a wooden deck. While both provide a degree of protection, the acrylic latex formulation typically exhibits superior resistance to moisture due to its inherent film-forming properties and the inclusion of water-repellent agents. Over time, the acrylic latex coating will demonstrate less water absorption and subsequent damage compared to the oil-based counterpart, particularly in environments characterized by frequent rainfall or high humidity. This differential performance underscores the importance of understanding the moisture-resistance characteristics of various coatings when selecting a solution for exterior wood protection.
The selection of a coating with optimal moisture resistance is a critical consideration in preserving the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of exterior wood. By prioritizing this aspect, it is possible to mitigate the risks associated with water damage, minimize maintenance requirements, and extend the service life of wooden components. The investment in a high-quality, moisture-resistant coating represents a proactive approach to safeguarding wood exteriors from the detrimental effects of environmental exposure. The choice to ensure that the paint for a wooded exterior is resistance to moisture or not, will determine the performance for the next coming years.
3. Adhesion Capabilities
The adherence of a coating to the underlying wood substrate directly dictates its protective efficacy and longevity. Insufficient adhesion leads to premature coating failure, manifested as peeling, blistering, or cracking, thereby exposing the wood to environmental degradation. Consequently, the selection of an exterior finish necessitates a careful evaluation of its adhesive properties, ensuring compatibility with the specific wood species and its ability to maintain a robust bond throughout varying environmental conditions. This attribute forms a foundational component in determining the optimal exterior protection.
Several factors influence the adhesive strength of an exterior coating. Surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and sanding, removes contaminants and creates a textured profile that enhances mechanical bonding. The coating’s formulation, specifically the type and concentration of resins and binders, determines its inherent adhesive properties. Certain wood species, such as redwood and cedar, contain natural extractives that can inhibit adhesion; therefore, specialized primers or coatings designed to mitigate this effect are often required. Real-world examples demonstrate the consequences of neglecting adhesion: a poorly adhering coating on a wood siding exposed to harsh weather will invariably fail, necessitating costly repairs and reapplication.
In summation, adhesion capabilities are not merely a desirable attribute but a critical determinant of an effective protective coating. The ability of the finish to securely bond with the wood, resist the disruptive forces of moisture and temperature fluctuations, and withstand the effects of natural extractives significantly impacts the long-term performance of the coating. By prioritizing adhesion through proper surface preparation and informed product selection, one maximizes the investment in exterior wood protection, minimizing maintenance and ensuring lasting aesthetic and structural integrity.
4. Flexibility of coating
The capacity of an exterior finish to accommodate dimensional changes in wood substrates is a key determinant in its long-term performance. Flexibility in a coating refers to its ability to expand and contract in response to temperature and humidity fluctuations without cracking, peeling, or otherwise losing its integrity. This property is particularly significant for wood, a hygroscopic material that undergoes constant expansion and contraction cycles. The effectiveness of the finish for wood is inextricably linked to its elasticity.
- Preventing Cracks and Peeling
A flexible coating can stretch and compress along with the wood, preventing the development of stress fractures. When a less flexible coating is applied, the stresses caused by the wood’s movement can exceed the coating’s tensile strength, leading to cracking and subsequent peeling. This, in turn, compromises the protective barrier, allowing moisture to penetrate the wood and accelerate decay. A flexible exterior finish provides a durable and long-lasting barrier against the elements.
- Maintaining a Weatherproof Seal
A coating’s ability to maintain its integrity despite dimensional changes is crucial for creating and maintaining a weatherproof seal. Cracks and fissures in a less flexible coating create pathways for moisture intrusion, which can lead to rot, mold growth, and structural damage. A flexible finish, on the other hand, remains intact, preventing water from reaching the wood and preserving its structural integrity. Properly sealing a wooden exterior is critical to long-term preservation.
- Extending Coating Lifespan
Flexibility directly influences the lifespan of an exterior coating. A coating that cracks and peels prematurely requires more frequent maintenance and reapplication, increasing the overall cost and effort associated with protecting the wood. A more flexible option, by contrast, is less prone to these types of failures and can provide reliable protection for a longer period, reducing the need for frequent repainting. This is a cost-effective solution.
- Compatibility with Wood Species
Different wood species exhibit varying degrees of dimensional instability. Softer woods, such as pine, tend to expand and contract more than denser hardwoods. A coating selected for its flexibility can better accommodate these variations, ensuring consistent performance across different types of wood. The selection is essential to durability, regardless of the materials used.
In summary, the flexibility of a coating is a pivotal consideration in selecting the most appropriate exterior finish. It provides sustained protection against environmental forces, promotes a reliable moisture barrier, prolongs the lifespan of the application, and accommodates the unique properties of varied wood types. The selection requires a balanced approach that weighs the benefits of increased elasticity against other crucial factors such as UV protection, adhesion, and resistance to mildew.
5. UV protection
The ability of an exterior finish to shield wood from ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a crucial determinant in its overall protective capability. Solar UV radiation causes significant degradation of both the coating itself and the underlying wood substrate, leading to fading, discoloration, embrittlement, and eventual structural compromise. Therefore, a robust UV protection mechanism is integral when deciding on the most suitable exterior paint finish for wood.
- Pigment Selection and UV Absorption
The type and concentration of pigments within a paint formulation directly impact its UV absorption characteristics. Certain pigments, such as titanium dioxide and iron oxides, exhibit exceptional UV absorption, effectively blocking harmful radiation from reaching the wood surface. Conversely, coatings with insufficient or inadequate pigment loading offer limited protection, resulting in accelerated degradation of both the finish and the wood. For example, a light-colored paint with low pigment density will provide less UV protection than a darker, more heavily pigmented coating.
- Binder Chemistry and UV Resistance
The chemical composition of the binder, the film-forming component of the paint, also influences its resistance to UV degradation. Acrylic latex binders, for instance, generally exhibit superior UV resistance compared to alkyd or oil-based binders. Over time, exposure to UV radiation can cause the binder to break down, leading to chalking, cracking, and loss of adhesion. A high-quality binder formulated with UV stabilizers can significantly extend the lifespan of the coating and protect the wood from damaging rays. Consider the impact of a high-quality binder.
- Clear Coats and UV Inhibitors
For clear finishes, which lack the inherent UV protection afforded by pigments, the incorporation of UV inhibitors is essential. UV inhibitors are chemical additives that absorb or reflect UV radiation, preventing it from penetrating the wood. The effectiveness of a clear coat in protecting wood from UV damage is directly proportional to the type and concentration of UV inhibitors employed. As an example, marine-grade varnishes, formulated with high levels of UV inhibitors, are commonly used to protect wooden boats and other structures exposed to intense sunlight. This is essential for protecting an exterior. These types of wood finishes are essential for protecting the wood from sun damage.
- Impact on Coating Lifespan and Maintenance
The degree of UV protection afforded by an exterior finish directly impacts its lifespan and the frequency of maintenance required. Coatings with poor UV resistance will degrade more rapidly, necessitating more frequent repainting or refinishing. Conversely, coatings with robust UV protection offer extended service life, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming maintenance. Homes in areas with high UV exposure, such as the southwestern United States, benefit greatly from coatings with high UV resistance due to high sun exposure.
In conclusion, UV protection is a critical parameter in the selection of an optimal exterior paint finish. The pigment, the binder, and the implementation of UV inhibitors are all required for protecting the surface. By selecting coatings formulated with robust UV protection mechanisms, it is possible to significantly extend the lifespan of both the finish and the wood, minimize maintenance requirements, and preserve the aesthetic appeal of wood exteriors. This attribute ensures sustained performance and preservation of value of a structure.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses prevalent inquiries and clarifies misunderstandings concerning the selection of an exterior finish for wood surfaces. The information provides a factual basis for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood in coastal environments?
Coastal environments present unique challenges due to salt spray and high humidity. An acrylic latex coating formulated with mildewcides and corrosion inhibitors is generally recommended. High-gloss or semi-gloss sheens offer increased protection and ease of cleaning.
Question 2: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood that is frequently exposed to direct sunlight?
Excessive sunlight accelerates the degradation of many coatings. Select a product specifically formulated with UV absorbers and stabilizers. Lighter colors reflect more sunlight, reducing heat buildup and prolonging the coating’s lifespan.
Question 3: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood trim versus wood siding?
Trim often requires a more durable and aesthetically pleasing finish. A premium acrylic enamel is suitable for trim, providing a smooth, durable, and weather-resistant surface. Siding benefits from a flexible coating that can accommodate dimensional changes; a quality acrylic latex paint is a suitable choice.
Question 4: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood decks?
Decks experience high foot traffic and exposure to the elements. A penetrating oil-based stain or a solid-color acrylic stain formulated with water repellents and UV inhibitors is often used. These products protect the wood while allowing it to breathe.
Question 5: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood that has already been painted?
Proper surface preparation is paramount. Ensure the existing coating is sound and free of loose material. If the existing coating is oil-based, prime with an oil-based primer before applying a new coat. If the existing coating is latex-based, a latex primer is appropriate.
Question 6: What type of exterior paint finish is best for wood with pre-existing mildew or fungal growth?
Thoroughly clean the affected area with a mildewcidal wash. Allow the surface to dry completely. Apply a primer containing mildewcides, followed by a topcoat formulated with mildew-resistant properties. Regular cleaning will help prevent recurrence.
The selection of an optimal finish requires careful consideration of the specific environmental conditions, the type of wood, and the intended use of the coated surface. Consulting with a professional paint specialist or contractor is advisable for complex or challenging applications.
The next section examines the critical steps involved in preparing wood surfaces prior to coating application.
Determining the Optimal Exterior Wood Finish
The selection of the most suitable protective coating for exterior wood surfaces involves a multi-faceted analysis. Factors such as climate, wood species, and desired aesthetic contribute to this evaluation. The preceding sections have elucidated key attributes that contribute to coating performance, emphasizing the significance of durability, moisture resistance, adhesion, flexibility, and ultraviolet radiation protection. The interplay of these factors directly influences the longevity and visual appeal of the finished product, necessitating careful consideration to ensure effective safeguarding of the wood.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate solution for exterior wood extends beyond mere aesthetics; it represents a critical investment in long-term preservation and structural integrity. Further research and consultation with industry experts are encouraged to facilitate informed decisions tailored to specific project requirements. The commitment to a proper coating strategy ensures lasting protection and sustained value for wood structures.