A durable and aesthetically pleasing coating applied to maple wood surfaces, this treatment enhances the wood’s natural grain and provides protection against wear, moisture, and UV damage. An example includes using it to treat kitchen cabinets to improve their resistance to everyday use and spills.
This protective layer serves to prolong the lifespan of maple products while also improving their visual appeal. Its popularity stems from its ability to highlight the wood’s inherent beauty and provide a smooth, consistent surface. Historically, various treatments have been used, but advancements in modern formulations provide greater durability and color retention.
The following sections will delve into the specific characteristics, application techniques, maintenance procedures, and a comparison with alternative wood coatings. This discussion aims to offer a comprehensive understanding of its use in both residential and commercial settings.
Essential Guidance for Preserving Maple Wood Surfaces
These recommendations ensure the longevity and aesthetic appeal of treated maple items. Adhering to these guidelines contributes significantly to maintaining the integrity of the coating and the underlying wood.
Tip 1: Select Appropriate Cleaning Agents: Use pH-neutral cleaners specifically designed for wood surfaces. Avoid abrasive materials or harsh chemicals, as these can damage the protective layer, leading to dullness and potential discoloration. For example, a mild dish soap diluted in water is generally a safe option.
Tip 2: Employ Gentle Cleaning Techniques: Utilize soft cloths or sponges during cleaning. Avoid excessive scrubbing or pressure, which can scratch or wear down the surface. Always wipe in the direction of the wood grain to minimize streaking.
Tip 3: Minimize Exposure to Moisture: Promptly wipe up any spills to prevent water damage or staining. Excessive moisture can penetrate the layer, causing it to swell, crack, or peel over time. Implement coasters and placemats to protect surfaces from condensation.
Tip 4: Control Environmental Conditions: Maintain a stable humidity level in the environment where the items are located. Extreme fluctuations in humidity can cause the wood to expand and contract, potentially compromising the integrity of the coating. Consider using a humidifier or dehumidifier as needed.
Tip 5: Shield from Direct Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can cause fading or discoloration of the treatment. Utilize window coverings or UV-resistant films to minimize the impact of ultraviolet radiation. Periodic rotation of items can also help ensure even exposure.
Tip 6: Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Conduct periodic inspections of the items to identify any signs of wear, damage, or deterioration. Address any issues promptly to prevent further problems. Minor scratches or blemishes can often be repaired with touch-up kits specifically designed for this purpose.
Tip 7: Reapply Protective Coatings as Needed: Depending on the level of use and environmental conditions, periodic reapplication of a protective topcoat may be necessary. This helps to maintain the durability and aesthetic appeal of the surfaces. Consult with a professional for recommendations on appropriate products and application techniques.
Consistent adherence to these practices will safeguard the investment in treated maple items, ensuring their continued beauty and functionality for years to come.
The subsequent sections will examine different application methods, discuss troubleshooting common issues, and present case studies illustrating the practical application of these principles.
1. Durability
Durability is a critical attribute of any effective treatment for maple wood. The treatment’s ability to withstand daily wear, abrasion, and impact directly determines the longevity and performance of the treated surface. Without sufficient resistance to physical stress, the finish will degrade, exposing the underlying wood to damage from moisture, stains, and ultraviolet radiation. For instance, a durable coating on maple flooring in a high-traffic area prevents scratches and scuff marks, maintaining its appearance for an extended period. Conversely, a less durable coating would quickly show signs of wear, requiring frequent refinishing or replacement.
The level of durability achieved depends on several factors, including the specific type of formulation used, the application method, and the curing process. Polyurethane coatings, known for their hardness and abrasion resistance, are often selected for high-use applications. Proper preparation of the wood surface, including sanding and cleaning, is essential to ensure optimal adhesion and performance. Furthermore, the application of multiple coats, each allowed to cure thoroughly, can significantly enhance the overall durability. Consider the application of a catalyzed varnish on maple kitchen cabinets. Its robust protective qualities ensures resistance to scratching from typical kitchen tools and cleaning products, which greatly extends cabinet life.
In summary, durability is paramount to an effective treatment of maple wood. It directly influences the lifespan, maintenance requirements, and overall value of the finished product. Selecting a treatment with appropriate durability characteristics, based on the intended application, is essential for achieving long-term performance and satisfaction. Neglecting this aspect can lead to premature failure, increased maintenance costs, and a compromised aesthetic appearance.
2. Aesthetics
The aesthetic qualities imparted by treatments on maple wood are a primary consideration for numerous applications. The interplay between the inherent characteristics of the wood and the properties of the coating determines the visual appeal of the finished product.
- Grain Enhancement
Aesthetics accentuate the natural patterns of maple, from subtle, uniform grains to more figured varieties like curly or bird’s-eye maple. Clear coats highlight these features, while tinted varieties can subtly alter the tone without obscuring the underlying figure. The choice depends on the desired effect and the specific character of the wood itself. An example is applying a clear satin treatment to bird’s-eye maple to amplify the unique pattern for a statement piece of furniture.
- Color Modulation
The coloring process profoundly impacts the final appearance. Transparent coatings preserve the wood’s original hue, while stains and pigments introduce a spectrum of color options. Achieving a consistent and even color requires careful application and attention to the wood’s absorbency. For instance, using a light amber stain on maple flooring can add warmth without losing the wood’s brightness, creating a welcoming atmosphere in a room.
- Sheen Level
The level of gloss significantly influences the perceived quality. High-gloss finishes reflect more light, creating a sleek, modern appearance, while matte or satin finishes offer a softer, more natural look. The appropriate sheen level depends on the intended style and the overall context of the application. A high-gloss finish on a maple countertop might highlight its smoothness, but a matte finish could be preferable to minimize glare and fingerprints.
- Surface Texture
While often overlooked, texture contributes to the overall aesthetic experience. A perfectly smooth surface conveys elegance, while a slightly textured finish can add character and improve grip. Some techniques, such as wire brushing, can enhance the wood’s natural grain, adding visual depth and tactile interest. For example, wire brushing a maple tabletop followed by a matte treatment can create a rustic yet refined aesthetic.
These aesthetic considerations contribute significantly to the value and desirability of maple wood products. By carefully selecting and applying appropriate treatments, it is possible to enhance the wood’s inherent beauty and create a wide range of visual effects to meet diverse design requirements.
3. Protection
Protection is a primary function of coatings applied to maple wood, safeguarding the material from various detrimental environmental factors and physical stresses that could compromise its integrity and appearance. Selecting the appropriate coating is essential for ensuring the longevity and preservation of maple wood surfaces.
- Moisture Resistance
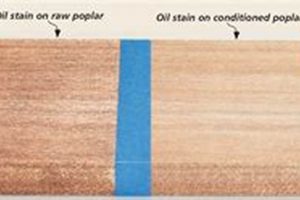
Maple wood is susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to swelling, warping, and ultimately, decay. A protective treatment provides a barrier against water penetration, preventing these adverse effects. For example, a moisture-resistant finish applied to maple kitchen cabinets helps to prevent damage from spills and humidity, preserving the structural integrity of the cabinetry. The effectiveness of this protection is crucial in environments prone to dampness or frequent exposure to liquids.
- UV Radiation Shielding
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can cause fading, discoloration, and degradation of maple wood. A treatment incorporating UV inhibitors helps to mitigate these effects, preserving the color and visual appeal of the wood over time. For instance, a UV-resistant coating on maple furniture placed near windows can prevent it from yellowing or fading, maintaining its original appearance. The degree of UV protection is particularly important for items exposed to direct sunlight.
- Abrasion Resistance
Maple wood surfaces are vulnerable to scratches, scuffs, and other forms of abrasion from everyday use. A durable treatment provides a layer of protection against these physical stresses, preventing damage to the underlying wood. A highly abrasion-resistant coating on maple flooring will minimize wear and tear from foot traffic, pets, and furniture, extending the lifespan of the floor. This type of protection is critical in high-traffic areas or situations where the wood is likely to experience frequent contact.
- Chemical Resistance
Exposure to various chemicals, such as household cleaners and solvents, can damage or stain maple wood. A treatment offering chemical resistance helps to protect the wood from these harmful substances, preventing discoloration and etching. For example, a chemical-resistant finish on a maple laboratory countertop will protect it from spills of corrosive materials, maintaining its integrity and appearance. The level of chemical resistance required depends on the specific environment and the types of chemicals likely to be encountered.
The protective qualities conferred by surface treatments on maple wood are integral to ensuring its long-term performance and aesthetic appeal. By selecting a treatment that addresses the specific environmental and usage conditions, it is possible to significantly extend the lifespan of maple wood items and preserve their value. These protective benefits underscore the importance of proper coating selection and application in maximizing the utility and longevity of maple wood.
4. Application
The method of application significantly influences the performance and aesthetic outcome of coatings on maple wood. Varied techniques offer distinct advantages and are selected based on factors such as the size and complexity of the surface, the type of coating material, and the desired finish quality. Proper execution is paramount to achieving optimal protection and visual appeal.
- Spraying Techniques
Spraying, encompassing airless, HVLP (High Volume Low Pressure), and conventional methods, provides an even distribution of the coating material, especially on intricate or large surfaces. This method minimizes brush strokes and ensures a smooth, uniform layer. In cabinetry finishing, spraying allows for consistent color and sheen across door panels and frames. However, spraying requires specialized equipment and appropriate ventilation to manage overspray.
- Brushing Methods
Brushing is a more traditional approach, suitable for smaller projects and detail work. The choice of brush type, natural or synthetic, impacts the finish quality. Natural bristles are often preferred for oil-based coatings, while synthetic bristles are better suited for water-based products. When applying a stain, brushing allows for controlled penetration into the maple’s grain. This technique demands careful attention to avoid brush marks and uneven application.
- Rolling Applications
Rolling is an efficient method for covering large, flat surfaces like flooring. The type of roller sleeve, foam or nap, influences the texture and uniformity of the coating. Foam rollers produce a smoother finish, while nap rollers can be used for textured or uneven surfaces. Applying a clear coat to a maple floor with a roller allows for quick coverage while minimizing drips. This technique requires overlapping strokes to prevent lines and ensure consistent coverage.
- Wiping Techniques
Wiping is commonly used for applying stains and sealers, allowing for controlled absorption and color depth. The excess material is removed with a clean cloth, leaving a thin, even layer. Staining maple tabletops often involves wiping to achieve a uniform color and highlight the wood’s grain. This technique requires prompt removal of excess stain to prevent blotchiness and achieve the desired tonal effect.
The selection and skillful execution of an appropriate method are crucial for realizing the full potential of coatings applied to maple wood. Consideration of the coating material’s properties, the surface characteristics, and the desired aesthetic informs the optimal choice. Proper application, in turn, maximizes the coating’s protective capabilities, enhances the wood’s beauty, and extends the lifespan of the finished product.
5. Maintenance
Proper maintenance is integral to preserving the integrity and aesthetic appeal of any maple wood surface treatment. Consistent care extends the life of the finish, protecting the underlying wood from damage and maintaining its visual quality. Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to premature degradation of the coating, necessitating costly repairs or replacements.
- Regular Cleaning Protocols
Consistent cleaning removes surface contaminants that can degrade the finish over time. Dust, dirt, and spills, if left unattended, can etch or stain the coating, diminishing its protective and aesthetic properties. A routine of gentle cleaning with appropriate, pH-neutral cleaning agents specifically formulated for wood is essential. For instance, periodically wiping down maple kitchen cabinets with a soft cloth and a mild detergent solution can prevent the buildup of grease and grime, preserving the finish’s luster and integrity.
- Environmental Control Measures
Maintaining stable environmental conditions, particularly humidity and temperature, is crucial. Excessive humidity can cause the wood to swell and contract, potentially leading to cracking or peeling of the treatment. Similarly, direct sunlight can cause fading and discoloration. Implementing measures to control these environmental factors, such as using humidifiers or dehumidifiers and employing window coverings or UV-resistant films, can significantly extend the life. Shielding maple furniture from direct sunlight is a straightforward example.
- Prompt Spill Management
Immediate attention to spills is paramount. Liquids left on the surface can penetrate the protective layer, causing staining, swelling, or damage to the underlying wood. Spills should be wiped up immediately with a clean, absorbent cloth. For example, promptly addressing a wine spill on a maple tabletop minimizes the risk of permanent staining and preserves the integrity of the finish.
- Periodic Inspection and Repair
Regular inspection for signs of wear or damage allows for timely intervention. Identifying and addressing minor scratches, blemishes, or areas of wear before they escalate can prevent more extensive damage. Touch-up kits specifically formulated for maple treatments can be used to repair minor imperfections, maintaining the finish’s protective and aesthetic qualities. Addressing a small scratch on a maple wood floor with a touch-up pen can prevent further damage from daily wear.
These facets of maintenance, when diligently practiced, significantly contribute to the longevity and visual appeal of treated maple items. Consistent care safeguards the investment in maple wood products, ensuring their continued beauty and functionality for years to come.
6. Coloration
Coloration, in the context of maple wood treatments, refers to the process of modifying or enhancing the natural color of the wood to achieve a desired aesthetic effect. This process is intrinsically linked to the treatment, influencing its visual impact and suitability for various applications. The cause-and-effect relationship is straightforward: the applied colorants directly alter the wood’s appearance, transforming it from its raw state to a specific hue or tone. Without coloration, the treatment would primarily serve a protective function, leaving the wood’s inherent color unchanged. The importance of coloration arises from the diverse aesthetic preferences and design requirements of end-users. For example, a light, natural treatment might be preferred for Scandinavian-inspired interiors, while a darker, richer tone might be chosen for traditional or formal settings. The practical significance of understanding coloration lies in the ability to select appropriate treatments that align with specific design goals and create visually appealing and harmonious spaces.
The application of colorants to maple wood involves various techniques, including staining, dyeing, and the use of pigmented treatments. Staining penetrates the wood fibers, highlighting the grain pattern and adding depth of color. Dyeing, on the other hand, provides a more uniform and transparent color, preserving the wood’s natural appearance. Pigmented treatments introduce opaque color, effectively masking the wood grain to a greater extent. The choice of technique depends on the desired level of color intensity, grain definition, and surface transparency. For instance, staining is commonly used on maple flooring to enhance the wood’s character and create a warm, inviting atmosphere, while dyeing might be preferred for furniture to achieve a consistent and refined appearance. In practice, these techniques often involve multiple steps, such as sanding, sealing, and applying multiple coats of colorant, to achieve the desired result.
In summary, coloration is an essential component of treatments, enabling the customization and aesthetic enhancement of maple wood surfaces. The selection of appropriate colorants and application techniques directly influences the final appearance and suitability for various applications. Challenges in coloration include achieving consistent color across different pieces of wood, preventing blotchiness, and ensuring the long-term durability of the color. Understanding the principles of coloration and the properties of different colorants is critical for achieving successful and visually pleasing results, contributing to the overall value and desirability of treated maple wood products.
7. Longevity
The relationship between treatments and the lifespan of maple wood is direct and consequential. A well-chosen and properly applied finish serves as a barrier, protecting the wood from environmental stressors and physical wear, thereby extending its usable life. Conversely, a substandard or poorly maintained finish can accelerate deterioration, shortening the wood’s lifespan and necessitating premature replacement or costly restoration. The significance of longevity as a component of treatments lies in its economic and environmental implications; a longer-lasting product reduces the frequency of replacement, conserving resources and minimizing waste. The use of durable, high-quality treatments on maple flooring in a residential setting exemplifies this relationship, as these finishes can withstand years of foot traffic and maintain their appearance, significantly extending the flooring’s lifespan compared to untreated wood.
Factors influencing longevity include the type of finish used, the application method, and the level of maintenance provided. Polyurethane treatments, known for their abrasion resistance, often extend the lifespan of maple surfaces in high-traffic areas. Careful application, ensuring proper adhesion and a uniform coating, is essential for maximizing protective benefits. Regular cleaning, prompt spill management, and periodic reapplication of topcoats further contribute to extending the life. The application of catalyzed conversion varnish on maple kitchen cabinetry provides a hard, durable surface resistant to moisture, chemicals, and physical wear, significantly extending the lifespan of the cabinets compared to less durable finishes. Neglecting these maintenance measures can compromise the finish’s integrity, leading to increased susceptibility to damage and a reduced lifespan.
In conclusion, the link between treatments and the longevity of maple wood is undeniable. A strategic approach to finish selection, application, and maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan of maple wood products, yielding both economic and environmental benefits. The primary challenges in achieving optimal longevity include selecting the appropriate finish for the intended application, ensuring proper surface preparation and application techniques, and implementing a consistent maintenance program. By addressing these challenges, it is possible to significantly extend the lifespan of maple wood products, preserving their value and minimizing their environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries concerning the selection, application, and maintenance of coatings for maple wood surfaces. This information is intended to provide clarity and guidance for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What are the primary benefits of applying a treatment to maple wood?
The application of a durable coating enhances the wood’s resistance to moisture, abrasion, and UV radiation. Furthermore, it accentuates the natural grain and provides a uniform surface, improving the overall aesthetic appeal.
Question 2: Which type of treatment offers the best protection for maple kitchen cabinets?
Catalyzed conversion varnish is frequently recommended due to its superior resistance to chemicals, moisture, and physical wear, making it well-suited for the demanding environment of a kitchen.
Question 3: How often should a maple wood surface be refinished?
The frequency of refinishing depends on the level of use and environmental conditions. High-traffic areas may require refinishing every few years, while less frequently used surfaces may only need attention every decade.
Question 4: Can discoloration of a treated maple surface be reversed?
The success of reversing discoloration depends on the cause and severity of the damage. In some cases, specialized cleaning agents or refinishing may restore the original color, while in other instances, replacement may be necessary.
Question 5: What is the optimal method for cleaning surfaces?
The recommended cleaning method involves using a soft cloth or sponge and a pH-neutral cleaning solution specifically designed for wood surfaces. Abrasive cleaners should be avoided to prevent damage to the finish.
Question 6: How can the lifespan of surfaces be maximized?
Lifespan extension is achieved through regular cleaning, prompt spill management, maintenance of stable environmental conditions, and periodic reapplication of protective topcoats.
In summary, diligent attention to the selection, application, and maintenance of surface coatings ensures the longevity and aesthetic quality of maple wood items.
The subsequent article sections will explore advanced techniques, troubleshooting common issues, and present detailed case studies.
Concluding Remarks on Maple Wood Finish
This exploration has underscored the multifaceted nature of a surface treatment applied to maple. Its significance spans protective qualities, aesthetic enhancements, and the crucial role in prolonging the material’s lifespan. The proper selection, application, and consistent maintenance of a quality coating are paramount to realizing its full potential. The article has illuminated the importance of understanding the interplay between durability, aesthetics, protection, and longevity in maximizing the value of maple wood products.
The decision to employ such a treatment represents a commitment to both beauty and long-term performance. Continued research and development in coating technologies promise further advancements in durability and environmental sustainability. Careful consideration of the information presented here will empower informed choices, ensuring enduring satisfaction with treated maple wood surfaces.




![Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] | Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing](https://bestfinaltouch.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-301-300x200.jpg)

