A coating designed to protect and enhance timber surfaces, particularly those utilizing native species, is a key element in woodworking and construction. This specialized treatment safeguards against environmental factors such as moisture, sunlight, and wear, thereby extending the lifespan and preserving the aesthetic appeal of wooden items. An example includes a sealant applied to a jarrah dining table to shield it from spills and scratches.
The proper application of such a treatment offers several advantages. It provides a durable barrier against decay, preventing fungal growth and insect infestation. Furthermore, it can accentuate the natural grain and color of the wood, bringing out its inherent beauty. Historically, natural oils were employed for this purpose, but modern formulations offer improved longevity and resistance to the elements. This preservation strategy is particularly important for hardwoods known for their unique textures and tones.
The following sections will delve into the various types of these coatings available, the appropriate methods for application, and considerations for selecting the best option for specific wood types and environmental conditions. Detailed analysis will be provided regarding the properties that define a high-quality outcome, ensuring optimal protection and an aesthetically pleasing result.
Expert Guidance on Timber Protection
Achieving a professional and durable result requires careful planning and execution. The following recommendations are intended to optimize the protection and aesthetic appeal of wooden surfaces.
Tip 1: Proper Surface Preparation is Paramount. Before application, ensure the wood is clean, dry, and free from any existing coatings, dirt, or contaminants. Sanding to a smooth, even surface is essential for optimal adhesion and a uniform finish. Any imperfections should be addressed prior to the application process.
Tip 2: Select the Appropriate Type for the Intended Use. Different formulations offer varying levels of protection against UV radiation, moisture, and abrasion. Interior applications require different characteristics than exterior projects, and selecting the correct product ensures longevity and performance.
Tip 3: Adhere Strictly to Manufacturer Instructions. Application techniques, drying times, and recommended number of coats vary between products. Deviating from these guidelines can compromise the integrity and appearance of the resulting coating.
Tip 4: Apply Thin, Even Coats. Multiple thin coats are preferable to a single thick coat, which can lead to runs, drips, and uneven drying. Thin coats allow for better penetration and a more durable, consistent finish. Ensure each coat is fully dry before applying the subsequent layer.
Tip 5: Consider Environmental Conditions. Avoid applying in direct sunlight, high humidity, or extreme temperatures. These conditions can adversely affect drying times and the overall quality of the coating. A well-ventilated environment is recommended.
Tip 6: Use Quality Applicators. Employ brushes, rollers, or spray equipment specifically designed for the product being used. Clean applicators thoroughly after each use to prevent contamination and ensure proper application in the future.
Tip 7: Test on an Inconspicuous Area. Before applying to the entire surface, test the product on a small, hidden area to ensure compatibility and desired aesthetic results. This allows for adjustments in technique or product selection if necessary.
By following these guidelines, woodworkers can significantly enhance the protection and beauty of their projects, ensuring a long-lasting and visually appealing outcome.
The subsequent sections will provide more in-depth guidance on selecting the ideal product for specific applications, as well as addressing common problems encountered during the application process.
1. Protection against environment
The selection and application of a suitable timber coating are intrinsically linked to the environment in which the wood will be situated. Environmental factors exert a significant influence on the longevity and aesthetic integrity of timber, necessitating the use of coatings designed to mitigate their detrimental effects. Without adequate protection, timber is vulnerable to degradation, compromising both its structural integrity and visual appeal.
- UV Radiation Resistance
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight causes fading, discoloration, and surface degradation in timber. Coatings formulated with UV absorbers or blockers provide a protective barrier, minimizing these effects and preserving the original color and appearance. For instance, exterior decking subjected to intense sunlight requires a coating specifically designed to withstand prolonged UV exposure.
- Moisture Control
Moisture absorption leads to swelling, warping, and decay in wood. Coatings that provide a water-repellent barrier prevent moisture penetration, reducing the risk of these issues. Coastal environments, where humidity and salt spray are prevalent, demand coatings with superior moisture resistance to protect timber structures from accelerated deterioration.
- Resistance to Temperature Fluctuations
Rapid temperature changes can cause expansion and contraction in wood, leading to cracking and splitting. Flexible coatings that can accommodate these dimensional changes without compromising their integrity are essential. Timber used in regions with extreme temperature variations requires a finish that maintains its protective properties across a wide temperature range.
- Protection Against Biological Attack
Wood is susceptible to attack by fungi, insects, and marine borers, which can cause significant structural damage. Coatings incorporating biocides or preservatives offer protection against these organisms. Timber used in ground contact or in areas with high termite activity necessitates a coating with enhanced resistance to biological degradation.
The effective mitigation of environmental stressors through the strategic selection and application of appropriate timber coatings is paramount to ensuring the long-term performance and preservation of wood structures. The specific environmental conditions to which the timber will be exposed should be a primary consideration in the selection process, guiding the choice of a coating that provides optimal protection and aesthetic enhancement.
2. Enhancing Natural Grain
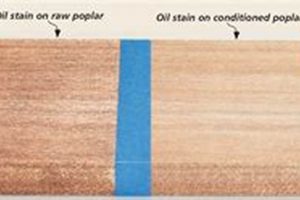
The ability of specialized coatings to enhance the natural grain of timber is a significant factor driving their application, especially within the context of woodworking and construction. The inherent beauty of wood lies in its grain pattern, a visual record of the tree’s growth history. A well-chosen coating accentuates this pattern, bringing out the wood’s depth and character. The selection of the coating directly impacts the extent to which the grain is emphasized, therefore it’s an inseparable element of the total visual experience.
Consider, for example, the application of a clear oil-based treatment to a piece of figured maple. The oil penetrates the wood fibers, enhancing the contrast between the lighter and darker areas of the grain, thereby creating a more pronounced and visually appealing surface. Conversely, a heavily pigmented stain could obscure the grain, diminishing the wood’s natural beauty. Similarly, penetrating oils often used on jarrah and blackwood floors emphasize the deep red and brown tones, highlighting the unique grain patterns characteristic of those species. Furthermore, specialized coatings can alter the light reflectivity of the wood, creating a matte or glossy appearance that further enhances or subtly alters the perceived grain. This interplay between coating properties and wood characteristics necessitates a careful evaluation of the desired aesthetic outcome prior to application.
In summary, the enhancement of natural grain is a crucial consideration in the selection and application of specialized coatings for timber. A judiciously chosen coating not only protects the wood but also serves as a medium for revealing its intrinsic beauty. Understanding the interaction between coating properties and wood characteristics is essential for achieving the desired aesthetic result and maximizing the visual impact of the finished product. The practical significance lies in the ability to transform ordinary wood into aesthetically pleasing pieces that highlight nature’s artistry.
3. Prolonging wood lifespan
The effective preservation of timber structures and artifacts relies heavily on protective coatings. These specialized treatments serve as a crucial barrier against the multitude of environmental and biological factors that contribute to wood degradation, thus significantly extending its useful lifespan. Properly selected and applied, these coatings provide essential defense mechanisms that mitigate the effects of moisture, ultraviolet radiation, fungal attack, and insect infestation.
- Moisture Barrier Formation
Water penetration is a primary cause of wood decay. Specialized coatings create a hydrophobic barrier that prevents moisture absorption, minimizing swelling, warping, and subsequent fungal growth. The effectiveness of this barrier is critical in environments with high humidity or frequent precipitation. For example, decking timber exposed to constant moisture requires a robust coating to prevent rot and maintain structural integrity.
- UV Radiation Shielding
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation breaks down lignin, a key component of wood structure, leading to surface degradation and discoloration. Coatings incorporating UV absorbers or reflectors mitigate this damage, preserving the wood’s original appearance and structural strength. External cladding benefits greatly from this protection, as it reduces the need for frequent refinishing and repairs caused by sun damage.
- Biocidal Properties
Fungal and insect infestations can rapidly compromise the structural integrity of wood. Some coatings incorporate biocides that inhibit the growth of fungi and deter insect activity. This is particularly important for timber used in ground contact or in areas prone to termite infestation. Wooden fence posts treated with such coatings exhibit significantly extended lifespans compared to untreated alternatives.
- Physical Protection Against Abrasion and Impact
Coatings provide a durable surface that resists scratches, dents, and other forms of physical damage. This protection is particularly relevant for high-traffic areas, such as flooring or furniture. The application of a hard-wearing coating to wooden flooring can significantly reduce wear and tear, prolonging its aesthetic appeal and structural soundness.
The combined effect of these protective mechanisms is a significant increase in the lifespan of treated timber. The correct selection and application of specialized coatings are integral to preserving the natural beauty and structural integrity of wood products, reducing the need for costly repairs and replacements. The investment in appropriate coatings yields substantial returns in terms of extended durability and long-term preservation.
4. Resistance to damage
The inherent properties of a timber coating directly influence its ability to withstand various forms of damage, impacting the longevity and aesthetic quality of the underlying wood. The resistance characteristics are vital when selecting a protective layer for Australian wood species, each possessing unique densities and grain structures requiring tailored protective strategies.
- Abrasion Resistance
The ability to withstand surface wear from friction is paramount, especially for high-traffic areas such as flooring or furniture. Coatings formulated with hard resins and additives enhance resistance to scratches, scuffs, and general wear, preserving the aesthetic integrity of the treated wood. Examples include polyurethane-based coatings commonly used on timber floors in commercial settings, resisting damage from foot traffic and cleaning equipment.
- Impact Resistance
Coatings must provide a degree of protection against impacts that could cause dents, chips, or cracks in the wood. Impact resistance is influenced by the coating’s flexibility and hardness. Elastomeric coatings, for example, offer enhanced impact resistance due to their ability to absorb and dissipate energy from impacts. This is particularly important for wooden components in sporting facilities or furniture subjected to heavy use.
- Chemical Resistance
Exposure to various chemicals, such as cleaning agents, solvents, or spills, can degrade or stain unprotected wood surfaces. Coatings formulated with chemical-resistant properties provide a barrier against these substances, preventing damage and maintaining the appearance of the wood. This is crucial in laboratory or industrial settings where timber surfaces may come into contact with corrosive chemicals, necessitating coatings with robust chemical resistance.
- Water Resistance
Coatings that prevent water penetration are critical for preventing swelling, warping, and rot in wood. Water-resistant coatings create a hydrophobic barrier that repels water, safeguarding the wood from moisture-related damage. This is particularly important for exterior timber structures exposed to rain, humidity, or saltwater spray. An example includes spar varnish used on marine applications, offering excellent water resistance and protection against the elements.
The selection of coatings that exhibit high resistance to damage is a key consideration for ensuring the long-term performance and aesthetic appeal of timber, particularly when utilizing unique Australian species. These protective barriers offer diverse forms of resistance against abrasion, impact, chemicals, and water intrusion. Understanding the specific environmental and usage conditions will dictate the optimal coating selection for specific timber projects, ensuring longevity and minimizing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
5. Variety of types
The range of available coatings designed for timber is extensive, driven by the diversity of wood species, application contexts, and desired aesthetic outcomes. These coatings, often referred to collectively as “Australian Wood Finish” due to their prominent use on native timbers, are tailored to address specific challenges and enhance the natural characteristics of the wood. This variety necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the properties and intended applications of each type.
- Oil-Based Finishes
Penetrating oils, such as linseed or tung oil, are designed to soak into the wood fibers, providing a natural-looking finish that enhances the grain. These finishes offer limited surface protection and require periodic reapplication. They are frequently used on furniture and interior woodwork where a soft, matte appearance is desired. An example is the use of tung oil on a handcrafted redgum dining table to enhance its natural color and grain pattern.
- Water-Based Acrylics
Acrylic coatings offer good durability, low odor, and ease of application. They form a protective film on the wood surface, providing resistance to scratches and stains. These finishes are suitable for both interior and exterior applications and are available in a range of sheen levels. For instance, water-based acrylics are often used on weatherboards to provide UV protection and resist cracking or peeling.
- Polyurethanes
Polyurethane coatings are known for their exceptional durability and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and water. They form a hard, protective layer on the wood surface, making them ideal for high-traffic areas such as flooring and countertops. Both oil-based and water-based polyurethanes are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, oil-based polyurethane is commonly applied to hardwood floors to provide a tough, long-lasting finish.
- Varnishes
Varnishes offer a high level of protection against moisture and chemicals, making them suitable for marine applications and exterior woodwork exposed to harsh weather conditions. They form a durable, glossy finish that can withstand significant wear and tear. Spar varnish, in particular, is designed to resist saltwater and UV radiation, making it a popular choice for boats and other marine structures. An example is its use to protect the brightwork on a timber sailing vessel.
The selection of the most appropriate “Australian Wood Finish” hinges on a careful consideration of the specific timber species, the intended use of the object, and the desired level of protection and aesthetic effect. Understanding the distinctions between these coatings enables informed decision-making, resulting in enhanced durability and visual appeal for wooden products.
6. Appropriate application methods
The efficacy of any coating system on native timbers is directly correlated with adherence to recommended application methodologies. Deviation from these methods can compromise the protective properties, longevity, and aesthetic qualities of the coating. Mastering these techniques is indispensable for preserving and enhancing the inherent characteristics of the wood.
- Surface Preparation Techniques
Proper surface preparation is paramount for adhesion. This includes sanding to a specified grit, cleaning to remove contaminants, and ensuring the wood is dry. Australian hardwoods, such as jarrah and spotted gum, require meticulous sanding to create a smooth surface for optimal coating penetration. Failure to properly prepare the surface can result in poor adhesion, premature coating failure, and compromised protection against moisture and UV radiation.
- Application Tool Selection
The choice of application tool brush, roller, or spray equipment is dictated by the type of coating and the complexity of the surface. Brushes are suitable for detailed work, while rollers are efficient for large, flat surfaces. Spray application provides a uniform finish but requires specialized equipment and technique. Selecting the correct applicator ensures even coating distribution, minimizes brush marks or roller stipple, and optimizes the aesthetic outcome. For example, applying a high-solids varnish with an inappropriate brush can result in uneven coverage and visible brush strokes.
- Environmental Conditions Control
Ambient temperature, humidity, and airflow significantly influence coating performance. Application outside the recommended temperature range can affect viscosity and drying time, leading to runs, sags, or blistering. High humidity can impede drying and promote the formation of a hazy or cloudy finish. Proper ventilation is essential for solvent evaporation and worker safety. Controlling these environmental variables is vital for achieving a durable, aesthetically pleasing coating on Australian timbers. Avoid application in direct sunlight or during periods of high humidity.
- Layering and Drying Time Adherence
Applying multiple thin coats, rather than one thick coat, enhances durability and prevents runs or drips. Each layer should be allowed to dry completely according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Insufficient drying time can result in trapped solvents, leading to a soft or tacky finish. Excessive drying time between coats can compromise intercoat adhesion. Following the recommended layering and drying time protocols is essential for achieving a robust, long-lasting coating system on native wood surfaces. Consult the technical data sheet for precise drying time recommendations.
These interconnected facets underscore the importance of diligence in application. Strict adherence to recommended practices ensures that the chosen coating provides optimal protection and enhances the natural beauty of Australian timbers, maximizing their longevity and aesthetic appeal. Improper application can negate the benefits of even the highest-quality coating.
7. Aesthetic consideration
Aesthetic considerations are intrinsically linked to the selection and application of coatings on timber, particularly when focusing on native Australian species. The visual outcome is often a primary driver in the decision-making process, influencing the choice of coating type, sheen level, and application technique. These coatings aim not only to protect the wood but also to enhance its natural beauty, accentuating grain patterns, color variations, and overall visual appeal. Failure to prioritize aesthetic considerations can result in a finished product that does not align with the desired visual outcome, diminishing the perceived value and appeal of the timber project. For example, a clear coating might be selected to highlight the natural warmth and complex grain of Tasmanian oak, while a tinted coating might be chosen to complement a specific interior design scheme. The selection is a direct response to a desired visual character.
The practical implications of aesthetic choices extend beyond mere visual appeal. The chosen coating can influence the perceived value and marketability of a product. A well-finished piece of furniture or a beautifully coated deck is more likely to command a higher price and attract more customers. Furthermore, aesthetic considerations can impact the user experience. A smooth, even finish is not only visually appealing but also feels pleasant to the touch. Conversely, a poorly applied coating with visible brush marks or an uneven sheen can detract from the overall quality and user satisfaction. The application of different finishes on the same type of timber will cause distinct visual impressions; a matte finish offers a natural, understated look, while a gloss finish adds a reflective sheen, highlighting the woods depth.
In conclusion, the intersection of aesthetic considerations and timber coatings is a critical factor in achieving successful and visually appealing results. Prioritizing aesthetic goals throughout the coating selection and application process enhances the value, marketability, and user experience of timber projects. Challenges remain in balancing aesthetic preferences with the practical requirements of protection and durability, necessitating careful consideration of all factors. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these elements allows for informed decisions and a superior finished product.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding protective coatings for timber, particularly those native to Australia. These answers aim to clarify selection, application, and maintenance aspects.
Question 1: What constitutes an “Australian Wood Finish?”
The term generally refers to coating systems designed for use on Australian timber species, often emphasizing the enhancement of natural grain and providing protection against local environmental conditions. There is no single, universally defined product.
Question 2: How does one select the correct coating for a specific timber type?
The selection process should consider the timber species, intended use (interior or exterior), and desired aesthetic outcome. Hardwoods typically require different treatments than softwoods, and exterior applications necessitate UV-resistant coatings.
Question 3: What surface preparation is required before applying a coating?
Surfaces must be clean, dry, and free of contaminants. Sanding is generally necessary to create a smooth, even surface that promotes adhesion. Existing coatings should be removed completely.
Question 4: How often should a wood finish be reapplied?
Reapplication frequency depends on the type of coating, exposure to environmental factors, and wear. Exterior applications typically require more frequent reapplication than interior applications. Inspect the finish regularly for signs of degradation.
Question 5: What are the common signs of coating failure?
Common indicators include cracking, peeling, blistering, discoloration, and loss of adhesion. These signs indicate that the coating is no longer providing adequate protection and should be addressed promptly.
Question 6: Are there any safety precautions to consider when applying coatings?
Adequate ventilation is essential, and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn, including gloves and respirators when necessary. Follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines for the specific product being used.
Effective timber preservation relies on the informed selection and application of appropriate coating systems. Understanding these fundamental principles enhances the longevity and aesthetic appeal of wooden structures and artifacts.
The following section will explore specific coating products and their suitability for various applications.
In Conclusion
This exploration has detailed the multifaceted aspects of protective coatings for timber, with a focus on those termed “Australian Wood Finish.” The discourse encompassed the importance of environmental protection, the enhancement of natural grain, the prolongation of wood lifespan, and the resistance to damage. Further, the breadth of available product types and the critical nature of appropriate application methods were examined. Aesthetic considerations were also highlighted as crucial elements in the decision-making process.
Ultimately, the responsible and informed application of a suitable coating constitutes a vital investment in the longevity and aesthetic preservation of timber. Continued diligence in selecting and implementing these protective measures will ensure the enduring beauty and structural integrity of wood elements in various applications. Further research and adherence to best practices are encouraged to maximize the benefits derived from “Australian Wood Finish” technologies.





![Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing Solve the Wood Finisher Crossword Clue! [Answer Guide] | Best Final Touch: Elevate Your Projects with Professional Finishing](https://bestfinaltouch.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-301-300x200.jpg)
