The process of applying a protective or decorative layer to metallic surfaces, often involving treatments to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or aesthetic appeal, requires specialized knowledge and adherence to stringent standards. This specialized field encompasses various techniques, from electroplating and anodizing to powder coating and passivation. A demonstration of competence within this domain necessitates a formal evaluation process, confirming proficiency and adherence to specified quality control measures.
Employing qualified professionals in surface treatment ensures consistent quality and reliability in the final product. This practice minimizes defects, extends product lifespan, and enhances overall performance. Furthermore, engagement with recognized professionals often provides access to advanced techniques and specialized expertise, contributing to greater efficiency and potentially lower costs in the long run. Historically, the drive for durability and aesthetic refinement has fueled advancements in this field, resulting in sophisticated processes and materials used today.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specific types of surface treatments, the criteria for evaluation and recognition, and the benefits of utilizing recognized experts in various industries. This exploration will also address the impact of environmental regulations and the future trends shaping the advancement of this important sector.
Expert Guidance on Surface Treatment Application
The following recommendations are offered to facilitate optimal outcomes in surface treatment application, emphasizing durability, quality, and adherence to industry standards.
Tip 1: Material Selection. Choosing the correct base metal and coating material is paramount. Compatibility considerations should include galvanic corrosion potential, thermal expansion coefficients, and intended environmental exposure.
Tip 2: Surface Preparation. Adequate surface preparation is critical for coating adhesion. This includes thorough cleaning to remove oils, oxides, and other contaminants, often achieved through mechanical abrasion or chemical etching.
Tip 3: Process Control. Maintaining strict control over process parameters during coating application is essential. This includes monitoring temperature, current density (in electroplating), and spray pressure (in powder coating) to ensure consistent coating thickness and properties.
Tip 4: Quality Assurance Testing. Implementing rigorous quality assurance testing throughout the process helps to identify and address any defects early on. Common tests include adhesion testing, thickness measurement, and corrosion resistance evaluation.
Tip 5: Environmental Compliance. Adherence to all relevant environmental regulations is mandatory. This includes proper disposal of waste materials, minimization of hazardous chemical usage, and implementation of sustainable practices.
Tip 6: Documentation and Traceability. Meticulous record-keeping of all process parameters, material batches, and test results is vital for traceability and problem-solving. This information also aids in process optimization and continuous improvement.
Tip 7: Continuous Training and Improvement. Investing in ongoing training for personnel ensures they remain current with best practices and emerging technologies. A culture of continuous improvement helps to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, leading to enhanced quality and reduced costs.
Adherence to these guidelines will contribute significantly to the successful application of surface treatments, resulting in improved product performance, extended service life, and compliance with industry regulations.
The next section will examine the practical application of these principles in specific industrial contexts.
1. Standards Compliance
Adherence to established standards is paramount in surface treatment application. These standards, often promulgated by organizations such as ISO, ASTM, or industry-specific bodies, dictate minimum requirements for process control, material selection, testing methodologies, and performance characteristics. The application of these standards directly impacts the reliability, durability, and overall quality of the finished product.
- Material Certification
Standards often mandate the use of materials that meet specific chemical and physical property requirements. This includes verification of material composition, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance through certified testing labs. For instance, plating solutions must adhere to specific impurity limits to ensure consistent deposition quality. Failure to comply with material certification standards can lead to premature failure of the finished product, increased warranty claims, and potential safety hazards.
- Process Control Protocols
Specific standards delineate precise procedures for surface preparation, application techniques, and post-treatment processes. This includes specifying parameters such as temperature, current density, pH levels, and immersion times. Documented process control protocols ensure repeatability and minimize process variability, leading to consistent coating thickness, adhesion, and corrosion protection. Deviation from these protocols can result in uneven coatings, reduced adhesion strength, and diminished product lifespan.
- Testing and Inspection Procedures
Standards prescribe specific testing and inspection methodologies to verify that the applied finish meets performance requirements. This includes destructive testing, such as salt spray testing to assess corrosion resistance, and non-destructive testing, such as thickness measurement using eddy current probes. Conformance to these testing standards provides quantifiable evidence of quality and ensures that the finish will perform as intended under specified operating conditions.
- Documentation and Traceability Requirements
Maintaining detailed records of all process parameters, material certifications, and test results is essential for traceability and accountability. Standards often mandate specific documentation requirements, including batch numbers, process logs, and inspection reports. This documentation enables identification of root causes in case of failures, facilitates process optimization, and provides verifiable evidence of compliance for regulatory audits and customer inquiries.
The multifaceted nature of standards compliance underscores its critical role in surface treatment application. Through diligent adherence to material certification, process control protocols, testing procedures, and documentation requirements, a surface treatment provider can demonstrably ensure the quality, reliability, and longevity of their finished products.
2. Corrosion Resistance
The capacity of a metal to withstand degradation caused by chemical or electrochemical reactions with its environment is paramount in numerous applications. This resistance is not an inherent property for all metals and often necessitates specific surface treatments to enhance protection against corrosive agents. Surface treatments applied via certified processes are designed to act as a barrier between the metal substrate and the environment, inhibiting or slowing down the rate of corrosion. The application of such treatments is not merely aesthetic; it directly impacts the structural integrity, longevity, and operational safety of the metal component. For example, in the automotive industry, certified zinc plating or e-coating processes are employed to protect steel components from road salt and moisture, thereby preventing rust and extending the vehicle’s lifespan. Similarly, in aerospace applications, anodizing or chromate conversion coatings are used on aluminum alloys to mitigate corrosion caused by atmospheric conditions and exposure to harsh chemicals.
Certified processes, often adhering to standards such as ISO or ASTM specifications, ensure that the surface treatment is applied correctly and consistently. These certifications validate the quality control measures in place, including material selection, process parameter monitoring, and performance testing. Consequently, the link between corrosion resistance and surface treatments is direct and quantifiable. The selection of the appropriate surface treatment depends on various factors, including the type of metal, the intended environment, and the required level of protection. A certified process includes rigorous testing to verify that the chosen treatment meets the specific corrosion resistance requirements. For example, salt spray testing, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and immersion tests are commonly used to evaluate the effectiveness of the applied coating. The results of these tests provide objective data to support the claim of enhanced corrosion resistance. Furthermore, certified surface treatment providers typically offer warranties or guarantees, providing assurance to customers regarding the performance and durability of the finished product.
In summary, the application of certified surface treatments is essential for achieving optimal corrosion resistance in metal components. Certified processes ensure that the correct materials are used, that the treatment is applied correctly, and that the finished product meets specified performance criteria. The practical significance of this understanding is that it enables engineers and designers to select appropriate surface treatments to enhance the lifespan, reliability, and safety of metal components in diverse applications. While challenges remain in developing new and more effective surface treatments, the continuous pursuit of innovation and adherence to certified processes remain critical for mitigating the detrimental effects of corrosion.
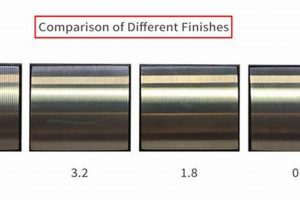
3. Aesthetic Enhancement
The appearance of a metal product significantly influences its market acceptance and perceived value. While functional properties such as corrosion resistance and durability are paramount, the visual appeal of a metallic surface plays a crucial role in consumer satisfaction and brand perception. Certified metal finishing processes directly contribute to aesthetic enhancement through various methods, including polishing, plating, coating, and texturing. These processes alter the surface characteristics of the metal, creating a desired visual effect. For example, electroplating with precious metals such as gold or silver imparts a luxurious appearance to jewelry and decorative items. Powder coating can provide a wide range of colors and textures, allowing manufacturers to customize the look of their products. The consistency and quality of these aesthetic enhancements are directly tied to the certification of the metal finishing process.
The connection between aesthetic enhancement and certification lies in the assurance of consistent, repeatable results. Certified processes adhere to strict quality control measures, ensuring that the final finish meets predetermined visual standards. This is particularly important in industries where visual uniformity is critical, such as the automotive and appliance sectors. In automotive manufacturing, for example, chrome plating is often used to enhance the appearance of trim and accessories. Certified plating processes guarantee a uniform, defect-free finish across all components, contributing to the overall aesthetic quality of the vehicle. Similarly, in appliance manufacturing, powder coating is employed to provide a durable and visually appealing finish to refrigerators, washing machines, and other products. Certification ensures that the color, gloss, and texture of the coating are consistent across all units, enhancing the product’s aesthetic appeal and perceived value. Furthermore, the selection of appropriate finishing techniques and materials, in accordance with certified protocols, directly affects long-term visual performance, mitigating issues like fading, discoloration, and scratches.
Ultimately, the successful integration of aesthetic enhancement into metal products requires a commitment to certified finishing processes. This ensures that the desired visual effect is achieved consistently, reliably, and durably. Challenges in achieving and maintaining optimal aesthetic quality include managing variations in raw materials, controlling process parameters, and addressing environmental factors. However, by adhering to certified standards and investing in ongoing process improvements, manufacturers can reliably deliver metal products that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements, contributing to enhanced customer satisfaction and market success. The importance of aesthetic considerations should not be overlooked, as it is a key driver of consumer preference and brand loyalty. Therefore, integrating certified metal finishing processes is essential for creating products that are visually appealing, durable, and competitive in the marketplace.
4. Process Validation
Process validation is a critical component of certified metal finishing, serving as the systematic establishment of documented evidence that provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting predetermined specifications and quality attributes. In the context of metal finishing, this involves a comprehensive assessment of all process parameters, including cleaning, surface preparation, application of coatings, and post-treatment processes. The objective is to ensure that each step is consistently executed within defined control limits to yield a predictable and acceptable outcome. Process validation is not merely a one-time activity but an ongoing commitment to maintain process integrity and product quality. For instance, in the aerospace industry, where metal components are subject to stringent performance requirements, process validation is mandatory for surface treatments such as anodizing and passivation. Any deviation from validated parameters can compromise the structural integrity or corrosion resistance of the finished part, potentially leading to catastrophic consequences. Therefore, the absence of thorough process validation renders any claim of “certified metal finishing” fundamentally invalid.
The practical application of process validation in metal finishing involves several key steps, including defining critical process parameters (CPPs), establishing acceptance criteria, conducting process performance qualification (PPQ), and implementing ongoing process monitoring. CPPs are those variables that have a direct impact on product quality, such as bath chemistry, temperature, current density, and immersion time. Acceptance criteria define the acceptable range for each CPP. PPQ involves running multiple production batches under controlled conditions to demonstrate process capability and consistency. Ongoing process monitoring entails the use of statistical process control (SPC) tools to track CPPs and identify any trends or deviations that may indicate a potential problem. Consider the electroplating process, where the thickness and uniformity of the plated layer are critical quality attributes. Process validation would involve establishing and monitoring CPPs such as plating solution composition, current density, and agitation rate. SPC charts would be used to track these CPPs and detect any excursions from established control limits. If a deviation is detected, corrective action would be taken to restore the process to its validated state.
In conclusion, process validation is inextricably linked to certified metal finishing. It provides the documented evidence necessary to demonstrate that a process is capable of consistently producing a product meeting predetermined specifications. The absence of rigorous process validation undermines the credibility and reliability of any certification claim. The challenges associated with process validation include the complexity of metal finishing processes, the variability of raw materials, and the need for continuous monitoring and improvement. However, by embracing a systematic and data-driven approach to process validation, metal finishers can enhance product quality, reduce defects, and build trust with their customers. Ultimately, the commitment to process validation is a commitment to excellence in metal finishing.
5. Longevity Assurance
Longevity assurance in metal components and products is intrinsically linked to certified metal finishing processes. The application of appropriate surface treatments, validated through certification, directly extends the operational lifespan of metallic substrates by mitigating degradation mechanisms such as corrosion, wear, and fatigue. This relationship highlights the crucial role of certified processes in ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
- Material Selection and Compatibility
The choice of base metal and finishing material is paramount for longevity. Certified processes mandate the use of compatible materials, minimizing galvanic corrosion potential and ensuring optimal adhesion between the substrate and the coating. For example, using a zinc-nickel alloy plating on a steel component intended for marine environments provides superior corrosion protection compared to standard zinc plating, effectively extending the component’s service life. Incompatible material pairings, conversely, can lead to accelerated degradation despite the application of a surface treatment.
- Process Control and Consistency
Certified metal finishing processes are characterized by stringent control over process parameters, such as temperature, current density, and immersion time. These controls ensure consistent coating thickness, uniformity, and adhesion, which are essential for long-term performance. For instance, in anodizing aluminum, precise control of the electrolyte composition, voltage, and temperature is crucial for creating a dense, durable oxide layer that provides long-lasting corrosion protection. Deviations from these controlled parameters can result in coatings with reduced protective properties and premature failure.
- Quality Assurance and Testing
Rigorous quality assurance testing is an integral part of certified metal finishing. Testing methods, such as salt spray testing, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and adhesion testing, are used to verify that the applied finish meets predetermined performance criteria. These tests provide quantifiable data that support claims of enhanced durability and extended service life. For example, a component that successfully withstands 1000 hours of salt spray exposure under a certified coating process demonstrates a significantly higher level of corrosion resistance compared to an untreated component.
- Traceability and Documentation
Certified metal finishing processes require meticulous record-keeping of all process parameters, material certifications, and test results. This documentation provides traceability, enabling the identification of root causes in case of failures and facilitating process optimization. Traceability also allows for the verification of compliance with relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements. Comprehensive documentation supports longevity assurance by enabling proactive maintenance and timely replacement of components before failure occurs, minimizing downtime and maximizing the overall lifespan of the system.
The elements of certified metal finishing encompassing judicious material selection, rigorous process control, stringent quality assurance, and meticulous traceability collectively contribute to longevity assurance. The integration of these facets enhances the durability and extends the lifespan of metal components across a wide array of industries, emphasizing the crucial importance of certification in achieving long-term reliability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Certified Metal Finishing
The following questions and answers address common inquiries regarding the importance, processes, and implications of certified metal finishing in various industries.
Question 1: What constitutes “certified” metal finishing?
A “certified” metal finishing process indicates that a third-party accreditation body has rigorously assessed and confirmed that the process adheres to established industry standards and quality control protocols. Certification assures consistency, reliability, and compliance with specified performance criteria.
Question 2: Why is certification important in metal finishing?
Certification mitigates risk. It provides assurance that the finished product will meet predetermined performance requirements, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic standards. It also enables traceability and accountability throughout the finishing process.
Question 3: What standards are commonly associated with certified metal finishing?
Common standards include ISO 9001, AS9100 (aerospace), and industry-specific ASTM standards. These standards outline requirements for process control, quality management, testing, and documentation.
Question 4: How does certification affect the cost of metal finishing?
While initial costs may be slightly higher due to certification requirements, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment. Reduced defects, improved product lifespan, and enhanced reliability contribute to lower overall costs.
Question 5: What are the implications of using non-certified metal finishing processes?
Utilizing non-certified processes can result in inconsistent quality, increased risk of defects, potential product failures, and compromised performance. Furthermore, it may lead to non-compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Question 6: How is a certified metal finishing provider selected?
Selection should be based on the provider’s experience, certifications, quality control practices, technical expertise, and ability to meet specific project requirements. It is advisable to request documentation of their certification status and review their quality control procedures.
Certification in metal finishing is a cornerstone of quality assurance and risk management. It enables businesses to make informed decisions, ensuring that their products meet required performance criteria and contribute to long-term reliability.
The subsequent section will delve into real-world case studies illustrating the benefits of employing certified metal finishing processes.
Certified Metal Finishing
This examination has elucidated the multifaceted benefits of certified metal finishing. From enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal to rigorous process validation and assured longevity, the adoption of certified practices represents a commitment to quality and reliability. The adherence to recognized standards, meticulous process control, and stringent testing protocols associated with certification demonstrably contribute to the enhanced performance and extended lifespan of metal components across diverse industrial applications.
The decision to employ certified metal finishing processes reflects a strategic imperative. Recognizing the inherent value in adhering to proven methodologies and verifiable standards mitigates risk and fosters confidence. Continued investment in these processes will undoubtedly shape the future of the industry, driving innovation and ensuring the enduring quality of metallic products.