
This tool is a type of pneumatic nail gun utilized for delicate woodworking and trim applications. It employs small-gauge fasteners, typically 18-gauge, to secure materials without significant splitting or marring of the... Read more »

The selection of a fastening tool for decorative moldings necessitates careful consideration. One must evaluate factors such as the molding’s size and material, as well as the desired aesthetic outcome. The chosen... Read more »

The disparity between slender fasteners designed for trim and those suited for more substantial woodworking projects lies primarily in their size, gauge, and head design. One type, characterized by a finer gauge... Read more »

The selection of a pneumatic nail gun often hinges on the project’s specific requirements. Two common types are distinguished primarily by the gauge and resulting holding power of the fasteners they utilize.... Read more »

The divergence between these two types of fasteners primarily lies in their size and application. One is generally thinner and used for delicate trim work where minimal visibility is desired, while the... Read more »

The choice between a tool that drives finer gauge fasteners and one that utilizes slightly thicker nails hinges on the specific application. One is designed for delicate trim and detailed work, minimizing... Read more »
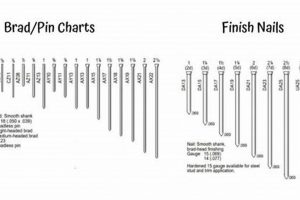
The comparison involves fasteners of differing sizes and the tools that drive them. One uses a smaller, headless or near-headless nail, designed for delicate work where minimal visibility is desired. The other... Read more »

The selection of an appropriate pneumatic fastening tool is paramount when installing decorative moldings. Two common choices for this application are tools designed to drive smaller-gauge fasteners intended to minimize visible entry... Read more »

The core distinction lies in the type of fastener each tool employs and the resulting impact on the work surface. One utilizes a thicker gauge nail, offering greater holding power but leaving... Read more »

This tool, used extensively in woodworking and carpentry, drives fasteners into materials for secure joining. Typically pneumatic or cordless electric, it provides a controlled and efficient method for attaching trim, molding, and... Read more »


