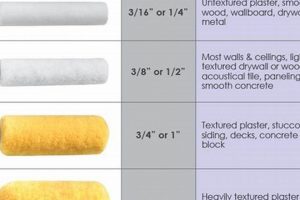
The selection of sheen for paint intended for overhead surfaces significantly impacts the overall aesthetic and perceived luminosity of a room. Different levels of reflectance influence how light interacts with the surface, affecting the appearance of imperfections and the degree of visual depth.
Employing a specific overhead coating contributes to a more uniform and less distracting visual plane. Historically, matte formulations were favored to minimize glare and conceal surface irregularities commonly found on ceilings. This approach also serves to create an impression of greater height and spaciousness.
Understanding the properties of various paint sheens allows for a more informed decision when addressing concerns such as light reflection, surface texture, and maintenance requirements. The following sections detail the specific characteristics and applications of different finishes suitable for overhead use.
Considerations for Selecting Overhead Coating Sheen
Optimal overhead coating selection necessitates careful evaluation of room attributes and functional requirements. The following guidelines assist in achieving a visually appealing and practically sound outcome.
Tip 1: Assess Existing Surface Condition: Before application, meticulously inspect the ceiling for imperfections such as cracks, dents, or uneven textures. Matte or flat finishes effectively mask these flaws, whereas glossier sheens tend to accentuate them. Address any significant damage with appropriate patching and smoothing compounds prior to painting.
Tip 2: Evaluate Room Lighting: The amount and type of light (natural or artificial) significantly influences the perceived appearance of the overhead surface. Rooms with ample natural light benefit from flatter finishes, which diffuse light and minimize glare. Conversely, darker rooms may benefit from a slightly higher sheen to enhance reflectivity and increase overall brightness.
Tip 3: Match Sheen to Room Function: High-humidity environments, such as bathrooms or kitchens, necessitate coatings with enhanced moisture resistance. While generally discouraged, should a higher sheen be desired in these areas, ensure proper ventilation to prevent moisture buildup and subsequent paint degradation.
Tip 4: Prioritize Uniformity: Regardless of the chosen sheen, strive for a consistent application to avoid noticeable variations in appearance. Employ proper painting techniques, such as maintaining a wet edge and using high-quality rollers, to ensure an even distribution of the coating.
Tip 5: Consider Recessed Lighting: The presence of recessed lighting fixtures can affect how a ceiling finish appears. Flat finishes are generally preferred to minimize light reflection and prevent unwanted glare or “hot spots” around the fixtures.
Tip 6: Test Before Committing: Prior to painting the entire ceiling, test a small, inconspicuous area to assess the chosen sheen’s suitability. This allows for adjustments based on the room’s specific lighting conditions and surface characteristics.
These considerations facilitate informed decisions, promoting aesthetically pleasing and durable overhead surfaces tailored to specific environmental and functional demands.
The next section will delve into specific paint formulations suitable for ceilings, further expanding on the options available.
1. Light Reflectance Value (LRV) and Overhead Coating Selection
Light Reflectance Value (LRV) quantifies the percentage of visible light reflected from a painted surface. This metric is directly correlated to the selection of a finish for overhead coatings. Low LRV finishes, such as matte or flat paints, absorb a significant amount of light, minimizing glare and diffusing light evenly across the surface. This characteristic is advantageous in concealing imperfections commonly found on ceilings, such as minor cracks or uneven textures. A practical example is the use of a flat white finish in a bedroom to reduce glare from overhead lighting and create a softer, more relaxing ambiance. The lower LRV minimizes the impact of any surface irregularities, resulting in a visually uniform plane.
Higher LRV finishes, such as eggshell or satin, reflect more light. While generally not recommended for ceilings due to their tendency to highlight imperfections, they may be considered in specific applications. For instance, a kitchen with limited natural light might benefit from a slightly higher LRV coating to increase overall brightness. However, meticulous surface preparation is crucial to mitigate the risk of accentuated flaws. The choice must also account for the type and placement of lighting fixtures, as increased reflectance can lead to undesirable glare around recessed lights or pendant fixtures.
In summary, LRV is a critical determinant in selecting the appropriate finish for overhead coatings. Lower LRV finishes prioritize imperfection masking and glare reduction, while higher LRV options aim to maximize light reflectance, requiring careful consideration of surface condition and lighting design. The selection process must balance these factors to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional outcome. The goal is to enhance the perceived quality of the ceiling and the overall ambience of the room.
2. Surface Imperfection Masking
The capability of a coating to conceal surface flaws is a primary consideration when determining the appropriate overhead surface treatment. The relationship between this masking ability and the ultimate coating selection is direct and significant, impacting the final aesthetic appeal of the space.
- Sheen Level and Light Diffusion
Lower sheen levels, such as matte or flat finishes, diffuse light across the surface, minimizing the reflection of light rays. This diffuse reflection effectively obscures minor imperfections, including hairline cracks, slight undulations, and patching imperfections. Conversely, higher sheen levels, like eggshell or satin, exhibit greater reflectivity, which accentuates these same flaws, making them more noticeable. In situations where the overhead surface is not perfectly smooth, a flatter finish is typically preferred to minimize visual distractions.
- Pore Size and Paint Absorption
The porosity of a coating directly influences its ability to conceal imperfections. Flatter finishes generally possess a larger pigment volume concentration (PVC), resulting in a more porous surface. This increased porosity allows the paint to fill minor surface irregularities, effectively leveling the surface and reducing the visibility of flaws. Glossier finishes, with lower PVC, tend to sit atop the surface, reflecting light off any existing imperfections rather than concealing them.
- Application Technique and Layer Build-Up
While the sheen level of a paint is crucial, proper application techniques also contribute to surface imperfection masking. Applying multiple thin coats of a flat finish allows for a gradual build-up of the coating, effectively filling minor imperfections over time. Conversely, applying a thick, uneven coat, regardless of the sheen, can exacerbate existing flaws, creating a textured appearance that highlights imperfections rather than concealing them. Proper surface preparation, including patching and sanding, remains essential regardless of the application technique.
- Pigment Type and Color Choice
The type and concentration of pigments within a coating can also influence its ability to mask imperfections. Darker colors generally tend to reveal surface flaws more readily than lighter colors. Similarly, certain pigments may have a coarser texture, which can further accentuate irregularities. Utilizing high-quality paints with finely ground pigments and selecting lighter, neutral colors can enhance the overall masking effect, complementing the benefits of a flatter finish.
Therefore, the selection of a coating for overhead surfaces, especially in situations where imperfections exist, hinges on a comprehensive understanding of sheen level, porosity, application technique, and pigment characteristics. By prioritizing factors that contribute to effective surface imperfection masking, it is possible to achieve a visually appealing and uniform overhead surface, even in the presence of underlying flaws.
3. Room size perception
The perceived dimensions of a room are inextricably linked to the selection of the overhead surface treatment. The interplay between light, color, and texture, as mediated by the chosen finish, can significantly alter how the volume of a space is experienced. Consequently, informed decisions regarding finish type are crucial for optimizing spatial perception.
- Light Reflectance and Perceived Height
Higher light reflectance values (LRV) associated with glossier finishes tend to make a ceiling appear lower. The increased reflection of light creates a brighter surface that draws the eye downward, effectively reducing the perceived vertical distance. Conversely, lower LRV finishes, such as matte or flat paints, absorb more light, creating a sense of depth and making the ceiling recede visually. This recession can enhance the perception of height, particularly in rooms with low ceilings.
- Color Saturation and Visual Expansion
The color of the overhead surface, in conjunction with its finish, impacts the perceived size of a room. Light, cool colors, especially when combined with matte finishes, tend to create a sense of openness and expansion. The diffuse reflection of light from these surfaces visually pushes the ceiling upward and outward. Conversely, darker, warmer colors, particularly when paired with glossier finishes, can make a room feel smaller and more enclosed. The increased absorption of light and heightened reflection draw the eye inward, diminishing the perceived spatial volume.
- Texture and Visual Depth
The texture of the overhead surface, as affected by the finish, also contributes to room size perception. Smooth, uniform surfaces, achieved with flat or matte finishes, create a sense of continuity and visual depth. The absence of distracting reflections allows the eye to travel unimpeded, enhancing the perception of spaciousness. Conversely, textured surfaces, often resulting from improper application or the use of high-sheen finishes on imperfect surfaces, can create visual clutter and diminish the sense of spaciousness. The irregularities disrupt the visual flow, making the ceiling appear closer and the room feel smaller.
- Glare and Visual Fatigue
Excessive glare, often associated with high-sheen finishes, can contribute to visual fatigue and a diminished sense of spaciousness. The intense reflection of light creates a distracting and uncomfortable visual environment, making the room feel smaller and more claustrophobic. Conversely, matte finishes minimize glare, creating a more comfortable and visually harmonious space. The reduced distraction allows the eye to relax, enhancing the perception of spaciousness and creating a more inviting atmosphere.
Therefore, the finish selected for overhead surfaces plays a pivotal role in shaping room size perception. By carefully considering factors such as light reflectance, color saturation, texture, and glare, it is possible to manipulate the visual properties of a space, optimizing its perceived dimensions and enhancing its overall aesthetic appeal. A nuanced understanding of these relationships is essential for achieving the desired spatial effect and creating a visually pleasing environment.
4. Moisture resistance demands
The presence of elevated moisture levels fundamentally dictates the appropriate selection of coating for overhead surfaces. In environments characterized by high humidity or direct exposure to moisture, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms, coatings with enhanced moisture resistance are essential to prevent degradation and maintain aesthetic integrity. Failure to account for moisture resistance demands can lead to a cascade of detrimental effects, including paint blistering, peeling, and the proliferation of mold and mildew. These issues not only compromise the visual appeal of the space but also pose potential health risks. For example, in a bathroom lacking adequate ventilation, the steam generated during showering can condense on the ceiling, saturating the paint and creating an ideal breeding ground for mold if a moisture-resistant finish is not utilized.
The correlation between sheen level and moisture resistance is significant, though not absolute. Higher sheen coatings, such as semi-gloss or gloss, generally exhibit greater moisture resistance due to their tighter molecular structure and lower porosity. These surfaces are less permeable to water vapor, reducing the likelihood of moisture penetration and subsequent damage. However, the use of higher sheen coatings on ceilings is often discouraged due to their tendency to accentuate surface imperfections. As an alternative, specialized ceiling paints formulated with mildewcides and enhanced binders offer a compromise, providing adequate moisture resistance without the high reflectivity of glossier finishes. Furthermore, proper surface preparation, including the application of a moisture-resistant primer, is crucial in creating a barrier against moisture intrusion, regardless of the chosen topcoat.
In conclusion, recognizing and addressing moisture resistance demands is paramount in the selection of coating for overhead surfaces. While higher sheen coatings offer inherent moisture protection, specialized ceiling paints and proper surface preparation techniques provide viable alternatives that balance performance and aesthetics. Overlooking these considerations can result in costly repairs, compromised air quality, and a diminished overall living environment. Therefore, a thorough assessment of environmental conditions and informed product selection are essential for ensuring the long-term durability and integrity of overhead surfaces in moisture-prone areas.
5. Cleaning ease
The ease with which an overhead surface can be cleaned is directly influenced by the selected coating’s finish. This characteristic is particularly important in areas prone to dust accumulation, cooking splatters, or other forms of soiling. Surfaces with smoother, less porous finishes facilitate easier removal of contaminants, minimizing the effort and resources required for maintenance. The selection of a coating for enhanced cleaning ease necessitates a trade-off with other factors, such as glare reduction and imperfection masking, typically prioritized in overhead applications.
Higher sheen levels, such as eggshell or satin, generally offer improved cleaning ease compared to matte or flat finishes. The reduced porosity of these smoother surfaces prevents dirt and grime from penetrating the coating, allowing for easier wiping with a damp cloth. However, the increased reflectivity of higher sheen coatings can accentuate imperfections, potentially detracting from the aesthetic appeal of the ceiling. In kitchen environments, where grease and cooking splatters are common, a slightly higher sheen may be preferred for its cleanability, provided that the underlying surface is properly prepared to minimize the visibility of imperfections. A flat paint, while adept at concealing flaws, may require more aggressive cleaning methods that could damage the finish over time.
Ultimately, the decision regarding coating selection for overhead surfaces must balance the desire for cleaning ease with other critical considerations, such as aesthetic preferences and the specific environmental conditions of the space. While higher sheen coatings offer improved cleanability, they may not be suitable for all applications. Specialized ceiling paints with stain-resistant properties provide a viable alternative, offering a compromise between cleaning ease and aesthetic appeal. Consistent maintenance practices, including regular dusting and prompt removal of stains, can also minimize the need for aggressive cleaning methods, regardless of the chosen finish. Therefore, cleaning ease is a significant factor influencing overhead surface coating decisions, yet it remains one element within a broader spectrum of considerations.
6. Application consistency
Achieving a uniform appearance on an overhead surface is critically dependent on application consistency, regardless of the coating selected. Variations in application technique directly impact the final appearance, potentially negating the benefits of even the highest-quality paints. Specifically, inconsistencies in roller pressure, overlap, and paint distribution can lead to visible differences in sheen, color saturation, and texture. For instance, using a flat paint, lauded for its ability to mask imperfections, will produce an uneven result if some areas receive more paint than others. The areas with greater paint volume will exhibit a slightly darker shade and potentially a subtle sheen differential, undermining the desired matte uniformity. Therefore, consistent application is not merely a procedural step but an integral component of realizing the intended aesthetic outcome when determining the appropriate overhead surface treatment.
The impact of application consistency is particularly pronounced when working with larger surface areas or in spaces with abundant natural light. In these scenarios, any variations in the coating become readily apparent, creating visual distractions that detract from the overall quality of the finish. To mitigate these risks, employing a systematic approach is essential. This includes maintaining a wet edge during application to avoid lap marks, using a consistent roller technique with appropriate overlap, and ensuring that the paint is thoroughly mixed and free of any lumps or inconsistencies. Furthermore, the use of high-quality application tools, such as premium rollers and brushes, can contribute significantly to achieving a uniform coating. For example, a low-quality roller may shed fibers or distribute paint unevenly, leading to a textured surface despite the use of a smooth finish.
In conclusion, application consistency is not a separate consideration but rather an inseparable element in determining the appropriate coating for overhead surfaces. Inconsistencies in application undermine the inherent properties of the selected paint, regardless of its sheen, color, or quality. Achieving a uniform appearance necessitates a meticulous approach, employing consistent techniques, high-quality tools, and a thorough understanding of the paint’s characteristics. Ultimately, the success of any overhead surface treatment hinges on the ability to translate the intended aesthetic vision into a tangible reality through consistent and skillful application.
7. Glare reduction
The primary function of selecting a particular overhead coating is often to control light reflection and minimize glare. Glare, defined as excessive and uncontrolled brightness, creates visual discomfort and reduces clarity, directly impacting the usability and aesthetic quality of a space. The choice of coating finish directly influences the degree to which glare is present. For instance, a gloss finish, highly reflective, creates significant glare under direct illumination, making it unsuitable for most ceilings. Conversely, a matte finish, by absorbing light, reduces glare, producing a softer, more comfortable visual environment. This is especially important in spaces with high levels of natural light or numerous artificial light sources. Consider a classroom; a ceiling coated in a gloss finish would reflect light from windows and overhead fixtures, creating glare that impairs students’ ability to focus. The appropriate selection of a matte or flat finish mitigates this issue, improving the learning environment.
The practical significance of glare reduction extends beyond visual comfort. Reduced glare enhances visibility, improving safety in areas with potential hazards. For example, in a workshop environment, eliminating glare allows workers to see machinery and tools more clearly, reducing the risk of accidents. Furthermore, managing glare improves the perceived quality of display lighting in retail settings, ensuring that merchandise is presented effectively. In residential spaces, minimizing glare reduces eye strain, creating a more relaxing and comfortable living environment. The careful selection of coating, therefore, contributes not only to aesthetics but also to safety and functional efficiency.
In summary, the relationship between glare reduction and overhead coatings is fundamental. The choice of finish determines the extent to which light is reflected, directly impacting glare levels. Prioritizing glare reduction through the selection of matte or flat finishes improves visual comfort, enhances safety, and optimizes lighting quality. While glossier finishes may offer other advantages, such as ease of cleaning, their inherent tendency to generate glare makes them unsuitable for most overhead applications, underscoring the importance of understanding and addressing glare as a primary consideration in the selection process.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection of coatings for overhead surfaces. These answers are designed to provide clarity and guidance for informed decision-making.
Question 1: Does the texture of a ceiling impact the optimal finish selection?
Yes, surface texture is a critical consideration. Uneven or heavily textured ceilings benefit from matte finishes, which minimize light reflection and conceal imperfections. Smooth ceilings may accommodate higher sheens, but meticulous surface preparation is essential to prevent the accentuation of any existing flaws.
Question 2: Are specialized ceiling paints necessary, or can standard wall paint be used?
While standard wall paint can be applied to ceilings, specialized ceiling paints often contain formulations designed to minimize spattering during application and provide enhanced hiding power. These characteristics can simplify the painting process and improve the final result. Additionally, some ceiling paints incorporate mildewcides, offering added protection in moisture-prone environments.
Question 3: How does room size factor into the decision-making process for overhead coating selection?
In smaller rooms, the impact of light reflection is amplified. Matte finishes are generally preferred to prevent a cramped or claustrophobic feeling. Larger rooms can accommodate slightly higher sheens, but careful consideration must be given to the potential for glare and the visibility of surface imperfections.
Question 4: Can color influence the perceived height of a ceiling?
Yes, color significantly affects the perception of ceiling height. Lighter colors tend to make a ceiling appear higher, while darker colors create the opposite effect. Cool colors, such as blues and greens, also contribute to a sense of spaciousness. The choice of color should be carefully coordinated with the overall room decor and desired aesthetic.
Question 5: Is primer always necessary before painting a ceiling?
The necessity of primer depends on the condition of the existing surface. Bare drywall, stained surfaces, or surfaces coated with oil-based paint require priming to ensure proper adhesion and prevent bleed-through. In cases where the existing surface is clean, sound, and previously painted with a latex-based paint, priming may not be necessary, although it can still improve the uniformity and durability of the finish.
Question 6: How does artificial lighting impact the appearance of different ceiling finishes?
The type and placement of artificial lighting significantly influence the perceived appearance of overhead coatings. Direct lighting accentuates surface imperfections, making matte finishes a more suitable choice. Indirect lighting, on the other hand, diffuses light more evenly, allowing for greater flexibility in finish selection. The color temperature of the lighting should also be considered, as it can affect the perceived warmth or coolness of the paint color.
Key takeaways from this section include the importance of considering surface texture, room size, color, and lighting when selecting coatings for overhead surfaces. Proper surface preparation and informed product selection are crucial for achieving a visually appealing and durable result.
The following section will delve into the practical application techniques for overhead coatings, providing guidance on achieving a professional-quality finish.
Conclusion
Determining the appropriate overhead coating involves a multifaceted assessment of environmental factors, aesthetic goals, and functional requirements. The preceding analysis has underscored the importance of considering light reflectance values, surface imperfection masking, room size perception, moisture resistance demands, cleaning ease, application consistency, and glare reduction. Each of these parameters exerts a significant influence on the ultimate suitability of a given finish, necessitating a deliberate and informed selection process.
The long-term performance and visual appeal of any overhead surface are contingent upon a holistic understanding of these interrelated factors. Continued research and practical application will further refine the methods by which optimal coatings are identified and implemented, contributing to enhanced interior design and improved environmental quality.