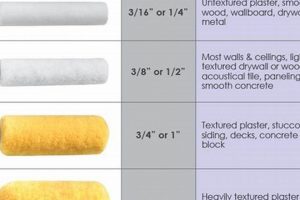
The outermost coating applied to an entry point significantly affects its appearance and longevity. This protective layer, available in various formulations, is designed to shield the door from environmental factors such as sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. For example, a high-quality acrylic latex product, properly applied, can resist cracking and fading, extending the lifespan of the door’s aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
Selecting a superior coating option provides several benefits. It enhances curb appeal, protects the underlying material from degradation, and can even improve energy efficiency by reflecting sunlight. Historically, the choice of these coatings was limited by available technology, with oil-based paints being a common, albeit less durable, option. Modern formulations offer improved performance characteristics, including better adhesion, resistance to mildew, and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, contributing to a healthier environment.
Understanding the properties of different coating types, proper surface preparation techniques, and appropriate application methods are essential for achieving optimal results. The subsequent sections will delve into these key aspects to guide the selection and implementation of a suitable coating for exterior doors.
Enhancing Door Aesthetics and Longevity
Selecting and applying a durable protective layer is crucial for maintaining the visual appeal and structural integrity of exterior doors. These tips offer guidance on achieving optimal results.
Tip 1: Surface Preparation is Paramount. Ensure the door’s surface is clean, dry, and free from loose paint or debris. Proper cleaning and sanding contribute significantly to adhesion.
Tip 2: Prime for Success. Apply a quality primer compatible with both the door material and the chosen product. Priming enhances adhesion and creates a uniform surface for application.
Tip 3: Select the Right Type. Consider acrylic latex or oil-based alkyd options. Acrylic latex offers flexibility and resistance to cracking, while oil-based options provide a hard, durable sheen.
Tip 4: Opt for a Satin or Semi-Gloss Sheen. These sheens offer a balance between durability and ease of cleaning. Higher gloss levels are more reflective and may show imperfections.
Tip 5: Apply Thin, Even Coats. Multiple thin coats are superior to a single thick coat. This prevents drips, sags, and ensures proper curing.
Tip 6: Consider the Weather. Avoid applying in direct sunlight or during periods of high humidity. Ideal conditions promote proper drying and curing.
Tip 7: Invest in Quality Tools. Use high-quality brushes and rollers designed for the chosen product. Proper tools contribute to a smooth, professional application.
Effective application results in a visually appealing and weather-resistant barrier, extending the door’s lifespan and minimizing maintenance requirements.
The following section will explore the implications of different environmental factors on coating performance, and strategies for mitigating their effects.
1. Durability
Durability, concerning exterior door coatings, refers to the ability to withstand environmental stresses and maintain its protective and aesthetic qualities over an extended period. This is a pivotal characteristic, serving as a primary determinant of the product’s long-term performance and value. The connection between durability and an optimal exterior door coating is direct: the higher the durability, the longer the door is protected from damage caused by weather, impact, and general wear and tear.
Consider the scenario of two doors, each finished with a different coating. The first, a low-grade product lacking in durability, may exhibit cracking, peeling, and fading within a year of exposure to typical weather conditions. The second, finished with a high-durability product, resists these effects for several years, maintaining its color, finish, and protective properties. This demonstrates the practical implications of durability. High-traffic entryways, exposed to frequent use and varying weather conditions, necessitate coatings with enhanced durability to prevent premature degradation and the associated maintenance costs.
The selection of a coating engineered for exceptional durability directly impacts the longevity and appearance of an exterior door. Investing in products with proven resistance to abrasion, moisture, and UV radiation mitigates the need for frequent reapplication or repairs. Therefore, durability is not merely a desirable attribute but an essential component defining the performance of an optimal exterior door coating. The challenge lies in identifying coatings that deliver a balance between durability, aesthetic appeal, and ease of application, considering specific environmental factors and usage patterns.
2. Adhesion
Adhesion is a fundamental property directly influencing the performance of any exterior door protective coating. It refers to the coating’s capacity to bond firmly to the door’s surface, resisting separation caused by environmental stressors or physical contact. A strong adhesive bond is not merely desirable; it is a critical prerequisite for a durable, long-lasting finish. Without adequate adhesion, the coating is vulnerable to peeling, cracking, and blistering, compromising both its protective function and visual appeal. A compromised coating allows moisture penetration, fostering decay in wooden doors and corrosion in metal doors.
The type of substrate wood, steel, fiberglass impacts adhesion requirements. Wood, being porous, benefits from coatings with deep penetrating capabilities, often enhanced by prior priming. Steel requires coatings formulated with rust inhibitors and bonding agents for metal surfaces. Fiberglass, with its smooth, non-porous surface, necessitates specialized adhesion promoters. The consequences of poor adhesion are evident in scenarios where coatings fail prematurely. For example, blistering paint on a wooden door indicates moisture ingress due to inadequate bonding, necessitating costly repairs and reapplication. Similarly, paint peeling from a steel door exposes the metal to oxidation, leading to rust and structural damage.
Achieving optimal adhesion involves meticulous surface preparation, appropriate primer selection, and compatibility between the substrate, primer, and chosen coating. Surface contaminants, such as dirt, grease, or loose particles, impede adhesion and must be removed through cleaning and sanding. Primers act as an intermediary layer, creating a receptive surface for the coating to bond to. Selecting compatible systems ensures chemical compatibility and prevents delamination. Therefore, adhesion is not an isolated property but a product of careful material selection and diligent application techniques. The practical significance of understanding adhesion lies in its ability to prevent premature coating failure, preserving the integrity and aesthetic of exterior doors, while minimizing long-term maintenance expenses.
3. Weather Resistance
Weather resistance is a critical attribute defining a quality exterior door coating. This encompasses the coating’s ability to withstand prolonged exposure to environmental elements, including sunlight (UV radiation), moisture (rain, humidity, snow), temperature fluctuations, and wind-borne debris. The protective layer serves as the primary defense against degradation caused by these factors. Without sufficient weather resistance, the door’s finish will deteriorate, leading to cracking, peeling, fading, and ultimately, compromising the structural integrity of the door itself. For instance, a door exposed to intense sunlight without proper UV protection will experience fading and chalking, necessitating frequent repainting. Similarly, a coating susceptible to moisture penetration will foster wood rot or metal corrosion, leading to expensive repairs or replacement.
The choice of coating directly impacts the door’s resilience to specific regional climates. Coastal areas with high humidity and salt spray necessitate coatings formulated with salt resistance. Regions with extreme temperature variations require coatings with exceptional flexibility to prevent cracking during expansion and contraction cycles. Furthermore, the presence of pollutants in urban environments demands coatings that are resistant to chemical degradation. The selection should be guided by performance data, manufacturer specifications, and independent testing results confirming the product’s ability to withstand anticipated environmental stressors. Proper application, including thorough surface preparation and adherence to recommended coating thickness, is crucial to maximizing weather resistance capabilities.
In summary, weather resistance is an indispensable component of a superior exterior door coating, ensuring long-term protection and aesthetic appeal. The capacity to resist the damaging effects of sunlight, moisture, temperature variations, and pollutants is essential for minimizing maintenance needs and preserving the door’s structural integrity. The informed selection and proper application of coatings engineered for specific regional climates translate directly into reduced long-term costs and extended service life for exterior doors.
4. UV Protection
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight is a significant cause of degradation in exterior door coatings. Prolonged exposure to UV rays breaks down the chemical bonds within the coating, leading to fading, chalking, and a reduction in overall durability. Incorporating effective UV protection is, therefore, a critical characteristic of any optimal exterior door coating. The presence of UV absorbers and stabilizers within the formulation mitigates the damaging effects of sunlight, preserving the coating’s color, gloss, and protective properties. For instance, doors facing south or west receive the most intense sunlight, making UV protection especially vital in these locations. Without it, the finish will degrade rapidly, necessitating more frequent repainting.
Coatings with superior UV protection often employ titanium dioxide or zinc oxide as pigment components. These compounds act as reflectors, deflecting UV rays away from the underlying resin. In contrast, coatings relying solely on organic pigments are more susceptible to UV damage. The practical implications of this are evident in the long-term appearance and performance of exterior doors. A door coated with a UV-resistant formulation will maintain its original color and sheen for a significantly longer period compared to one lacking this protection. This translates to reduced maintenance requirements and lower long-term costs. Furthermore, effective UV protection contributes to the overall longevity of the door itself, preventing premature weathering and preserving its structural integrity.
The selection of a coating incorporating robust UV protection is a proactive measure to combat the deteriorating effects of sunlight. By understanding the mechanisms by which UV radiation damages coatings and recognizing the role of specific additives in mitigating this damage, informed decisions can be made regarding the selection of coating systems. Investing in products designed for UV resistance is a key factor in achieving a durable, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing exterior door finish. The benefits extend beyond mere aesthetics, contributing to the preservation of the door’s functionality and value.
5. Color Retention
Color retention, in the context of exterior door finishes, denotes the coating’s ability to maintain its original hue and vibrancy over time, despite exposure to environmental factors. This characteristic is intrinsically linked to what constitutes an optimal finish, as it directly impacts the door’s aesthetic appeal and perceived value. Degradation in color, whether through fading, chalking, or discoloration, diminishes the overall visual impact and can signal underlying deterioration in the coating itself. The connection is causal: high-quality formulations, engineered for superior color retention, resist the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and atmospheric pollutants, preserving the intended aesthetic for an extended period.
The importance of color retention extends beyond mere aesthetic preference. Faded or discolored doors can detract from a property’s curb appeal, potentially reducing its market value. Conversely, a vibrant and well-maintained entryway creates a positive impression and reflects favorably on the property owner. For example, a bright red door that gradually fades to a dull pink under sunlight loses its intended boldness and impact. This illustrates the practical consequence of selecting coatings lacking adequate color retention properties. Furthermore, coatings formulated with high-quality pigments and UV absorbers tend to exhibit improved durability and resistance to other forms of degradation, such as cracking and peeling. The initial investment in a superior product, therefore, often translates into long-term savings due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
In summary, color retention is not merely a superficial attribute but an integral component of a high-performing exterior door finish. Its ability to withstand environmental stressors and maintain its intended hue significantly impacts the door’s aesthetic value, long-term durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. By understanding the mechanisms that cause color degradation and prioritizing coatings with proven color retention properties, informed decisions can be made to preserve the beauty and integrity of exterior doors. The challenges lie in accurately assessing a product’s color retention capabilities prior to application and accounting for regional climatic variations that may exacerbate color fading.
6. Ease of Application
Ease of application, in the context of exterior door coatings, refers to the characteristics of a product that facilitate efficient and effective application by both professionals and homeowners. While durability, UV protection, and color retention are crucial performance factors, the practical benefits of these qualities are diminished if the coating is difficult to apply correctly. A product described as the “best exterior door paint finish” must therefore possess attributes that promote smooth application, adequate open time, and minimal susceptibility to common application errors like brush marks, drips, or uneven coverage. The connection between ease of application and overall performance is direct: a product that is easy to apply correctly is more likely to achieve its intended protective and aesthetic characteristics. Conversely, a difficult-to-apply product increases the risk of application flaws that compromise its long-term performance.
Consider two different coatings: one that dries too quickly, leading to visible brush strokes and lap marks, and another that exhibits self-leveling properties and remains workable for a reasonable duration. The second coating, due to its superior application properties, allows for a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing finish, even in the hands of less experienced individuals. This translates into lower labor costs for professional painters and improved satisfaction for DIY homeowners. Ease of application also influences coating thickness uniformity, a critical factor for achieving optimal protection against weathering and UV degradation. A coating applied unevenly may provide inadequate protection in thinner areas, leading to premature failure. Furthermore, products that require extensive surface preparation or specialized application techniques increase both the time and expense associated with the project.
In summary, ease of application is an integral and often overlooked component of the “best exterior door paint finish.” It directly impacts the likelihood of achieving the coating’s intended performance characteristics and influences both the cost and convenience of the application process. By prioritizing products with user-friendly application properties, both professionals and homeowners can maximize the long-term benefits of their investment in a protective and aesthetically pleasing exterior door coating. The challenge lies in balancing ease of application with other critical performance attributes, ensuring that the selected coating delivers both superior application characteristics and long-term durability and protection.
Frequently Asked Questions About Exterior Door Coatings
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and application of protective coatings for exterior doors. The information presented aims to provide clarity and guidance for homeowners and professionals alike.
Question 1: What type of protective coating offers the longest lifespan on an exterior door?
The lifespan of an exterior door coating is contingent upon several factors, including the type of product, surface preparation, application technique, and prevailing environmental conditions. Generally, high-quality acrylic latex products offer a balance of durability, UV resistance, and flexibility, contributing to extended lifespan when properly applied. Oil-based alkyd options, while offering excellent hardness, may become brittle over time, leading to cracking.
Question 2: How crucial is priming before applying a protective coating on an exterior door?
Priming is a critical step that significantly impacts the adhesion and overall performance. A primer creates a uniform surface, seals porous substrates, and promotes bonding between the door material and the protective coating. Skipping the priming step often results in premature coating failure, peeling, and reduced weather resistance.
Question 3: What sheen level is recommended for an exterior door protective coating?
Satin or semi-gloss sheens are generally recommended for exterior doors. These sheens offer a balance between durability, ease of cleaning, and aesthetic appeal. Higher gloss levels are more reflective, potentially highlighting imperfections, while matte finishes are more susceptible to staining and dirt accumulation.
Question 4: How does climate affect the choice of a protective coating for an exterior door?
Climate plays a significant role in the coating selection process. In regions with high humidity and frequent rainfall, products with excellent moisture resistance and mildew inhibitors are essential. In areas with intense sunlight, UV-resistant formulations are crucial to prevent fading and chalking. Extreme temperature fluctuations necessitate coatings with high flexibility to prevent cracking and peeling.
Question 5: Can existing protective coatings be applied over a previous coat?
Application over an existing coating is possible, but requires thorough preparation. The existing surface must be cleaned, sanded, and free from loose or peeling coatings. Compatibility between the existing and new coating is also essential to prevent adhesion problems. In some cases, complete removal of the old coating may be necessary for optimal results.
Question 6: What are the most common causes of protective coating failure on exterior doors?
Common causes of failure include inadequate surface preparation, use of low-quality products, improper application techniques, and exposure to harsh environmental conditions. Neglecting any of these factors can compromise the coating’s performance and longevity.
In summary, selecting and applying a suitable protective coating for exterior doors requires careful consideration of various factors. Prioritizing quality, proper preparation, and appropriate application techniques contributes significantly to achieving a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish.
The subsequent section will delve into specific product recommendations and application guidelines for various exterior door materials.
Concluding Remarks on Exterior Door Coatings
The foregoing analysis has underscored the multifaceted nature of selecting a suitable coating. Achieving an optimal outcome requires careful consideration of durability, adhesion, weather resistance, UV protection, color retention, and ease of application. Balancing these factors ensures a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing, and protective barrier against environmental elements.
The selection of a high-quality exterior door coating represents a significant investment in property preservation. Informed decision-making, coupled with proper application techniques, translates to enhanced curb appeal, reduced maintenance costs, and extended door lifespan. Prioritizing these considerations ultimately safeguards both the structural integrity and visual impact of exterior doors.